1. Understanding Risk Curve Diversification
2. The Importance of Spreading Risk
3. The Dimensions of Risk Curve Diversification
4. The Role of Asset Allocation in Diversification
5. The Benefits of Diversifying Across Asset Classes
6. Diversifying Across Geographical Regions
7. Diversifying Across Sectors and Industries
Risk curve diversification: Spreading risk across multiple dimensions
1. Understanding Risk Curve Diversification
Understanding risk Curve diversification
When it comes to investing, diversification is a key strategy to minimize risk. However, diversification doesn't just mean spreading your investments across different assets or industries. It also means diversifying your risk across different dimensions. This is where risk curve diversification comes in. Understanding risk curve diversification is essential for any investor looking to minimize their risk exposure.
1. What is Risk Curve Diversification?
Risk curve diversification is a strategy that involves spreading your risk across different time horizons. This means investing in assets that have different levels of risk and return, and that have different time horizons for those returns. For example, you may invest in short-term bonds for immediate income, medium-term bonds for moderate growth, and long-term equities for long-term growth.
2. Why is Risk Curve Diversification Important?
Risk curve diversification is important because it helps to minimize the impact of market volatility on your portfolio. By investing in assets with different time horizons, you can reduce the risk of losing money during market downturns. Additionally, risk curve diversification can help you to achieve a more balanced portfolio that is better suited to your investment goals.
3. How to Implement Risk Curve Diversification?
There are several ways to implement risk curve diversification. One option is to invest in mutual funds or ETFs that are designed to provide exposure to different parts of the risk curve. For example, you may invest in a fund that focuses on short-term bonds, a fund that focuses on medium-term bonds, and a fund that focuses on long-term equities. Another option is to build your own portfolio by investing in individual assets that have different time horizons.
4. What are the pros and Cons of risk Curve Diversification?
The main advantage of risk curve diversification is that it can help to reduce your risk exposure and provide a more balanced portfolio. However, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider. For example, investing in assets with different time horizons can make it more difficult to rebalance your portfolio. Additionally, some investors may find it challenging to determine the appropriate allocation to each part of the risk curve.
5. What is the Best Option?
The best option for implementing risk curve diversification will depend on your individual investment goals and risk tolerance. If you are a beginner investor or prefer a more hands-off approach, investing in mutual funds or ETFs may be the best option. On the other hand, if you have more experience and prefer to build your own portfolio, investing in individual assets may be more appropriate. Regardless of which option you choose, it's important to regularly monitor your portfolio and make adjustments as needed to ensure that you maintain a balanced and diversified portfolio.
Understanding risk curve diversification is an important part of any investor's toolkit. By spreading your risk across different dimensions, you can reduce your risk exposure and achieve a more balanced portfolio. Whether you choose to invest in mutual funds or etfs or build your own portfolio, it's important to regularly monitor your investments and make adjustments as needed to ensure that you are on track to meet your investment goals.
Understanding Risk Curve Diversification - Risk curve diversification: Spreading risk across multiple dimensions
2. The Importance of Spreading Risk
Spreading risk is an essential part of any investment strategy. It is the process of diversifying your investments across multiple dimensions to minimize the impact of any one investment's loss. When you spread your risk, you are not putting all your eggs in one basket, and you are not relying on a single investment to make or break your portfolio. Instead, you are creating a safety net that can help protect your investments from unforeseen events.
There are many reasons why spreading risk is crucial. One of the most obvious is that it can help reduce your overall risk. When you have a diverse portfolio, you are less likely to be impacted by a single event that could cause significant losses. For example, if you invest all your money in a single stock, and that company goes bankrupt, you could lose everything. However, if you spread your risk across multiple stocks, you would be less likely to experience such a significant loss.
Here are some other reasons why spreading risk is important:
1. It can help you achieve your investment goals. By spreading your risk, you can invest in a variety of assets that have different risk levels and returns. This can help you achieve your investment goals more effectively.
2. It can help you manage volatility. When you spread your risk, you are less exposed to the volatility of individual investments. This can help you manage the ups and downs of the market more effectively.
3. It can help you minimize taxes. By spreading your risk, you can take advantage of tax-advantaged investments that can help you minimize your tax liability.
4. It can help you manage liquidity. When you spread your risk, you can invest in assets that have different liquidity levels. This can help you manage your cash flow more effectively.
