MPN AJIT SURYA SINGH
- 1. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia CHITTARANJAN NATIONAL CANCER INSTITUTE Dr. Ajit kumar singh 2nd year PGT MD Laboratory medicine CNCI Kolkata Moderator Dr. Saunak Mitra Mustafi MD ( Pathology ) Professor, Department of laboratory services Chittaranjan National Cancer Institute (CNCI) Kolkata, 700160
- 2. Definition : o Myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN). o Originate in an abnormal pluripotent bone marrow stem cell. o Consistently associated with t(9:22) resulting BCR-ABL 1 fusion gene , located on chromosome number 22. o Results in production of abnormal tyrosine kinase protein
- 3. The 2008 World Health Organization Classification System for Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
- 4. The 2017 WHO Classification of MPN: The 2017 WHO Classification of MPN Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), BCR-ABL1–positive Chronic neutrophilic leukemia (CNL) Polycythemia vera (PV) Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) Primary myelofibrosis, prefibrotic/early stage Primary myelofibrosis, overt fibrotic stage Essential thrombocythemia (ET) Chronic eosinophilic leukemia, not otherwise specified (CEL, N O S ) Myeloproliferative neoplasm, unclassifiable (MPN-U)
- 6. INCIDENCE ▶ It accounts for ∼15% of all cases of leukemia. ▶ The annual incidence of CML is 1-2 cases per 100,000 individuals. ▶ Male : female ratio 1.6:1 ▶ Median age at diagnosis: 55–65 years. ▶ Uncommon in children (3% of patients with CML are younger than 20 years) ▶ Incidence increases slowly with age, with a steeper increase after the age of 40–50 years. ▶ With TKI therapy, the annual mortality has been reduced from 10–20% to about 2%.
- 7. ETIOLOGY ▶ No familial associations ▶ Large doses of radiation ▶ Exposure to ionizing radiation ▶ Atomic bomb survivors had an increased incidence ▶ No clear correlation with exposure to cytotoxic drugs
- 8. Pathophysiology ▶ Balanced Reciprocal Translocation between chromosome 9 and 22 (Philadelphia Chromosome) ▶ Detected in 90% of patients with CML ▶ Fusion between the Abelson (ABL) tyrosine kinase gene at chromosome 9 and the break point cluster (BCR) gene at chromosome 22, resulting in a chimeric oncogene (Bcr-Abl) ▶ Results in the formation of the BCR-ABL1 fusion protein. ▶ This BCR-ABL1 oncoprotein exhibits constitutive kinase activity.
- 9. ABL1 breakpoint: • ABL1 gene is located on 9q34. • ABL1 breakpoint typically occurs between exon 1 and 2 (a2).
- 10. At least 3 different breakpoints: 1. Major breakpoint cluster region (M-BCR): • Encodes a p210 fusion protein. • M-BCR present in 99% of CML and 40% of adult Ph(+) B-cellALL cases. 2. Minor breakpoint cluster region (m-BCR): • m-BCR encode a p190 fusion protein. • m-BCR present in 90% of pediatricALL and 60% of adultALL. • m-BCR is also present in rare CML cases (1%). 3. Micro breakpoint cluster region (µ-BCR): • µ-BCR encodes a p230 fusion protein. • CML cases with this fusion show prominent neutrophils &/or conspicuous thrombocytosis. BCR breakpoints
- 13. COURSE OF THE DISEASE • CML has 3 phases 28 Clinical course ▶ Chronic phase ▶ Accelerated phase ▶ Blast crisis
- 14. I. Chronic Phase o Most patients are asymptomatic o Incidental leukocytosis/splenomegaly o Bleeding and infectious complications are uncommon in the chronic phase
- 15. o Early CML (“chronic phase”) does not behave like a malignant disease. o However, untreated CML is inherently unstable, and without treatment the disease progresses to an accelerated and then acute blast phase, which is morphologically indistinguishable from acute leukemia.
- 16. CLINICAL FEATURES: • Age: oThe median age at diagnosis is 65 years, but children as young as 3 years can be affected. • Gender: oA slight male predominance is observed. • Clinical picture: oPatients are often initially identified due to leukocytosis being found during routine blood work, because approximately half of the patients at diagnosis do not have symptoms. oThe other half complain of fatigue, malaise, weight loss, or night sweats. • Physical examination: oSplenomegaly and hepatomegaly are seen in about 50% and 20% of patients, respectively.
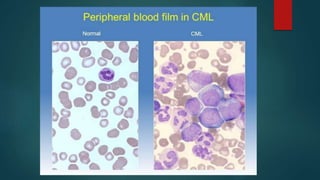
- 17. MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY: CHRONIC PHASE: Peripheral Blood: WBCs: • Granulocytic leukocytosis with left shift to immaturity. • Predominance of neutrophils and myelocytes (2 peaks). • < 10 % blasts (Usually 1 – 9%). • Basophilia. • Often eosinophilia. • Absolute monocyte count is elevated (> 1 x 109/L); but the percentage is usually < 3%. • No significant granulocytic dysplasia or toxic changes.
- 19. RBCs: • No or mild anemia. • Circulating nucleated red blood cells. Platelets: • Preserved/elevated platelet count. Marked thrombocytosis is unusual. • Atypical large platelets or megakaryocytic cytoplasmic fragments; megakaryocytic nuclei. circulating
- 20. Bone marrow aspirate: Cellularity: • Hypercellular for age due to marked granulocytic proliferation. Erythroid Series: • Erythroid precursors are reduced in percentage but show normal maturation. Granulocytic Series: • Usually 1 – 9%. • Myeloid : erythroid (M:E) ratio > 10:1. • Predominance of neutrophils and myelocytes (2 peaks). • Minimal/absent dysplasia.
