1. The Landscape of Disruptive Technology Funding
2. Fueling Innovation at the Ground Level
3. Personalized Support for Pioneering Ventures
4. Harnessing the Power of the Crowd
6. Strategic Partnerships for Mutual Growth
7. Large-Scale Investment for Major Impact
Exploring Funding Mechanisms for Disruptive Tech
1. The Landscape of Disruptive Technology Funding
The funding landscape for disruptive technologies is a complex and multifaceted domain, characterized by a dynamic interplay of risk, innovation, and potential high reward. Stakeholders in this field range from venture capitalists and angel investors to government agencies and crowdfunding platforms, each with their own set of priorities, risk tolerances, and strategic approaches. The allure of funding the next big breakthrough often competes with the pragmatic need to manage financial risk, making the investment in disruptive tech both an art and a science.
1. Venture Capitalists (VCs): VCs are often the most significant players in the funding of disruptive technologies. They bring not only capital but also strategic guidance and networking opportunities to the table. For instance, a VC firm specializing in biotechnology might fund a startup working on crispr gene-editing technology, recognizing its potential to revolutionize medicine.
2. Angel Investors: These individuals provide funding during the early stages of a startup's life cycle, often when the risk is highest. An example is an angel investor backing a nascent quantum computing firm, betting on its long-term success despite the current technological hurdles.
3. Government Grants and Subsidies: Governments worldwide recognize the importance of fostering innovation and may offer grants or subsidies to support research and development in disruptive tech. The European Union's Horizon 2020 program, for example, has provided funding for a wide range of projects, from renewable energy to advanced robotics.
4. Crowdfunding: Platforms like Kickstarter and Indiegogo allow entrepreneurs to raise funds directly from the public. This method democratizes the funding process and can be particularly effective for consumer-facing technologies. Pebble, the smartwatch company, famously raised over $10 million through Kickstarter, highlighting the potential of this approach.
5. Corporate Investment: Established companies often invest in disruptive technologies to stay ahead of the curve. Google's parent company, Alphabet, has made numerous investments in AI startups through its venture arm, GV, recognizing AI's transformative potential across industries.
6. Private Equity: private equity firms sometimes step in to fund more mature disruptive tech companies that require larger amounts of capital to scale up. For example, a private equity firm might invest in a company developing autonomous vehicle technology that is ready to begin mass production.
7. Incubators and Accelerators: These organizations support startups by providing not only funding but also mentorship and resources. Y Combinator, one of the most well-known accelerators, has helped launch companies like Dropbox and Airbnb, which have gone on to disrupt their respective industries.
8. Debt Financing: While not as common for early-stage startups, debt financing can be a viable option for more established companies in the disruptive tech space. This might take the form of a bank loan or issuing corporate bonds.
Each funding mechanism comes with its own set of advantages and challenges, and the right choice depends on the specific circumstances of the technology and the company seeking investment. The key is to understand the nuances of each option and to craft a funding strategy that aligns with the company's goals and the disruptive potential of the technology. The landscape of disruptive technology funding is ever-evolving, and staying informed about the latest trends and shifts is crucial for anyone looking to navigate this exciting field.

The Landscape of Disruptive Technology Funding - Exploring Funding Mechanisms for Disruptive Tech
2. Fueling Innovation at the Ground Level
Venture capital stands as a pivotal force in the modern entrepreneurial ecosystem, serving as a catalyst for innovation and growth. It is a type of private equity and a form of financing that investors provide to startup companies and small businesses that are believed to have long-term growth potential. Unlike traditional financing methods, venture capital typically comes from well-off investors, investment banks, and any other financial institutions. However, it does not always take a monetary form; it can also be provided in the form of technical or managerial expertise. Venture capital is typically allocated to small companies with exceptional growth potential, or to companies that have grown quickly and appear poised to continue to expand.