When it comes to spreading risk, there are many different strategies that you can use. Here are some of the most common:
1. Asset allocation. This is the process of dividing your portfolio among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash. By diversifying your portfolio across different asset classes, you can reduce your risk.
2. Sector diversification. This is the process of investing in different sectors of the economy, such as technology, healthcare, and energy. By diversifying your portfolio across different sectors, you can reduce your exposure to any one sector.
3. Geographic diversification. This is the process of investing in different countries or regions of the world. By diversifying your portfolio across different geographies, you can reduce your exposure to any one country or region.
4. Company diversification. This is the process of investing in different companies within a sector or geography. By diversifying your portfolio across different companies, you can reduce your exposure to any one company.
Overall, spreading risk is a critical part of any investment strategy. It can help you achieve your investment goals, manage volatility, minimize taxes, and manage liquidity. By using a combination of asset allocation, sector diversification, geographic diversification, and company diversification, you can create a diversified portfolio that can help protect your investments from unforeseen events.
The Importance of Spreading Risk - Risk curve diversification: Spreading risk across multiple dimensions
3. The Dimensions of Risk Curve Diversification
When it comes to diversifying your risk curve, it is important to understand that there are multiple dimensions that need to be considered. These dimensions include asset class, geography, industry, and time horizon. Each dimension plays a crucial role in ensuring that your portfolio is diversified enough to withstand any market volatility. In this section, we will explore each dimension and provide insights on how to diversify your risk curve across multiple dimensions.
1. Asset Class
The first dimension to consider when diversifying your risk curve is asset class. This refers to the different types of investments you hold in your portfolio, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. diversifying across asset classes is important because each asset class has its own unique risk and return characteristics. For example, stocks tend to be more volatile but offer higher returns over the long term, while bonds are less volatile but offer lower returns. By holding a mix of asset classes, you can reduce your overall portfolio risk.
2. Geography
The second dimension to consider is geography. This refers to the different regions and countries where you invest your money. Investing in different regions can help
The Dimensions of Risk Curve Diversification - Risk curve diversification: Spreading risk across multiple dimensions
4. The Role of Asset Allocation in Diversification
Asset allocation is a crucial part of diversification, which is a strategy to spread out investment risk across different asset classes. asset allocation is about dividing investments into different categories, such as stocks, bonds, and commodities, based on their attributes and performance. Asset allocation is not about picking individual securities, but rather about creating a balanced portfolio that reflects the investor's risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon. The goal of asset allocation is to achieve a higher return while minimizing risk.
1. The importance of asset allocation in diversification
asset allocation is essential in diversification because it helps an investor to spread risk across multiple dimensions. By investing in different asset classes, the investor can reduce the overall risk of the portfolio. For example, if an investor only invests in stocks, the portfolio would be vulnerable to market fluctuations. However, if the investor also invests in bonds, the portfolio would be less exposed to market volatility because bonds tend to be less volatile than stocks.
2. The benefits of diversification through asset allocation
Diversification through asset allocation provides several benefits to investors, such as reducing risk, enhancing returns, and providing a hedge against inflation. By investing in different asset classes, investors can achieve a higher return while minimizing risk. For example, if an investor had invested only in stocks during the financial crisis of 2008, they would have lost a significant amount of money. However, if they had diversified their portfolio by investing in bonds, they would have minimized their losses.
3. The different types of asset classes
There are several different types of asset classes that investors can choose from when allocating their investments. These include equities, fixed income, commodities, real estate, and alternative investments. Equities are stocks in publicly traded companies, while fixed income includes bonds and other debt securities. Commodities are physical goods such as gold, oil, and other natural resources. Real estate includes commercial and residential properties, while alternative investments can include hedge funds, private equity, and venture capital.
4. The optimal asset allocation strategy
The optimal asset allocation strategy for an investor depends on several factors, such as their risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon. A common rule of thumb is to subtract the investor's age from 100 to determine the percentage of their portfolio that should be invested in stocks. For example, if an investor is 30 years old, they should invest 70% of their portfolio in stocks and 30% in bonds. However, this rule of thumb is not suitable for all investors, and it is essential to consult with a financial advisor to create a customized asset allocation strategy.