- 21. Megakaryocytic Series: • Usually increased megakaryocytes. • Distinctive megakaryocytic morphology; small and monolobulated (so-called dwarf megakaryocytes). Other Findings: • Sea-blue histiocytes due to increased cell turnover. These cells carry BCR-ABL1 because they are progeny of the affected leukemic stem cell.
- 22. Bone marrow core biopsy: Cellularity: • 95% cellular due to marked granulocytic predominance. Erythroid Series: • Decreased erythroid lineage. Granulocytic Series: • Marked granulocytic predominance. • M:E ratio > 10:1. Megakaryocytic Series: • Small, monolobulated, (dwarf) megakaryocytes. Other Findings: • May see increased reticulin fibrosis.
- 24. Disease progression: ACCELERATED PHASE (AP): The 2017 WHO criteria for diagnosis of accelerated phase include: Any one or more of the previous hematologic/cytogenetic criteria or response to TKI criteria diagnose CML accelerated phase 1.Hematologic criteria: - Persistent or increasing WBC count (>10 x 109/L), unresponsive to therapy. - Persistent or increasing splenomegaly, unresponsive to therapy. - Persistent thrombocytosis (>1000 x 109/L), unresponsive to therapy. - Persistent thrombocytopenia (<100 x 109/L) unrelated to therapy. - 20% or more basophils in the peripheral blood. - 10% - 19% blasts in the peripheral blood or bone marrow.
- 25. 3. Provisional response to tyrosine kinase inhibitor criteria: - Hematologic resistance to the first TKI (or failure to achieve a complete hematologic response to the first TKI). or - Any hematologic, cytogenetic, or molecular indications of resistance to two sequential TKIs. or - Occurrence of two or more mutations in BCR-ABL1 during TKI therapy. 2.Cytogenetic criteria: Additional clonal chromosomal abnormalities in Ph+cells at diagnosis that include “major route” abnormalities (second Ph,trisomy 8, isochromosome 17q, trisomy 19), a complex karyotype, or abnormalities of 3q26.2. Any new clonal chromosomal abnormality in Ph+ cells that occurs during therapy
- 26. Blast phase (BP): The BP is diagnosed when: - Blasts equal or are greater than 20% of the peripheral blood WBC or of the nucleated cells of the BM, or - When there is an extramedullary blast proliferation, or - Large foci of blasts Types of blast phase: • 70-80% myeloid: (70% granulocytic, 10-20% megakaryocytic, < 10% e r t h o i d < 5% monocytic). • 20-30% lymphoid: (90% B-lymphoblastic leukemia, T-lymphoblastic leukemia uncommon) o Presence of lymphoblasts (detection of any lymphoblasts should raise concern for impending lymphoid blast phase). • < 5% biphenotypic.
- 27. ANCILLARY TESTS: 1. Immunohistochemistry: • Role is minimal in chronic-phase CML. • Blast markers: CD34 &/or CD117, TdT:Assess for increased &/or clustered blasts. 2. Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping: • Plays minimal role in chronic-phase CML. • Useful in blast lineage determination in accelerated/blast phase.
- 28. 3.Conventional Cytogenetic Analysis (Karyotyping): • Should be performed routinely in work-up for myeloid neoplasm. • Detection of t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2): O t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2) (or variant) diagnosis. &/or BCR-ABL1 gene fusion required for of cases (not detected by O t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2) reportedly cryptic in 5% karyotyping). ■Do FISH or molecular for BCR-ABL1 fusion. • Clonal evolution in accelerated/blast phase: oAdditional Philadelphia chromosome, trisomy 8, isochromosome (17q), and trisomy 19 (major route abnormalities).
- 29. 4.Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH): • Reveals/confirms genetic fusion of BCR-ABL1. • Advantages: O More sensitive than conventional cytogenetics. O Detects most cryptic rearrangements. • Disadvantages: O Rare cryptic rearrangements may be missed. O Not sensitive enough for MRD or early relapse detection. B C R A B L 1 BCR-ABL BCR-ABL
- 30. 5.PCR for BCR-ABL ▶ Qualitative PCR allow for the diagnosis of CML ▶ Quantitative PCR is used to quantify the amount of disease ▶ Allows for the identification of cryptic BCR-ABL translocations ▶ Does not require a bone marrow aspirate for optimal results
- 31. Prognostic Factors ▶ Sokal Index ▶ Most important prognostic indicators ▶ Percentage of circulating blasts ▶ Spleen size ▶ Platelet count ▶ Age ▶ Cytogenetic clonal evolution ▶ This system was developed based on chemotherapy-treated patients
- 33. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS • Essential thrombocythemia • Leukemoid reactions • Atypical Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia BCR-ABL1 Negative • Chronic neutrophilic leukemia • Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia
- 34. 1. Leukemoid reaction: Criteria CML Leukemoid Reaction 1. Clinical features Splenomegaly According to the cause 2. Peripheral blood: - Myelocyte & neutrophil peaks: Present Not present - Basophilia & eosinophilia: Present Not present - Toxic granulation: Not present Present 3. BM examination: Trilineage hyperplasia Granulocytic hyperplasia 4. NAP score: Low Normal or increased 5. Philadelphia chromosome Positive Negative DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
- 36. 2.Atypical Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia BCR-ABL1 Negative: • Unfortunate disease name. No relationship to CML. • BCR-ABL1 Negative • Dysplasia prominent • Recurrent SETBP1 mutations
- 37. TREATMENT 1. Initial Cytoreduction T herapy 2 . T yrosine Kinase Inhibitor T herapy 3. Interferon therapy 4. Chemotherapy 5. Allogeneic Stem Cell T ransplantation 6 . T reatment of accelerated/blast phases 7 . T reatment of CML in pregnancy 8 . T reatment cessation 35
- 38. Initial therapy T reatment • Allopurinol 300 mg/day orally with adequate hydration Rasburicase 0.2 mg/kg i.v (one doses) for Hyperuricemia* • Leukapheresis–helps reduce leucocyte burden, only in conjunction with definitive therapy • Hydroxyurea -Reversible suppression of hematopoiesis 1 to 6 g/day orally (titre based on counts) • Anagrelide –to reduce the platelet burden
- 39. Tyrosine Kinase inhibitor therapy First generation Second generation Imatinib T reatment Dasatinib Nilotinib Bosutinib Ponatinib Bafetinib
- 40. Imatinib ▶MOA ▶ Induces Apoptosis in cell with Bcr-Abl ▶ Blocking the ATP binding site and thereby preventing a conformational switch to the active form ▶ Shows specificity for Bcr-Abl, the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor.