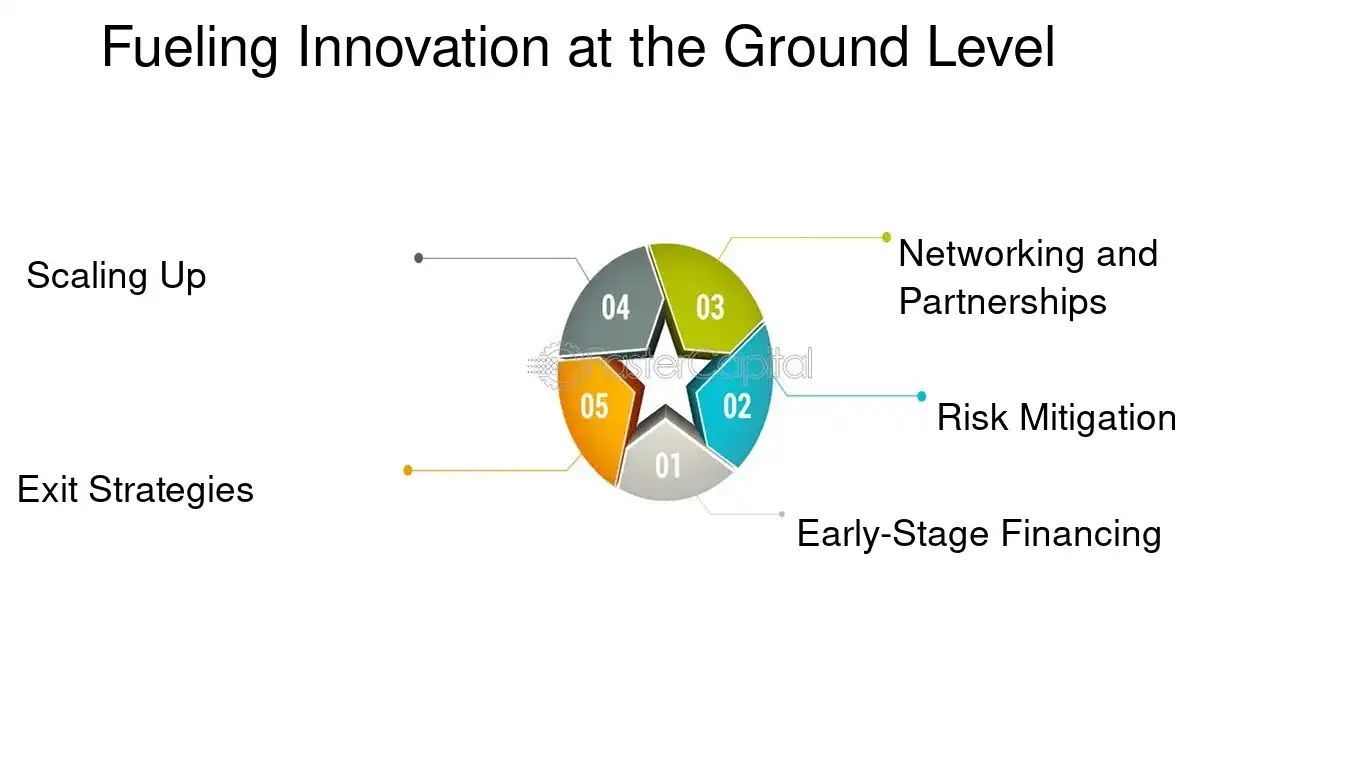
1. early-Stage financing: At the ground level, venture capital is instrumental in transforming a mere idea into a marketable product. seed funding allows entrepreneurs to develop a prototype and conduct market research. For example, Dropbox, in its early days, received seed funding to build its product and validate the market, which was crucial for its subsequent success.
2. Risk Mitigation: Venture capitalists bring more than just money to the table; they often have industry expertise and can provide strategic guidance. They help in identifying potential risks and crafting strategies to mitigate them. For instance, when Snapchat was in its nascent stage, venture capitalists played a key role in shaping its business model and user acquisition strategy.
3. Networking and Partnerships: Access to the venture capitalist's network can be invaluable for a startup. This can lead to strategic partnerships, customer leads, and even new hires. Twitter's early investment from Union Square Ventures and other VCs helped it gain crucial connections that supported its growth.
4. Scaling Up: Once a company has established its product-market fit, venture capital can help it scale up operations quickly and efficiently. This is essential in industries where the first mover advantage is significant. Uber's rapid expansion was fueled by successive rounds of venture capital, allowing it to quickly dominate the ride-sharing market.
5. Exit Strategies: Venture capitalists are experienced in navigating the path to an exit, whether it's through an initial public offering (IPO), acquisition, or merger. Facebook's IPO in 2012, which was one of the biggest in tech history, was preceded by significant venture capital investment.
Venture capital is not without its criticisms. Some argue that it can lead to a focus on rapid growth at the expense of profitability or long-term viability. Others point out that the pressure for a quick exit can stifle true innovation. However, the role of venture capital in fueling ground-level innovation is undeniable. It provides the resources necessary for disruptive technologies to develop and reach the market, ultimately contributing to economic growth and technological advancement. The symbiotic relationship between startups and venture capitalists is one that continues to evolve, but its core premise remains the same: to nurture the seeds of innovation into the forests of tomorrow's industries.
Fueling Innovation at the Ground Level - Exploring Funding Mechanisms for Disruptive Tech
3. Personalized Support for Pioneering Ventures
angel investors play a crucial role in the ecosystem of funding disruptive technologies. Unlike traditional venture capital firms that may focus on later-stage investments, angel investors often step in during the nascent stages of a startup's life cycle, providing not just capital but also mentorship and access to a wider network. This personalized support can be pivotal for pioneering ventures that are pushing the boundaries of innovation. Angel investors typically have a high tolerance for risk and an eye for potential, which is essential when backing ventures that may disrupt existing markets or create entirely new ones.