5. The drawbacks of asset allocation
While asset allocation is an effective diversification strategy, it also has some drawbacks. One of the main disadvantages of asset allocation is that it can limit an investor's potential returns. By investing in different asset classes, investors may miss out on the full potential of one asset class that may be performing exceptionally well. Additionally, asset allocation requires ongoing monitoring and rebalancing, which can be time-consuming and costly.
Asset allocation is a crucial part of diversification that helps investors spread risk across multiple dimensions. By investing in different asset classes, investors can achieve a higher return while minimizing risk. However, the optimal asset allocation strategy depends on several factors, and it is essential to consult with a financial advisor to create a customized plan. While asset allocation has some drawbacks, it remains an effective way to diversify an investment portfolio.
The Role of Asset Allocation in Diversification - Risk curve diversification: Spreading risk across multiple dimensions
5. The Benefits of Diversifying Across Asset Classes
Diversification Across Asset Classes
One of the most important concepts in finance is diversification. It is a strategy that aims to reduce risk by spreading investments across different assets, sectors, and regions. Diversification helps investors to lower their exposure to any single asset, thereby reducing their overall risk. Diversification can be achieved across different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, commodities, and real estate. In this section, we will discuss the benefits of diversifying across asset classes.
1. Reduced Risk
The primary benefit of diversifying across asset classes is that it reduces risk. When an investor puts all their money in one asset class, they are exposed to the risks associated with that asset class. For example, if an investor only invests in stocks, they are exposed to the risks associated with the stock market such as volatility, economic downturns, and company-specific risks. However, if the investor diversifies their portfolio by investing in other asset classes such as bonds and real estate, they can reduce their overall risk exposure.
2. Increased Returns
Diversification across asset classes can lead to increased returns. When an investor diversifies their portfolio, they are able to take advantage of the growth potential of different asset classes. For example, if an investor only invests in stocks, they may miss out on the potential returns of bonds or real estate. However, by diversifying their portfolio, they can take advantage of the growth potential of all these asset classes.
3. Better risk-Return tradeoff
Diversification across asset classes can also lead to a better risk-return tradeoff. This means that investors can achieve higher returns for the same level of risk or lower risk for the same level of returns. By diversifying their portfolio across different asset classes, investors can achieve a better balance between risk and returns.
4. Protection Against Inflation
Diversification across asset classes can also protect investors against inflation. Inflation can erode the value of investments over time. However, if an investor diversifies their portfolio across different asset classes, they can protect themselves against inflation. For example, if an investor invests in stocks, bonds, and real estate, they can protect themselves against inflation as the value of these assets tends to increase with inflation.
5. Flexibility
Diversification across asset classes also provides investors with flexibility. By diversifying their portfolio, investors can adjust their portfolio to changing market conditions. For example, if the stock market is experiencing a downturn, investors can shift their investments to other asset classes such as bonds or real estate.
Diversification across asset classes is an essential strategy for investors who want to reduce their risk exposure and achieve better returns. By diversifying their portfolio across different asset classes, investors can achieve a better risk-return tradeoff, protect themselves against inflation, and have the flexibility to adjust their portfolio to changing market conditions.

The Benefits of Diversifying Across Asset Classes - Risk curve diversification: Spreading risk across multiple dimensions
6. Diversifying Across Geographical Regions
One of the most effective ways to diversify your investment portfolio is to spread your assets across different geographical regions. This strategy can help you reduce your exposure to risks associated with any one region by investing in various markets that are not correlated with each other. Geographical diversification can also provide you with opportunities to capitalize on the growth potential of different regions and gain exposure to different currencies, political systems, and economic conditions.
There are several benefits to diversifying your portfolio across geographical regions:
1. Reducing overall risk: Investing in multiple regions can help you reduce the risk of losing your entire investment if one region experiences a downturn. By spreading your investments across different regions, you can reduce your exposure to regional risks such as political instability, natural disasters, or economic downturns.
2. taking advantage of growth opportunities: Different regions may have different growth rates and unique economic conditions that can provide investment opportunities. For example, emerging markets such as China, India, and Brazil may offer higher growth potential than developed markets such as the United States and Europe.
3. Gaining exposure to different currencies: Investing in different regions can also provide exposure to different currencies. This can be beneficial if you want to hedge against currency risk or if you believe that a particular currency will appreciate in value.