- 41. Tyrosine Kinase inhibitor therapy Imatinib Mesylate • Dosage –400 mg/day orally 400 mg BD • Well tolerated • Myelosuppression iscommon in CML patients • Elevated hepatic transaminases (Acute liver failure described) • Periorbital edema • Cutaneous reactions • Osteoporosis 40 T reatment
- 42. Resistance to imatinib Four mechanisms has been described: 1. Gene amplification i.e more Bcr-Abl are produced ▶ Treated by increasing dose to 800mg 2. Enhanced expression of multidrug exporter proteins ▶ Treated by increasing dose to 800mg 3. Mutations at the kinase site ▶ Replace with Nilotinib or Dasatinib 4.Alternative signaling pathways functionally compensating for the imatinib - sensitive mechanisms (SRC family of kinases get mutated and they start phosphorylating the kinases) ▶ Replace with Dasatinib
- 43. Treatment of CML in pregnancy T reatment • Untreated CML placental insufficiency (leukostasis) • Risk of teratogenicity with Imatinib • IFNissafe –can be used • Leukapheresis –1st trimester • Hydroxyurea –2nd and 3rd trimester • Restart T KItherapy soon after delivery 55
- 44. Factors influencing choice of therapy ▶ Phase ▶ Availability of a donor for allogeneic stem cell transplant ▶ Patient age ▶ Presence of medical co-morbidities ▶ Response to treatment with TKIs
- 47. TERMINOLOGY: Definition: • Classic myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) characterized by: oIncreased red blood cells (RBCs). oJAK2 gene gain of function somatic mutation. Phases of PV: 1. Pre-polycythemic phase with mild erythrocytosis (so-called masked PV): Borderline to only mild erythrocytosis. 2. Overt polycythemic phase:Associated with significantly increased Hb, Hct, and RBC mass. 3. Spent phase and post-polycythemic myelofibrosis: • Decrease in RBC mass; patient often anemic. • Further enlargement of spleen. • Marked reticulin and collagen fibrosis of BM. • Extramedullary hematopoiesis.
- 48. ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS: I. JAK2 V617F mutation: • Detected in > 95% of PV cases. • Point mutation in exon 14 of pseudokinase domain: oSubstitution of a G to T at 1849 position. oThis substitution leads to substitution of valine for phenylalanine (V617F). oMutation involves myeloid lineages and is absent in lymphocytes. • Consequences of JAK2 V617F mutation: oGain-of-function somatic mutation. oConstitutively activate STAT-mediated transcription in absence of EPO ligand.
- 49. II. JAK2 exon 12 mutations: • Uncommon, except in JAK2 V617F-negative PV. • Present in 3% of PV cases. • JAK2 exon 12 mutations appear to result specifically in an erythrocytosis phenotype.
- 50. CLINICAL FEATURES: • Age: oThe average age at diagnosis is 60 years. • Gender: oSlight male predominance. • Clinical picture: oMany patients are asymptomatic. oThe diagnosis may be suspected by the findings of plethora and splenomegaly on examination or abnormalities on a routine blood count that, in addition to increased HGB and HCT, often include leukocytosis and/or thrombocytosis. oThe main causes of morbidity and mortality are due to complications of blood hyperviscosity, which stems from increases in red cell mass and contributes to an increased risk of venous and arterial thrombosis.
- 51. MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY: 1. Pre-polycythemic and polycythemic p h a s e s : Peripheral Blood: WBCs: • Neutrophilia and, rarely, basophilia may be present. • Occasional immature granulocytic cells may be seen in polycythemic phase. RBCs: • Mild to significantly increased normochromic/normocytic RBCs. • The RBC indices are usually normal unless there is concomitant iron deficiency. Platelets: • Prominent thrombocytosis in 15% of cases.
- 52. Bone marrow examination: Cellularity: • Typically, hypercellular for age. • Increased subcortical cellularity. • Panmyelosis: prominent erythroid, granulocytic and megakaryocytic proliferation. Erythroid series: • Erythropoiesis is prominent, often occurs in expanded erythroid islands. • It demonstrates normoblastic maturation. Granulocytic series: • Granulopoiesis may show a shift toward immaturity. • There is no increase in the percentage of blasts. • There is no significant dysplasia. Megakaryocytic series: • Increased number of megakaryocytes with variably hyperlobated forms.
- 54. 2. Peripheral Blood: • Peripheral blood with anemia &/or leukoerythroblastic picture. • Prominent anisopoikilocytosis, including teardrop forms and nucleated RBCs. • Immature granulocytic cells but no significant dysplastic cells. Spent phase and post-polycythemic myelofibrosis:
- 55. Bone marrow examination: • Cellularity: Variable cellularity hypocellular for age. but often • Erythroid & Granulocytic Series: Decreased erythropoiesis and granulopoiesis. • Megakaryocytic Series: Megakaryocytes generally similar to those seen in antecedent PV. • Other Findings: oProminent reticulin and collagen fibrosis. oOsteosclerosis may be seen in late-stage disease. oIncreasing splenomegaly or constitutional symptoms.