From the perspective of a startup, angel investors are often seen as a blessing. They are usually successful entrepreneurs or executives who have a wealth of experience to share. Their investment is often seen as a vote of confidence in the startup's vision and team. For the angel investor, the motivation to invest is twofold: there is the potential for a significant financial return, and there is also the opportunity to guide and witness the growth of cutting-edge technology.
1. early-Stage support: Angel investors typically get involved during the early stages of a startup, often when the company is still refining its product or service. This early-stage support is critical as it can help startups overcome initial hurdles without the pressure of high-interest loans or the need to meet the stringent requirements of traditional lenders.
2. Mentorship and Expertise: Many angel investors bring their own entrepreneurial experience to the table. They can provide strategic advice, help in avoiding common pitfalls, and offer insights into scaling a business effectively.
3. Networking Opportunities: Angel investors often have extensive networks and can introduce founders to potential customers, partners, and future investors. This networking can be invaluable for a startup looking to gain traction in a competitive market.
4. Flexible Investment Terms: Unlike institutional investors, angel investors may offer more flexible investment terms, which can be advantageous for startups that need to pivot their business model or extend their runway.
5. Follow-on Investments: Angel investors may also participate in subsequent funding rounds, providing continued support as the startup grows.
For example, consider a startup developing a revolutionary biodegradable plastic alternative. An angel investor in this company might not only provide the funds needed to complete initial research and development but also offer guidance on navigating regulatory hurdles and establishing key industry partnerships.
Angel investors are more than just financiers; they are partners in innovation. Their personalized support can make the difference between a pioneering venture's success or failure, making them an integral part of the funding landscape for disruptive technologies. Their impact is often seen in the long-term success of the companies they choose to support, shaping the future of technology and industry.

Personalized Support for Pioneering Ventures - Exploring Funding Mechanisms for Disruptive Tech
4. Harnessing the Power of the Crowd
Crowdfunding has emerged as a revolutionary approach to raising capital, particularly for startups and projects that might otherwise struggle to secure funding through traditional means. This method leverages the collective effort of a large number of individuals, often facilitated by online platforms, to pool resources and support initiatives they believe in. Unlike conventional funding avenues, which typically involve a few investors contributing large sums, crowdfunding is characterized by many people contributing smaller amounts. This democratization of funding not only provides access to capital but also validates and markets the idea to a broader audience.
1. The Democratization of Investment: Crowdfunding platforms have lowered the barrier to entry for investing, allowing people from all walks of life to support projects they're passionate about. This has led to a more diverse range of ideas and products being funded, from innovative gadgets on Kickstarter to community projects on GoFundMe.
2. pre-Market validation: By presenting a concept to potential backers, creators can gauge interest and demand before committing significant resources. For example, the Pebble Smartwatch raised over $10 million on Kickstarter, demonstrating a clear market demand before production.
3. marketing and Community building: A successful crowdfunding campaign can serve as a powerful marketing tool. The process of engaging with backers creates a community of supporters who are invested in the project's success. Take the case of the game "Exploding Kittens," which not only raised funds but also built a fanbase that contributed to its ongoing success.
4. Risk and Reward Sharing: Crowdfunding allows the risk of new ventures to be spread across a larger group of stakeholders. This can encourage innovation, as the financial risk to individual backers is minimized. However, it's important to note that backers often receive rewards or equity in return for their investment, aligning their interests with the success of the project.
5. Regulatory Considerations: With the rise of crowdfunding, regulatory bodies have had to adapt. In the United States, the JOBS Act has made it easier for startups to raise money through crowdfunding by relaxing some securities regulations, thus fostering a more conducive environment for small-scale investments.
6. The Role of social media: Social media plays a crucial role in the success of crowdfunding campaigns. It allows creators to share their stories, updates, and appeals for support directly with a global audience. The viral nature of social media can significantly amplify the reach of a campaign, as seen with the ALS ice Bucket challenge, which raised awareness and funds for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis research.
7. Challenges and Criticisms: Despite its benefits, crowdfunding is not without challenges. There are concerns about project creators failing to deliver on promises, the potential for fraud, and the lack of investor protection. Additionally, the sheer number of projects vying for attention can make it difficult for worthy initiatives to stand out.
Crowdfunding represents a shift in how ideas are brought to life and how the public can participate in innovation. It's a mechanism that not only funds but also fosters community engagement, market validation, and a shared journey from concept to reality. As this funding mechanism continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play a significant role in the development of disruptive technologies and the realization of creative endeavors.