4. Hedging against inflation: Investing in different regions can also help you hedge against inflation. If one region experiences high inflation, investments in other regions may not be affected to the same extent.
When it comes to diversifying across geographical regions, there are several options to consider:
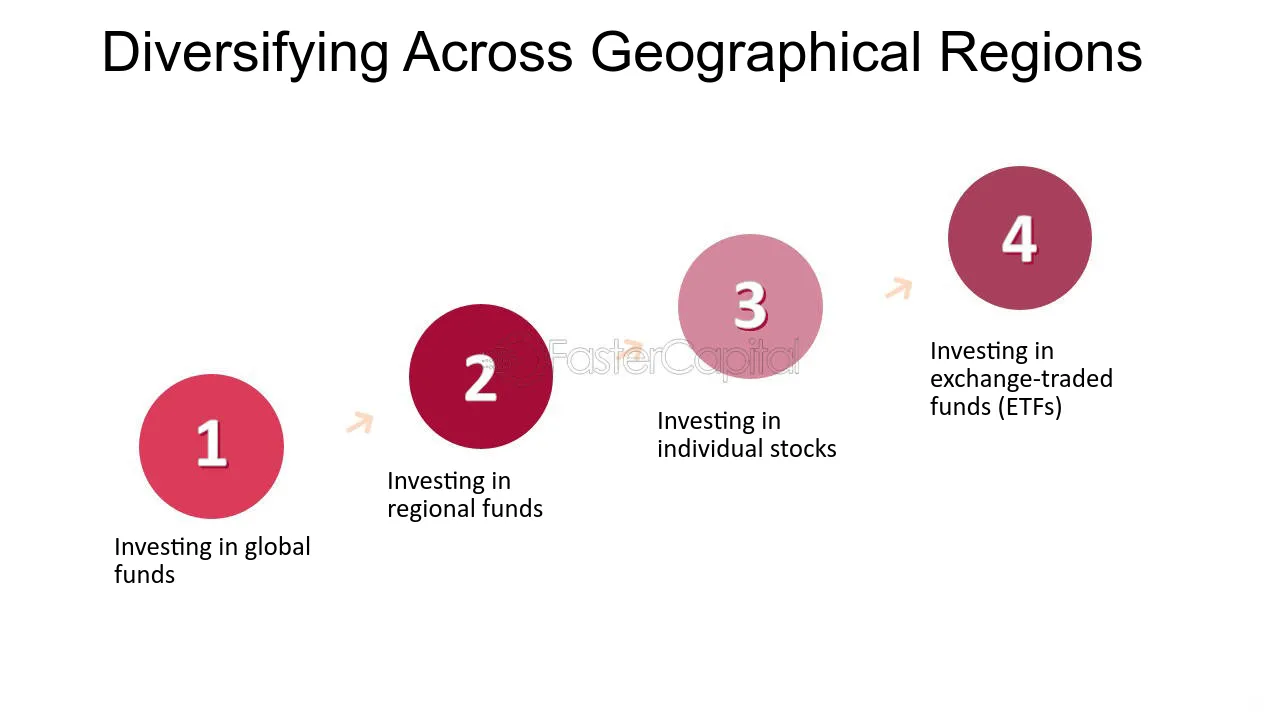
1. Investing in global funds: Global funds invest in companies from around the world, providing exposure to multiple regions in one investment. These funds are managed by professional investment managers who select the companies and regions to invest in.
2. Investing in regional funds: Regional funds focus on specific regions, such as Europe, Asia, or Latin America. These funds can provide exposure to the economic conditions and growth potential of a particular region.
3. Investing in individual stocks: You can also invest in individual stocks of companies that are based in different regions. This option requires more research and analysis, as you will need to select the companies and regions to invest in.
4. investing in exchange-traded funds (ETFs): ETFs are similar to mutual funds, but they trade like stocks on an exchange. ETFs can provide exposure to multiple regions and sectors, and they typically have lower fees than mutual funds.
When it comes to the best option for diversifying across geographical regions, it depends on your investment goals and risk tolerance. If you want a diversified portfolio with exposure to multiple regions, global or regional funds may be a good option. If you want to take a more active role in selecting individual stocks, investing in individual stocks or ETFs may be more suitable.