- 56. ANCILLARY TESTS: 1. Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping: • No consistent immnuophenotypic abnormality transformation. described in absence of leukemic 2. Conventional Cytogenetic Analysis (Karyotyping): • Common cytogenetic abnormalities: oTrisomy 8, trisomy 9, del(20q), del(13q), and del(9p). oComplex cytogenetic abnormalities in post-polycythemic myelofibrosis. • Cytogenetic abnormalities in PV patients with transformation to myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) or blast phase: oDetected in virtually all patients with transformation to MDS/blast phase. oInclude those commonly seen in therapy-related MDS/acute myeloid leukemia.
- 57. 3. Molecular Genetic Testing: JAK2 V617F mutation: • Gain-of-function mutation. • Mutation occurs in all cells of myeloid lineages. • Present in 95% of patients with PV. • JAK2 V617F mutation is homozygous in most PV cases. JAK2 exon 12 mutations: • Relatively specific for JAK2 V617F-negative PV. • 4% frequency among all patients with PV. • JAK2 exon 12 mutations are often heterozygous. • Associated with predominantly erythroid myelopoiesis and younger age at diagnosis.
- 58. 4. Other Laboratory tests: Serum erythropoietin (EPO): • Serum EPO levels are typically decreased in PV, in contrast to e le v a t e d levels usually found in secondary polycythemia. • Measurement of EPO levels is an important study that should be performed early in the workup of polycythemia. • Anormal EPO level does not necessarily exclude PV or secondary erythrocytosis.
- 59. DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA: The 2017 WHO Diagnostic Criteria for Polycythemia Vera (PV) Major Criteria: 1. Hemoglobin > 16.5 g/dL in men, > 16.0 g/dL in women; or hematocrit > 49% in men, > 48% in women; or increased red cell mass (More than 25% above mean predicted value). 2. BM biopsy showing hypercellularity for age with trilineage growth (panmyelosis) including prominent erythroid, granulocytic, and megakaryocytic proliferation with pleomorphic, mature megakaryocytes (differences in size). 3. Presence of JAK2 V617F or JAK2 exon 12 mutation. Minor Criterion: - Subnormal serum erythropoietin level. Diagnosis of polycythemia vera (PV) requires meeting either all three major c r i t e r i aor the first two major criteria and the minor criterion.
- 60. The 2017 WHO Diagnostic Criteria for Post-polycythemia vera Myelofibrosis: Required Criteria: 1. Documentation of a previous diagnosis of WHO-defined polycythemia vera. 2. Bone marrow fibrosis grade 2-3 (on 0-3 scale). Additional Criteria (two are required): 1. Anemia or sustained loss of either phlebotomy (in the absence of cytoreductive therapy) or cytoreductive treatment requirement for erythrocytosis. 2. Leukoerythroblastic picture in PB smear. 3. Increasing splenomegaly: ■ defined as either an increase in palpable splenomegaly of > 5 cm from baseline (distance from the left costal margin) or the appearance of newly palpable splenomegaly. 4. Development of > 1 of 3 constitutional symptoms: ■ > 10% weight loss in 6 months. ■ Night sweats. ■ Unexplained fever (> 37.5° C).
- 63. TERMINOLOGY: Definitions: • Specific subtype of myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN). • Hematopoietic proliferation essentially restricted to megakaryocytic lineage. • Exclusion of other classic MPNs: oChronic myeloid leukemia, BCR-ABL1 positive. oPolycythemia vera. oPrimary myelofibrosis, early phase.
- 64. ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS: Molecular Mutations: 3 driver mutations are identified: I. JAK2 V617F mutation: • 1st driver mutation to be identified. II. MPL W515L mutation: • 2nd driver mutation to be identified. • 3-5% of ET cases harbor this mutation. • Substitution of a G to T at nucleotide 1544. • Results in substitution of amino acid tryptophan to leucine (W515L). • General outcome of mutation is promotion of constitutive, cytokine-independent activation of JAK/ STAT signaling pathway.
- 65. III. CALR mutation: • 3rd driver mutation to be identified. • 20-25% of ET cases harbor this mutation (CALR + ET). • 2 most common types of mutations: oType 1 mutation:A52-bp deletion (Most common type). oType 2 mutation: A5-bp insertion. • Abnormal function of CALR-mutated protein: oSuggestion that mutant calreticulin activates JAK-STAT pathway. oResults in excessive platelet production. • JAK2, CALR, and MPL mutations are most often mutually exclusive. oPresence of 1 of these mutations distinguishes reactive disorder from neoplasm. oThese mutations do not distinguish PMF from PV or ET.
- 66. CLINICAL FEATURES: • Age: o The median age at diagnosis is 60 years. • Gender: o Slight female predominance. • Clinical picture: o Patients are usually asymptomatic. o Patients may exhibit symptoms such as headaches, blurred vision, dizziness, and erythromelalgia (redness, burning, pain of distal ends of toes and fingers) due to thrombotic occlusion of the microvasculature. o Catastrophic large vessel thrombosis includes stroke, myocardial infarction, deep venous thrombosis (including splanchnic vein thrombosis), and peripheral arterial thrombosis. o Bleeding is less common than thrombosis. o Splenomegaly is not as prominent as that of the other MPNs, and it occurs in 15–20% of patients.
- 67. MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY: Peripheral Blood: WBCs: • The WBC count and leukocyte differential are usually normal. • Mild leukocytosis is sometimes seen. • White blood cell morphology unremarkable. • No leucoerythroblastic reaction. • Neutrophilia uncommon. • No significant left shift in granulocytic series. • No significant basophilia. • Circulating blasts unusual.
- 68. RBCs: •Red blood cell morphology unremarkable. •Significant anisopoikilocytosis is uncommon and teardrop-shaped RBCs are not observed. Platelets: •Variable thrombocytosis but ≥ 450 x 10⁹/L. •Striking platelet anisocytosis: oSmall and large platelets. oHypogranular forms may be seen. oCirculating megakaryocytic nuclei.