Build a great product that attracts users
FasterCapital's team of experts works on building a product that engages your users and increases your conversion rate
5. Public Sector Backing
In the realm of disruptive technology, the role of government grants and subsidies cannot be overstated. These financial incentives are designed to support innovative projects that may otherwise struggle to secure funding through traditional channels. By providing this backing, the public sector plays a pivotal role in fostering innovation and ensuring that groundbreaking ideas can make it past the conceptual stage and into development. This support is not only about the monetary boost but also about the validation and credibility that come with government endorsement. From renewable energy initiatives to advanced medical research, these grants and subsidies have been instrumental in propelling technologies that have the potential to revolutionize industries and improve quality of life.
1. Eligibility Criteria: Government grants and subsidies often have specific eligibility criteria to ensure that the funding is directed towards projects that align with national or regional strategic goals. For example, the European Union's Horizon 2020 program has funded a wide range of projects, from AI-driven healthcare solutions to sustainable urban development initiatives, all of which are aimed at addressing societal challenges and boosting economic growth.
2. application process: The application process for these grants can be quite rigorous, involving detailed proposals, budgets, and projected outcomes. In the United States, the small Business Innovation research (SBIR) program requires applicants to go through a competitive process that assesses the technical merit and potential impact of their proposed innovation.
3. Types of Support: Support can come in various forms, including direct financial grants, tax incentives, or subsidized resources. In South Korea, the government offers tax deductions for research and development activities, encouraging companies to invest in new technologies.
4. Success Stories: There are numerous success stories where government backing has led to successful outcomes. One notable example is the Tesla Gigafactory in Nevada, which received significant tax incentives from the state government. This support was crucial in Tesla's efforts to scale up battery production and reduce costs, ultimately contributing to the broader adoption of electric vehicles.
5. Challenges and Criticisms: Despite the benefits, government grants and subsidies are not without their challenges and criticisms. There is often debate over the allocation of funds, with some arguing that it can lead to market distortions or favoritism. Moreover, the bureaucratic nature of the application and reporting process can be a barrier for smaller organizations or startups.
6. Future Outlook: Looking ahead, the importance of government grants and subsidies is likely to grow as we face global challenges like climate change and pandemics. These issues require collaborative efforts and significant investment in research and development, which the private sector alone may not be able to provide.
Government grants and subsidies serve as a crucial bridge between innovative ideas and their realization. By understanding the intricacies of this funding mechanism, stakeholders in the disruptive tech industry can better navigate the landscape and leverage public sector backing to bring transformative technologies to market.

Public Sector Backing - Exploring Funding Mechanisms for Disruptive Tech
6. Strategic Partnerships for Mutual Growth
In the dynamic landscape of disruptive technology, corporate investment has emerged as a pivotal force driving innovation and growth. Strategic partnerships between established corporations and burgeoning tech startups are increasingly becoming a cornerstone for mutual development. These alliances offer a symbiotic relationship where startups gain access to capital, mentorship, and market reach, while corporations infuse fresh, innovative solutions into their product lines or services. The essence of these partnerships lies in the shared vision of achieving accelerated growth and tapping into new market opportunities.