Diversifying your portfolio across different geographical regions can help you reduce overall risk, take advantage of growth opportunities, gain exposure to different currencies, and hedge against inflation. There are several options to consider, including global funds, regional funds, individual stocks, and ETFs. The best option for you will depend on your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Diversifying Across Geographical Regions - Risk curve diversification: Spreading risk across multiple dimensions
7. Diversifying Across Sectors and Industries
One of the most important aspects of diversifying your investment portfolio is spreading your risk across multiple sectors and industries. Investing in a single sector or industry can be risky, as any negative news or market event can significantly impact the performance of your portfolio. By diversifying across sectors and industries, you can mitigate this risk and potentially achieve more stable returns.
From a macroeconomic perspective, investing in a diversified portfolio across sectors and industries can provide exposure to different economic cycles and trends. For example, during a recession, some sectors such as consumer staples and healthcare tend to perform better than others such as consumer discretionary and technology. By investing in a diversified portfolio, you can benefit from the performance of sectors that are performing well while minimizing the impact of those that are not.
Here are some key considerations when diversifying across sectors and industries:
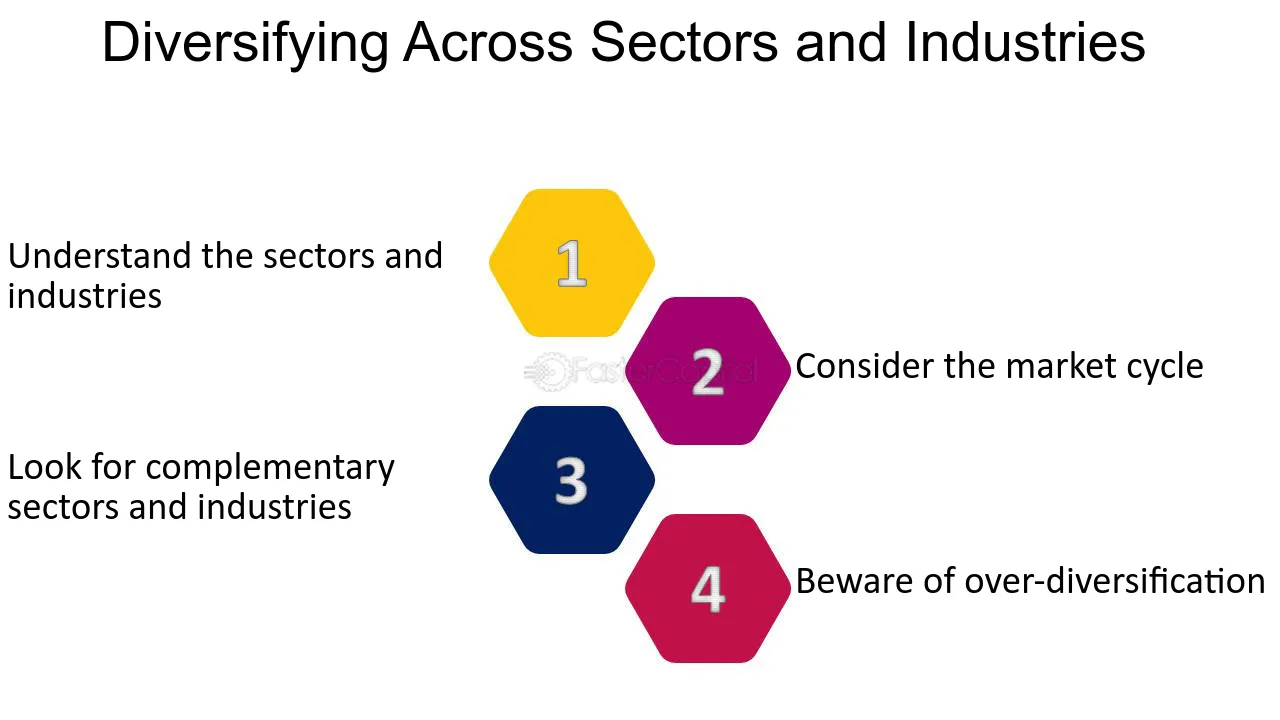
1. Understand the sectors and industries: Before investing in a sector or industry, it is important to understand its fundamentals and key drivers. For example, the healthcare sector is driven by demographic trends such as aging populations and increasing healthcare spending, while the technology sector is driven by innovation and disruption.