- 69. Bone marrow: Cellularity: • Normal cellularity to mildly hypercellular. Erythroid and Granulocytic Series: • Generally, no significant granulocytic or erythroid proliferation. • Occasionally may encounter mild granulocytic hyperplasia. oConsider early phase of primary myelofibrosis. • Blasts < 5%.
- 70. Megakaryocytic Series: • Striking megakaryocytic proliferation: oIncreased numbers. oLoosely clustered. oMarkedly enlarged, hyperlobated. oET megakaryocytes are largest of all BM disorders. Other Findings: • Absent/minimal reticulin fibrosis.
- 71. BM aspirate shows the phenomenon of “pseudoparticle” formation that may occur as a result of marked thrombocytosis and extensive platelet clumping in vitro. These particles mimic BM particles but have less cellular element. In ET, BM aspirate typically reveals intact granulopoiesis and erythropoiesis with unremarkable morphology. The very large hyperlobated megakaryocytes are characteristic.
- 72. BM core biopsy shows normal bone and mild hypercellularity. Increased megakaryocytes form loose clusters and demonstrate hyperlobulation. BM core biopsy features of ET. Increased megakaryocytes form loose clusters and demonstrate hyperlobulation.
- 73. ANCILLARY TESTS: 1. Histochemistry: • Reticulin: oAbsent to minimal fibrosis. oProgressive fibrosis in rare cases. 2. Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping: • Blasts < 5% in typical ET. • Rare cases of leukemic transformation of ET. oBlasts > 20%; usually myeloid phenotype. 3. Conventional Cytogenetic Analysis (Karyotyping): • Usually normal karyotype (in 90% of cases). • Cytogenetic abnormalities are detected in less than 10% of ET cases at diagnosis.
- 74. 4. Molecular Genetic Testing: • JAK2 V617F mutations present in 60% of cases. • JAK2 exon 12 mutations are absent. • CALR mutations in 20-25% of cases. • MPL mutations present in 3-5% of cases.
- 75. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: 1. Reactive/Secondary t h r o m b o c y t o s i s :
- 77. Megakaryocytes in E T Megakaryocytes in prePMF
- 78. DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA: The 2017 WHO Diagnostic Criteria of Essential T h r o m b o c y t h e m i a(ET) Major Criteria: 1. Platelet count > 450 x 109/L. 2. BM biopsy showing: • Proliferation mainly of the megakaryocyte lineage with increased numbers of enlarged, mature megakaryocytes with hyperlobulated nuclei. • No significant increase or shift toward immaturity in neutrophil granulopoiesis or erythropoiesis and very rarely minor (grade 1) increase in reticulin fibers. 3. Not meeting the WHO criteria for BCR-ABL1+ CML, PV, PMF, MDS, or other myeloid neoplasms. 4. Presence of JAK2, CALR, or MPL mutation. Minor Criterion: - Presence of a clonal marker or absence of evidence for reactive thrombocytosis. Diagnosis of ET requires meeting all four major criteria or the first three major criteria and the minor criterion.
- 80. Pathologic Interpretation Pearls: Sustained thrombocytosis: Platelet count ≥ 450 x 10⁹/L. Reactive thrombocytosis excluded. Red blood cell and white blood cell cytology and counts unremarkable. Enlarged megakaryocytes with hyperlobulation. Absent/minimal fibrosis. Clonal: o JAK2 V617F positivity in 60%. o CALR mutations in 20-25%. o MPL mutations in 3-5%. SUMMARY:
- 82. TERMINOLOGY: Definition: • Specific subtype of myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN). • Clonal hematopoietic stem cell disorder. • Hematopoietic proliferation that shows predominantly megakaryocytic and granulocytic proliferation with ultimate fibrosis. • Exclusion of other classic MPNs: oChronic myeloid leukemia (CML), BCR-ABL1 positive. oPolycythemia vera (PV). oEssential thrombocythemia (ET).
- 83. ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS Molecular Mutations: 3 driver mutations are identified: I. JAK2 V617F mutation: • 1st driver mutation to be identified. II. MPL W515L mutation: • 2nd driver mutation to be identified. • 6-7% of PMF cases harbor this mutation. • Substitution of a G to T at nucleotide 1544. • Results in substitution of amino acid tryptophan to leucine (W515L). • General outcome of mutation is promotion of constitutive, cytokine-independent activation of JAK/ STAT signaling pathway.
- 84. III. CALR mutation: • 3rd driver mutation to be identified. • 20-25% of PMF cases harbor this mutation. • 2 most common types of mutations: oType 1 mutation:A52-bp deletion (Most common type). oType 2 mutation: A5-bp insertion. • Abnormal function of CALR-mutated protein: oSuggestion that mutant calreticulin activates JAK-STAT pathway. oResults in excessive platelet production. • JAK2, CALR, and MPL mutations are most often mutually exclusive. oPresence of 1 of these mutations distinguishes reactive disorder from neoplasm. oThese mutations do not distinguish PMF from PV or ET.
- 85. Triple negative PMF: •10-15% of PMF cases are negative for all 3 mutations: JAK2, CALR, and MPL. •Associated with poor prognosis.
- 86. Phases of primary myelofibrosis ( P M F ) : There are 2 phases of PMF: I. Prefibrotic phase (prePMF) It is characterized by: - Marked thrombocytosis in the peripheral blood. - Hypercellular BM with granulocytic and atypical megakaryocytic proliferation. - Absent or only slight reticulin fibrosis. - Minimal if any EMH. II. Fibrotic phase ( O v e r t PMF) It is characterized by: - Variable BM cellularity. - Reticulin or collagen fibrosis, osteosclerosis. often - Prominent hepatosplenomegaly due to EMH. - Leucoerythroblastic reaction in the peripheral blood.