From the perspective of startups, such partnerships can be a lifeline, providing not only financial backing but also validation of their technology and business model. For corporations, these collaborations are a strategic maneuver to stay ahead in the game by embracing cutting-edge technologies without the inherent risks of internal R&D. Here's an in-depth look at how these strategic partnerships can unfold:
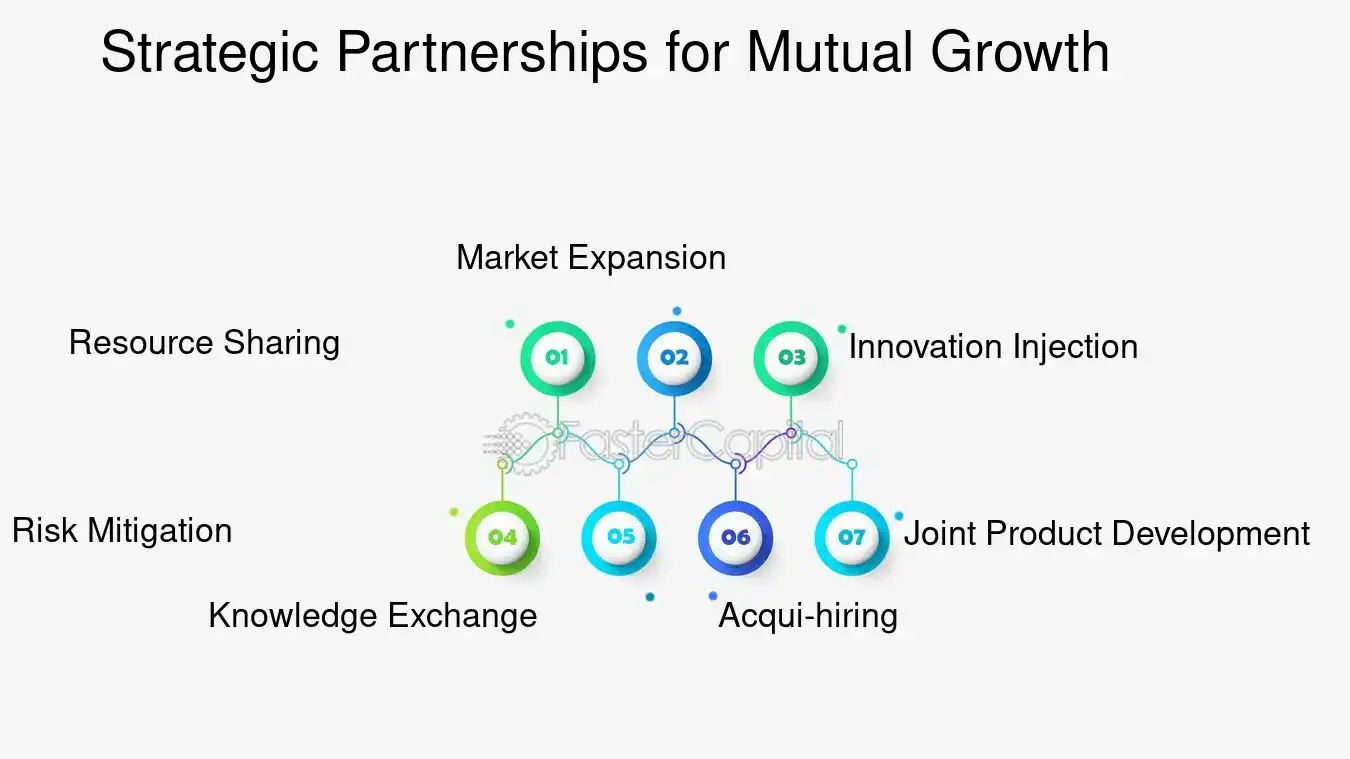
1. Resource Sharing: Startups often operate with limited resources. A partnership can open doors to a corporation's extensive resources, including research labs, marketing teams, and distribution networks. For example, when IBM partnered with the AI-powered health platform PathAI, it provided the startup with access to its cloud and AI capabilities, significantly enhancing PathAI's diagnostic services.
2. Market Expansion: Corporations can leverage startups to enter new markets or segments. This is particularly evident in the case of Google's acquisition of Nest, which allowed Google to establish a strong presence in the smart home industry.
3. Innovation Injection: Startups are hotbeds for innovation, and through strategic investments, corporations can integrate these innovations into their offerings. Microsoft's investment in OpenAI is a prime example, where the partnership is set to bolster Microsoft's Azure platform with advanced AI capabilities.
4. Risk Mitigation: By investing in multiple startups, corporations can spread their risk. If one venture fails, the loss can be offset by the success of others. Intel Capital's diverse investment portfolio across various tech sectors illustrates this approach.
5. Knowledge Exchange: There's a two-way street of knowledge transfer in these partnerships. Corporates learn about agility and disruptive thinking from startups, while startups imbibe best practices in scaling and operations management.
6. Acqui-hiring: Sometimes, the investment is driven by the talent within a startup. Tech giants like Facebook and Google often acquire startups primarily to onboard their innovative teams.
7. joint Product development: collaborative efforts in product development can lead to groundbreaking innovations. The partnership between Pfizer and BioNTech to develop a COVID-19 vaccine is a testament to the power of strategic collaboration.
strategic partnerships in corporate investment are not just about financial transactions; they are about building bridges between the old and new guards of the business world. These alliances are shaping the future of technology, and in turn, the future of how we live and work. As the tech landscape evolves, we can expect to see more of these partnerships, each with the potential to revolutionize industries in ways we can only begin to imagine.
Strategic Partnerships for Mutual Growth - Exploring Funding Mechanisms for Disruptive Tech
7. Large-Scale Investment for Major Impact
private equity stands as a formidable force in the financial world, particularly when it comes to fostering the growth and expansion of disruptive technologies. This form of investment is characterized by its large-scale capital injections, typically directed towards companies that exhibit high growth potential but require substantial funding to realize their ambitions. Unlike public markets, where investments are often spread thinly across numerous shareholders, private equity allows for concentrated investments, providing not just capital but also strategic guidance and operational expertise. This hands-on approach can be instrumental in steering a company through the complex landscape of scaling disruptive technologies.
From the perspective of startup founders, private equity can be a double-edged sword. On one hand, it offers the much-needed capital to scale operations, invest in research and development, and expand market reach. On the other hand, it often comes with a loss of control and stringent performance expectations. For instance, a startup specializing in AI-driven healthcare solutions might partner with a private equity firm to accelerate its product development. The firm's involvement could lead to a rapid scale-up and entry into new markets, but it might also push the startup towards aggressive revenue targets.