2. Consider the market cycle: Different sectors and industries have different performance characteristics depending on the market cycle. For example, during a bull market, technology and consumer discretionary sectors tend to perform well, while during a bear market, defensive sectors such as consumer staples and utilities tend to perform better.
3. Look for complementary sectors and industries: Investing in complementary sectors and industries can provide diversification benefits while still maintaining exposure to a particular theme or trend. For example, investing in both renewable energy and utilities can provide exposure to the theme of clean energy while mitigating risk.
4. Beware of over-diversification: While diversification is important, over-diversification can lead to diluted returns and increased complexity. It is important to strike a balance between diversification and concentration.
In terms of implementing a diversified portfolio across sectors and industries, there are several options available:
1. sector-specific etfs: investing in sector-specific ETFs can provide exposure to a particular sector while still achieving diversification benefits. For example, the Technology Select Sector SPDR ETF (XLK) provides exposure to the technology sector.
2. Industry-specific ETFs: Similar to sector-specific ETFs, industry-specific ETFs can provide exposure to a particular industry. For example, the iShares U.S. Aerospace & Defense ETF (ITA) provides exposure to the aerospace and defense industry.
3. Broad-based ETFs: investing in broad-based ETFs such as the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) can provide exposure to multiple sectors and industries while achieving diversification benefits.
Overall, diversifying across sectors and industries is an important aspect of risk curve diversification. By understanding the fundamentals of different sectors and industries, considering the market cycle, looking for complementary investments, and avoiding over-diversification, investors can achieve a more stable and diversified portfolio. There are several options available for implementing a diversified portfolio, including sector-specific ETFs, industry-specific ETFs, and broad-based ETFs. Ultimately, the best option will depend on individual investment goals and risk tolerance.
Diversifying Across Sectors and Industries - Risk curve diversification: Spreading risk across multiple dimensions
8. Diversifying Across Time Horizons
Investing is a risky game, and diversification is one of the best ways to manage that risk. However, diversification doesn't just mean spreading your investments across different asset classes. It also means diversifying across time horizons. In other words, you need to invest in assets that have different timeframes for expected returns. This is because different assets have different risk and return profiles over different time periods. By diversifying across time horizons, you can potentially reduce your overall portfolio risk and improve your chances of achieving your investment goals.
1. short-term Investments: short-term investments are those that have a maturity period of less than one year. These include money market funds, certificates of deposit (CDs), and Treasury bills. Short-term investments are generally considered to be less risky than long-term investments, but they also offer lower returns. Short-term investments can be a good option for investors who need to preserve their capital or who have a short-term investment horizon. For example, if you are saving up for a down payment on a house, you might consider investing in a CD that matures in six months.
2. medium-Term investments: Medium-term investments are those that have a maturity period of one to five years. These include corporate bonds, municipal bonds, and some types of mutual funds. Medium-term investments offer higher returns than short-term investments, but they also come with higher risk. Medium-term investments can be a good option for investors who have a longer investment horizon but still want to preserve some liquidity. For example, if you are
Diversifying Across Time Horizons - Risk curve diversification: Spreading risk across multiple dimensions
9. Achieving a Balanced Risk Curve Diversification Strategy
Achieving a Balanced Risk Curve Diversification Strategy
When it comes to investing, diversification is the key to reducing risk. However, it's not just about spreading your investments across different types of assets. A truly effective diversification strategy also involves spreading your risk across multiple dimensions. This means investing in a variety of different sectors, geographic regions, and asset classes, among other things. In this section, we'll take a closer look at how to achieve a balanced risk curve diversification strategy.