- 87. CLINICAL FEATURES: • Age: o The median age at diagnosis is 67 years.About 5% of cases present before 40 years. • Gender: o No significant prediliction. • Clinical picture: o Patients are usually asymptomatic. o Patients may exhibit symptoms such as headaches, blurred vision, dizziness, and erythromelalgia (redness, burning, pain of distal ends of toes and fingers) due to thrombotic occlusion of the microvasculature. o Catastrophic large vessel thrombosis includes stroke, myocardial infarction, deep venous thrombosis (including splanchnic vein thrombosis), and peripheral arterial thrombosis. o Bleeding is less common than thrombosis. o Splenomegaly is not as prominent as that of the other MPNs, and it occurs in 15–20% of patients.
- 89. MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY Peripheral blood: I. Prefibrotic phase (prePMF) RBCs: Modest anemia. WBCs: Mild leukocytosis. Platelets: Moderate to marked thrombocytosis. Blood film morphology: - The most striking finding is often the marked increase in platelets. - Mild neutrophilia with a left shift may be seen. - No significant dysplasia. - Variable, often subtle, basophilia. - Myeloblasts, nucleated RBCs, and teardrop-shaped RBCs are rarely observed in the early stages
- 90. II. Fibrotic phase (Overt PMF) There is gradual worsening of hematologic parameters as the disease progresses. RBCs: More severe anemia than PrePMF. WBCs: - Mild leukocytosis. - Severe leucopenia may occur as BM failure becomes more prominent as a result of increasing fibrosis. Platelets: Lower platelet count than PrePMF. Blood film morphology: The classic findings of patients with overt PMF are: - Leucoerythroblastic reaction with numerous teardrop- shaped RBCs. - Bizarre, abnormal platelets. - Blasts occasionally account for 5% or more. Blast percentages of 10% to 19% in PB indicate that there is progression to AP, and 20% or more blasts is sufficient for the diagnosis of blast transformation.
- 91. BM Examination: I. Pre-fibrotic phase (PrePMF): Cellularity: - In prePMF, BM is hypercellular. Erythroid series: - Erythropoiesis is reduced in most cases. Granulocytic series: - There is an increased number of neutrophils. - Although there may be a left shift in granulopoiesis, neutrophils at the metamyelocyte through segmented stages usually predominate. - The percentage of myeloblasts is not increased. Megakaryocytic series: - There is an increased number of atypical megakaryocytes. - Megakaryocytes in PMF are morphologically more atypical than in any other MPN: • They vary from small to large. Some have an abnormal nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio and disorganized, plump, cloudlike, or balloonlike nuclear lobation. Reticulin stain: - Reticulin fibers vary in quantity and thickness but are often not increased in prePMF, except focally around blood vessels.
- 92. Pre-fibrotic
- 93. II. Fibrotic phase (Overt PMF): Cellularity: -As prePMF progresses to the fibrotic stage, the marrow cellularity decreases. Erythroid and Granulocytic series: depressed. Megakaryocytic series: • Megakaryocytic atypia: • Dense clusters. • Hyperchromatic and bizarre nuclei. • Cloud-like nuclei. Reticulin fibrosis: Reticulin or even overt collagen fibrosis of the marrow becomes more o b v io u s . Other findings: • Osteosclerosis. • Moderate to marked reticulin/collagen fibrosis. • Dilated sinuses.
- 94. Fibrotic
- 95. MF-0: Scattered linear reticulin with no intersections (cross-overs) corresponding to normal BM MF-1: Loose network of reticulin with many intersections, especially in perivascular areas ANCILLARY TESTS: 1. Histochemistry (Reticulin s t a i n ) : Semiquantitative Grading of MF
- 96. MF-2: Diffuse and dense ↑ in reticulin with extensive intersections, occasionally with focal bundles of collagen and/or focal osteosclerosis. MF-3: Diffuse and dense ↑ in reticulin with extensive intersections and coarse bundles of collagen, often with osteosclerosis
- 97. 2. Molecular Genetic Testing: • JAK2 V617F mutations present in 60% of cases. • JAK2 exon 12 mutations are absent. • CALR mutations in 25% of cases. • MPL mutations present in 6-7% of cases. • 10 – 15% of cases are negative for JAK2 V617F, CALR and MPL (triple negative PMF).
- 98. Molecular Approach in BCR-ABL negative MPN: oThese include: PV, ET and PMF. 1. BCR-ABL1 fusion must be ruled out to exclude chronic myelogenous leukemia. 2. Cases of suspected PV would be considered for JAK2 V617F and JAK2 exon 12 mutations. 3. If a diagnosis of ET or PMF is favored, mutations may be sought in MPL, JAK2 (V617F), or CALR. ■Because these mutations are considered mutually exclusive, a stepwise reflex algorithm may be used: ■Based on frequency, best order is JAK2 V617F > CALR > MPL. 4. Next generation sequencing assessment of all of these mutations at once ( ± additional genes) may become increasingly cost effective and widespread.
- 99. DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA: The 2017 WHO Diagnostic Criteria of Pre-fibrotic/Early PMF (PrePMF): Major criteria: 1.Megakaryocytic proliferation and atypia, without reticulin fibrosis > grade 1, accompanied by increased age- adjusted BM cellularity, granulocytic proliferation and often decreased erythropoiesis 2. Not meeting WHO criteria of BCR/ABL+ CML, PV, ET, MDS or other myeloid neoplasms. 3. Presence of JAK2, MPL or CALR mutation or in the absence of these mutations, presence of another clonal marker or absence of minor reactive BM reticulin fibrosis. Minor criteria: Presence of at least one of the following, confirmed in two consecutive determinations: a. Anemia not attributed to a comorbid condition. b. Leukocytosis ≥ 11 x 109/L. c. Palpable splenomegaly. d. LDH increased to above upper normal limit of institutional reference range. Diagnosis of prePMF requires meeting all three major criteria and at least one minor criterion.