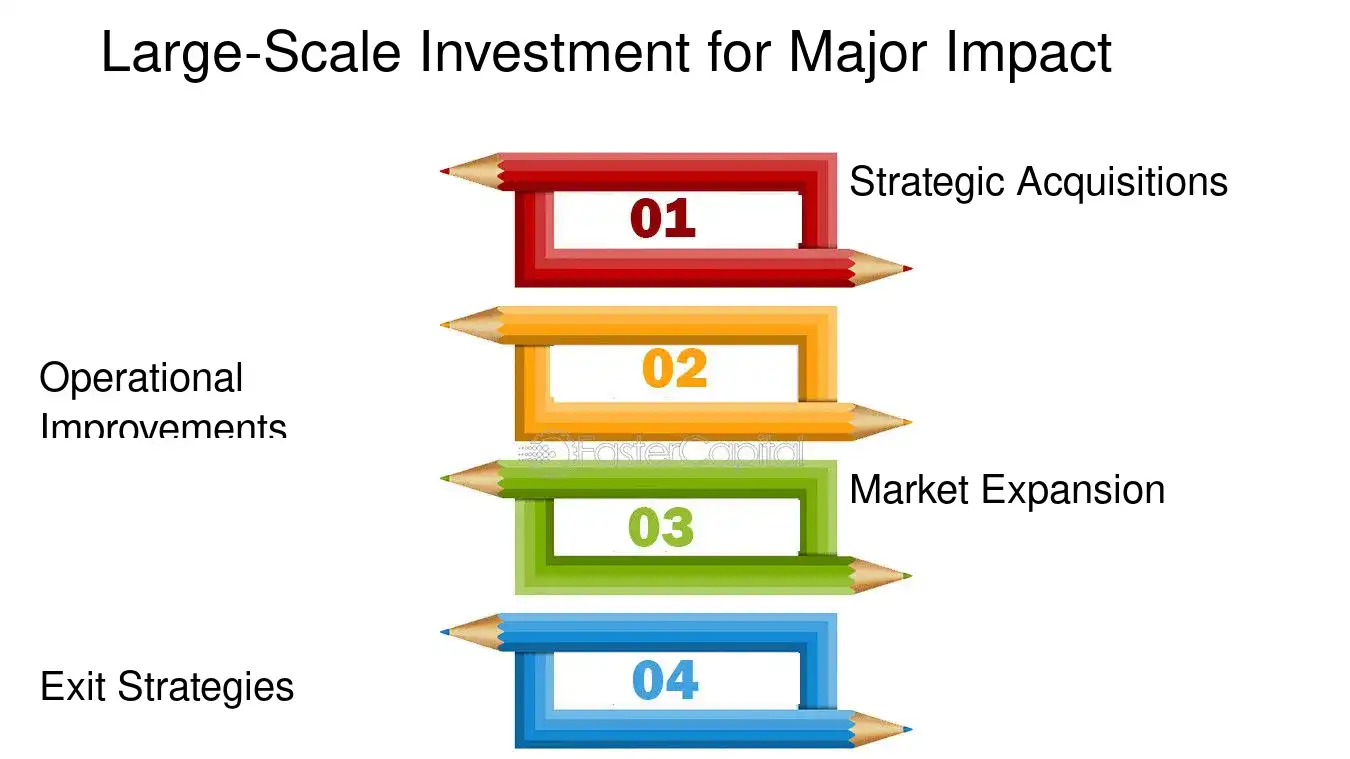
1. Strategic Acquisitions: Private equity firms often employ the strategy of acquiring complementary companies to build a more competitive and diversified entity. For example, a firm might acquire multiple small biotech startups specializing in gene editing and combine them to form a larger, more comprehensive gene therapy company with a robust pipeline of products.
2. Operational Improvements: Post-acquisition, private equity investors typically look to enhance the value of their portfolio companies through operational improvements. This might involve streamlining processes, adopting new technologies, or restructuring management to drive efficiency and growth.
3. Market Expansion: With the backing of private equity, companies can pursue aggressive market expansion strategies. This could mean entering new geographical territories or diversifying into adjacent product lines. A case in point is a private equity-backed renewable energy company branching out from solar to wind energy to capitalize on the growing demand for clean energy solutions.
4. Exit Strategies: Private equity investments are not indefinite; they come with a planned exit strategy, usually within a 4-7 year timeframe. The exit could be through an initial public offering (IPO), a sale to another private equity firm, or a strategic sale to a larger corporation. The exit event is critical as it is the point at which the private equity firm realizes the return on its investment.
The impact of private equity on the technology sector can be profound. By providing the capital and expertise needed to scale, private equity can help turn a promising technology into a market-dominating product. However, the pressure to deliver returns can also drive companies towards short-termism, potentially stifling true innovation. It's a delicate balance, but when managed correctly, private equity can indeed be a large-scale investment for major impact.