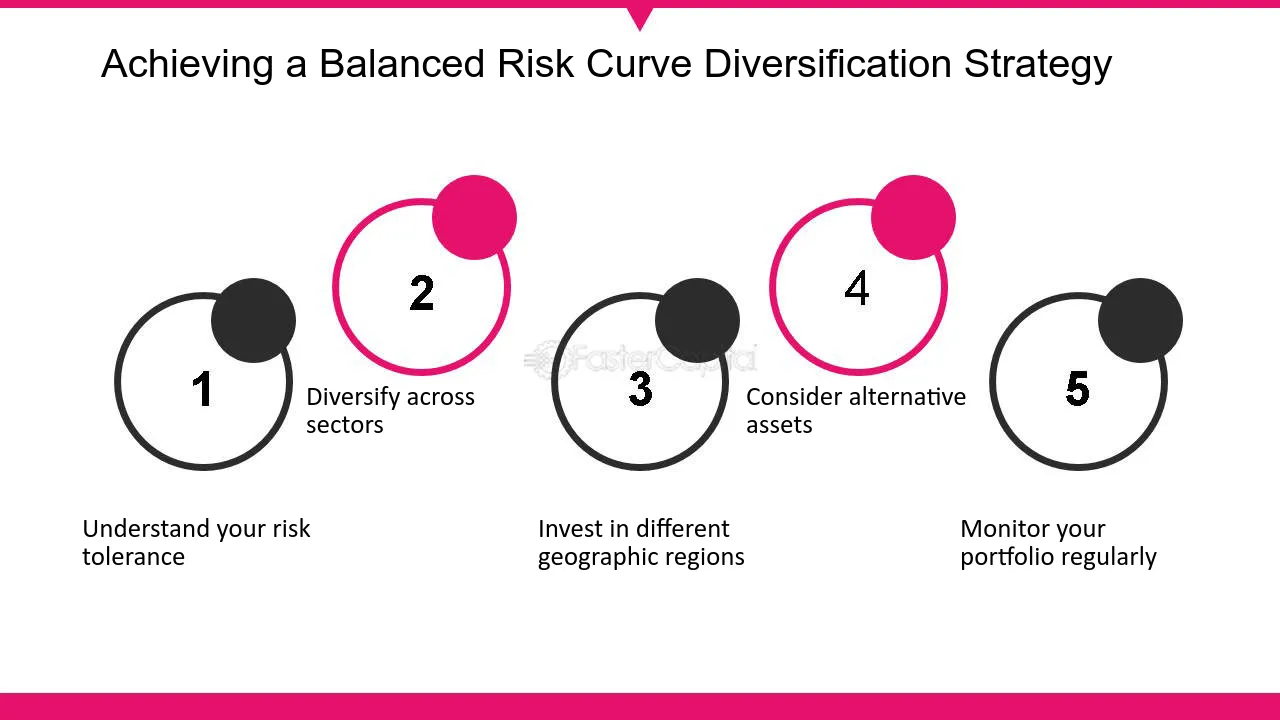
1. Understand your risk tolerance
One of the most important factors to consider when developing a diversification strategy is your risk tolerance. This refers to your ability to handle fluctuations in the value of your investments. If you're someone who is uncomfortable with the idea of losing money, you may want to focus on low-risk investments like bonds and cash. On the other hand, if you're willing to take on more risk in exchange for potentially higher returns, you may want to consider investing in stocks or alternative assets like real estate or commodities.
2. Diversify across sectors
Another important dimension to consider when diversifying your portfolio is the sector in which your investments are located. Different sectors tend to perform differently depending on the economic climate. For example, during a recession, consumer staples like food and household goods tend to perform better than consumer discretionary items like luxury goods. By investing in a variety of sectors, you can help protect yourself against downturns in any one particular area.
3. Invest in different geographic regions
Investing in different geographic regions is another effective way to diversify your portfolio. This can help protect against risks like political instability, natural disasters, and economic downturns in any one particular country or region. For example, if you're based in the United States, you may want to consider investing in emerging markets like China or India, which have the potential for high growth but also come with higher risks.
4. Consider alternative assets
In addition to traditional stocks and bonds, there are a variety of alternative assets that you can invest in to diversify your portfolio. These include things like real estate, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. Alternative assets can provide unique benefits like inflation protection and low correlation with traditional assets. However, they also come with their own risks and require a different set of skills and knowledge to invest in effectively.
5. Monitor your portfolio regularly
Finally, it's important to remember that diversification is not a one-time event. As economic conditions change and your own risk tolerance evolves, you may need to adjust your portfolio accordingly. Regularly monitoring your investments and rebalancing your portfolio can help ensure that you maintain a balanced risk curve over time.
Achieving a balanced risk curve diversification strategy requires careful consideration of a variety of factors, including your risk tolerance, sector exposure, geographic diversification, and alternative assets. By taking a holistic approach to diversification and regularly monitoring your portfolio, you can help protect yourself against market volatility and achieve your long-term investment goals.
Achieving a Balanced Risk Curve Diversification Strategy - Risk curve diversification: Spreading risk across multiple dimensions