- 100. The 2017 WHO Diagnostic Criteria of Overt Primary M y e l o f i b r o s i s Major criteria: 1.Megakaryocytic proliferation and atypia, accompanied by either reticulin and/or collagen fibrosis grades 2 or 3. 2. Not meeting WHO criteria of BCR/ABL+ CML, PV, ET, MDS or other myeloid neoplasms. 3. Presence of JAK2, MPL or CALR mutation or in the absence of these mutations, presence of another clonal marker or absence of minor reactive BM reticulin fibrosis. Minor criteria: Presence of at least one of the following, confirmed in two consecutive determinations: a. Anemia not attributed to a comorbid condition. b. Leukocytosis ≥11 x 109/L. c. Palpable splenomegaly. d. LDH increased to above upper normal limit of institutional reference range. e. Leucoerythroblastosis. Diagnosis of Overt PMF requires meeting all three major criteria and at least one minor criterion.
- 102. TERMINOLOGY: Definition: • Specific subtype of myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN). • Clonal hematopoietic stem cell disorder manifesting predominantly in granulocytic lineage. • Characterized by: oPersistent peripheral blood neutrophilia. oPersistent BM granulocytic proliferation. oThere is no BCR-ABL1 fusion gene. oHepatosplenomegaly common. oActivating mutation of CSF3R gene. Mutation present in most cases. oReactive conditions resulting in neutrophilia must be excluded in cases lacking clonal genetic marker. oOther myeloid neoplasms must be systematically excluded in cases lacking CSF3R mutation.
- 103. CLINICAL FEATURES: • Age: oThe average age at diagnosis is 60 years. • Gender: oSlight male predominance. • Clinical picture: oMajority of patients asymptomatic. oIncidental detection of leukocytosis on CBC. oHepatomegaly. oSplenomegaly: the most consistent clinical finding. oWeight loss. oEasy bruising.
- 104. MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY: Peripheral Blood: •WBC ≥ 25.0 x 10⁹/L. •Neutrophilia and increased band forms ( ≥ 80% of WBC). •Toxic changes with prominent granules may be seen. Must exclude reactive condition. •Absence of dysplasia. •No significant basophilia. •Immature granulocytes constitute < 10% of WBC. •Blasts rarely noted. •RBCs & platelets: usually unremarkable.
- 105. Bone marrow: • Cellularity: Hypercellular; > 90%; due to granulocytic predominance. • Erythroid series: Reduced in percentage but show normoblastic maturation. • Granulocytic Series: oThe percentage of blasts and promyelocytes in BM is not increased at diagnosis (Blasts < 5%). oThere is an increase in the percentage of myelocytes, metamyelocytes, bands, and segmented neutrophils. oThere is no significant dysplasia. oBasophilia and eosinophilia are generally not observed. • Megakaryocytic Series: Normal. • Other findings: No significant fibrosis.
- 107. DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA: The 2017 WHO Diagnostic Criteria of Chronic Neutrophilic Leukemia (CNL) 1. Peripheral blood white blood cell count ≥ 25 x 109/L - Segmented neutrophils plus band forms are > 80% of white blood cells. - Neutrophil precursors (promyelocytes, myelocytes, metamyelocytes) are <10% of white blood cells. - Myeloblasts rarely observed. - Monocyte count <1 x 109/L. - No dysgranulopoiesis. 2. Presence of CSF3R T6181 or other activating CSF3R mutation. OR - In the absence of a CSFR3R mutation, persistent neutrophilia (at least 3 months) and no identifiable cause of physiological or reactive neutrophilia, including absence of a plasma cell neoplasm or, if present, demonstration of clonality of myeloid cells by cytogenetic or molecular studies.
- 108. 3. Hypercellular bone marrow: - Neutrophilic granulocytes increased in percentage and number. - Neutrophil maturation appears normal. - Myeloblasts < 5% of nucleated bone marrow cells. 4. Not meeting the WHO criteria for any other myeloid neoplasm: - Specifically, no BCR-ABL1; no rearrangement of PDGFRA, PDGFRB, or FGFR1; no PCM1-JAK2, ETV6-JAK2, or BCR-JAK2. All criteria must be met for the diagnosis of chronic neutrophilic leukemia t obe made.
- 110. Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia (CEL, NOS)
- 111. t Definition: • Clonal hematopoietic myeloproliferative neoplasm. oManifests as sustained proliferation of eosinophils and precursors. CLINICAL ISSUES: Incidence: • Rare. • Difficult to determine accurately. • Significant degree of diagnostic overlap with idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. TERMINOLOGY:
- 112. Clinical Presentation: • Asymptomatic: oIncidental identification of eosinophilia on complete blood cell count. • Symptomatic: oFever. oFatigue. oPruritus. oGastrointestinal disturbance. oEndomyocardial fibrosis. oCentral nervous symptoms.
- 113. MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY: Peripheral Blood: •Eosinophilia: oMostly mature eosinophils. oOccasional eosinophil precursors. oEosinophil count ≥ 1.5 x 10⁹/L. •Other features: • Neutrophilia common. • Blasts < 20% (usually > 2%). • No significant population of mast cells. • No circulating lymphoma cells.
- 114. Bone Marrow: • Cellularity: oUsually hypercellular due to eosinophilia. • Erythroid and Megakaryocytic Series: oIntact erythropoiesis and megakaryopoiesis. • Granulocytic Series: oEosinophilia. oBlasts < 20% (usually > 5%). oDysplasia is uncommon. oExclude myelodysplasia with eosinophilia. associated oCharcot-Leyden crystals may be observed.