Large Scale Investment for Major Impact - Exploring Funding Mechanisms for Disruptive Tech
8. Leveraging Loans for Technological Advancements
debt financing is a critical tool for companies looking to invest in technological advancements. Unlike equity financing, which dilutes ownership, debt financing allows companies to retain full control while accessing the capital needed to fund research and development, scale operations, or bring innovative products to market. This method of financing is particularly attractive for tech companies that are in the growth phase and have the cash flow to service debt. The allure of debt lies in its potential to amplify returns on investment while maintaining the existing ownership structure.
From the perspective of lenders, technology firms represent both an opportunity and a risk. The rapid pace of innovation can quickly make a technology obsolete, potentially jeopardizing the borrower's ability to repay the loan. However, lenders also recognize that successful tech ventures can yield substantial returns. As such, debt instruments are often carefully structured to balance these risks and rewards.
Here are some in-depth insights into leveraging loans for technological advancements:
1. interest Rates and terms: The cost of debt is primarily determined by interest rates, which can vary based on the lender's assessment of risk. For tech companies, this could mean higher rates due to the volatile nature of the industry. However, favorable terms can often be negotiated based on the company's financial health and growth prospects.
2. Covenants and Restrictions: Loans come with covenants, or agreements, that can restrict certain company actions, such as taking on additional debt or making large capital expenditures without lender approval. These are designed to protect the lender's interests but can limit a company's flexibility.
3. impact on Credit ratings: Taking on debt affects a company's credit rating, which can influence future borrowing costs. A strong rating can lead to lower interest rates, while a poor rating can make debt financing more expensive or even unattainable.
4. Debt-to-Equity Ratio: This ratio is a key indicator of financial health. A high debt-to-equity ratio can signal to investors and lenders that a company is aggressively financing growth through debt, which could be a red flag if cash flows are not sufficient to cover debt obligations.
5. Convertible Debt: Some tech companies opt for convertible debt, which can be converted into equity at a later date. This can be an attractive option for companies with high growth potential but currently limited cash flow.
6. Case Studies:
- Tesla's Convertible Bonds: Tesla has utilized convertible bonds to finance its growth. These bonds allowed Tesla to raise capital without immediately diluting shareholder equity, with the option for bondholders to convert their debt into stock at a predetermined price.
- IBM's Strategic Acquisitions: IBM has used debt financing to fund strategic acquisitions, such as its purchase of Red Hat. This move allowed IBM to rapidly expand its cloud computing capabilities and compete more effectively in the tech market.
7. Government and Institutional Loans: Some tech companies benefit from government or institutional loans designed to support innovation. These loans often come with favorable terms and demonstrate the public sector's commitment to fostering technological progress.
8. Repayment Strategies: Successful tech companies often have strategic repayment plans in place, which may include refinancing options or scheduled paydowns aligned with cash flow projections.
Debt financing is a powerful mechanism for tech companies seeking to advance their technological capabilities. It offers the means to fuel growth and innovation while preserving ownership and control. However, it requires careful consideration of the terms, conditions, and potential impacts on the company's financial future. By strategically leveraging loans, tech companies can position themselves at the forefront of their industry, driving disruptive change and delivering value to stakeholders.

Leveraging Loans for Technological Advancements - Exploring Funding Mechanisms for Disruptive Tech
9. Navigating the Future of Tech Financing
As we stand on the precipice of a new era in technology, the landscape of financing these innovations is as dynamic and evolving as the technologies themselves. The future of tech financing is not just about sourcing capital but about creating ecosystems that foster sustainable growth, innovation, and value creation. It's a multifaceted journey that involves understanding the nuances of venture capital, government funding, crowdfunding, and other emerging financial instruments. Each of these avenues offers unique advantages and challenges, and navigating them requires a keen understanding of the market, the technology, and the various stakeholders involved.
From the perspective of venture capitalists, the focus is on identifying startups with the potential for exponential growth and market disruption. They are not just financiers but also advisors, guiding nascent companies through the treacherous waters of the tech industry. On the other hand, government grants and funds often prioritize societal benefits and long-term research, sometimes at the expense of immediate financial returns. Crowdfunding, a relatively new player in the field, democratizes the investment process, allowing the public to fund projects they believe in, which can be particularly beneficial for niche or consumer-focused technologies.
Here are some in-depth insights into navigating the future of tech financing:
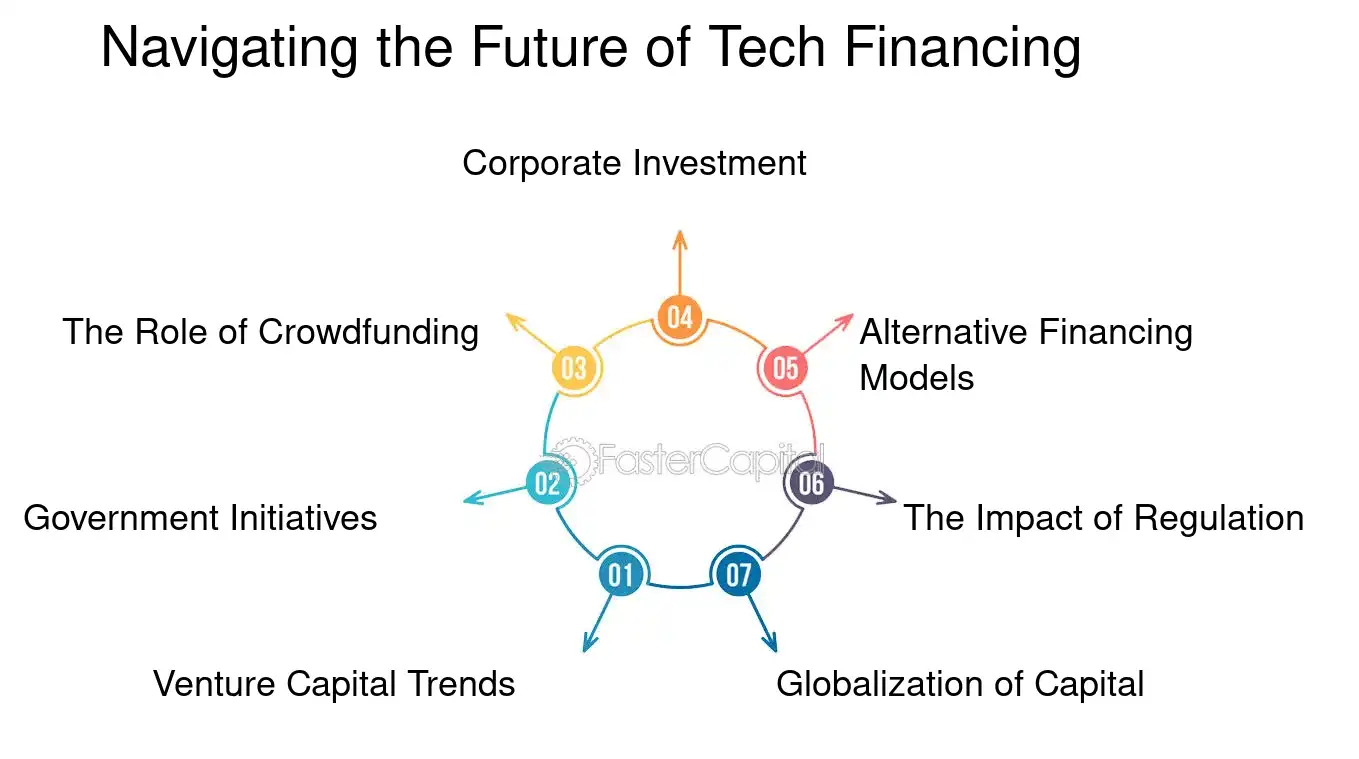
1. venture Capital trends: The venture capital world is increasingly looking towards AI, biotechnology, and renewable energy. For example, consider the rise of AI-driven healthcare startups that have attracted significant investments due to their potential to revolutionize patient care.
2. Government Initiatives: Many governments are launching initiatives to support tech innovation, such as tax incentives for R&D and public-private partnerships. An example is the European Union's Horizon 2020 program, which has funded a wide range of tech projects across the continent.
3. The Role of Crowdfunding: Platforms like Kickstarter and Indiegogo have enabled entrepreneurs to bypass traditional funding routes, bringing products like the Pebble Smartwatch to life through direct consumer support.
4. Corporate Investment: Large tech companies are increasingly investing in startups, not just for financial returns but also to foster innovation that aligns with their strategic goals. Google's investment in SpaceX is a prime example of this trend.
5. Alternative Financing Models: New models like revenue-based financing, where investors receive a percentage of ongoing revenue, are gaining traction. This model has been particularly successful for SaaS companies with predictable revenue streams.
6. The Impact of Regulation: Financial regulations, such as the JOBS Act in the United States, have opened up new opportunities for startups to raise capital through equity crowdfunding and mini-IPOs.
7. Globalization of Capital: The flow of tech financing is becoming increasingly global, with cross-border investments becoming the norm. This is exemplified by the rise of Chinese investment in Silicon valley startups.
The future of tech financing is not a single path but a web of interconnected routes, each with its own set of opportunities and challenges. navigating this complex terrain requires a strategic approach, an understanding of the broader economic and technological trends, and a willingness to adapt to the ever-changing landscape of innovation. By leveraging the right mix of funding sources and staying attuned to the shifts in the market, tech companies can not only secure the capital they need but also build the partnerships and networks that will propel them to long-term success.
Navigating the Future of Tech Financing - Exploring Funding Mechanisms for Disruptive Tech