- 115. ANCILLARY TESTS: 1. Immunohistochemistry: • Assess for mast cell disease: oTryptase and CD25. oMast cells may be spindled and individually distributed; not in aggregates. • Assess for Hodgkin/non-Hodgkin lymphoma: oIf morphology in BM negative: ■No further testing except for consideration of CD30 for occult T-cell lymphoma. oIf morphology in BM positive: ■No further testing if morphologic features similar to lymphoma diagnosed in extramedullary site.
- 116. 2. Conventional Cytogenetics Analysis (Karyotyping): •Document clonality if present. •Exclude recurring genetic abnormality diagnostic of different neoplasm e.g. ot(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2); BCR-ABL1 fusion in chronic myeloid leukemia. oRearrangement of PDGFRB (5q31~33), FGFR1 (8p11.23-p11.22), and PCM1- JAK2;t(8;9)(p22;q24.1). oCBFB-MYH11 inAML with inv(16). 3. Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization (FISH): •Perform testing for FIP1L1-PDGFRAfusion since cytogenetically cryptic. •Investigate possible PDGFRB, FGFR1, and PCM1-JAK2 abnormalities by chromosomal analysis.
- 117. The 2017 WHO Diagnostic Criteria of CEL 1. Eosinophilia (eosinophil count ≥1.5 x 109/L). 2. WHO criteria for BCR-ABL1-positive CML, polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, PMF, CNL, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, and BCR-ABL1-negative atypical CML are not met. 3. No rearrangement of PDGFRA, PDGFRB, or FGFR1, and no PCM1-JAK2, ETV6-JAK2, or BCR-JAK2 fusion. 4. Blast cells constitute <20% of the cells in the peripheral blood and bone marrow, a n d inv(16)(p13.1q22), t(16;16) (p13.1;q22), t(8;21)(q22;q22.1), and other diagnostic features of AML are absent. 5. There is a clonal cytogenetic or molecular genetic abnormality or blast cells account for ≥ 2 % of cells in the peripheral blood or ≥5% in the bone marrow. All criteria must be met for diagnosis of CEL. DIAGNOSTIC DIAGNOSTIC
- 119. TERMINOLOGY: Definition: • The designation MPN, unclassifiable, should be applied only to: oCases that have definite clinical, laboratory, and morphologic features of an MPN but fail to meet the criteria for any of the specific MPN entities. OR oCases present with features that overlap two or more of the MPN categories. • The designation MPN, unclassifiable, should not be used if: oLaboratory data necessary for classification are incomplete or were never obtained. oThe size or quality of BM specimen is inadequate for complete evaluation. oThe patient has received prior growth factor or cytotoxic therapy.
- 120. DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA: The 2017 WHO Diagnostic Criteria of MPN, unclassifiable (MPN-U) 1. Features of an MPN are present. 2. WHO criteria for any other MPN, myelodysplastic syndrome, myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative disorder, or BCR-ABL1–positive chronic myeloid leukemia are not met. 3. Demonstration of JAK2, CALR, or MPLmutation characteristically associated with MPN. OR - In the absence of these mutations, presence of another clonal marker. OR - In the absence of a clonal marker, no evidence that bone marrow fibrosis is secondary to infection, autoimmune disorder or other chronic inflammatory condition, hairy cell leukemia or other lymphoid neoplasm, metastatic malignant neoplasm, or toxic (chronic) myelopathy. All criteria must be met for diagnosis of MPN-U.
- 121. SUMMARY
- 122. MPN COMPARATIVE FEATURES: Blood Features BM Features Molecular/Genetics I. CML, BCR-ABL1 Positive, Chronic Phase: Marked leukocytosis. Marked hypercellular. t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2) isvirtually present in 100% of metaphases. Predominance of mature neutrophils (peaks). Predominance of myeloid lineage cells. BCR-ABL1 gene fusion is the d e f in in g feature; required for diagnosis. Left shift to blasts (< 10%). Maturation intact; granulocytic lineage predominates in BM with normal maturation and without dysplasia. Responsive to tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy with marked reduction of incidence of blast phase. Absolute basophilia. Blasts < 10 %. Frequent thrombocytosis. Increased small hypolobated megakaryocytes. Nucleated RBCs (nRBCs) common. Other dysplastic features uncommon. Dysplasia absent. Absent fibrosis.
- 123. Blood Features BM Features Molecular/Genetics II. Polycythemia Vera, Chronic Phase: Erythrocytosis. Hypercellular. Must be BCR-ABL1 negative. Variable leukocytosis and nRBCs. Maturation intact; panmyelosis. o JAK2 V617F in >95% of cases. o JAK2 exon 12 in the remainder. Variable basophilia; thrombocytosis. Blasts <2%. JAK2 inhibitor therapy is potential treatment option. Dysplasia absent. Increased, usually hyperlobated megakaryocytes. Fibrosis absent/minimal.
- 124. Blood Features BM Features Molecular/Genetics III. Essential Thrombocythemia: Thrombocytosis: sustained. Variable cellularity (may be normal). Must be BCR-ABL1 negative. Variable WBC and basophil count. Increased, markedly hyperlobated megakaryocytes. o JAK2 V617F in 50% of cases. o CALR mutation in 40%. o MPL W151L/K mutation in small subset. RBCs parameters usually normal. Other lineages unremarkable. Some cases are triple negative. Blasts <2%. Mutation status linked to outcome and thrombosis risk.
- 125. Blood Features BM Features Molecular/Genetics IV. Primary Myelofibrosis, Early to Overt Fibrotic Phases: Leukocytosis and thrombocytosis common in early disease. Marked hypercellularity; granulocytic lineage predominance; cellularity decreases as fibrosis progresses. Must be BCR-ABL1 negative. Leucoerythroblastic blood picture common in fibrotic phase. Dilated sinuses with intrasinusoidal megakaryocytes. o JAK2 V617F in 60% of cases. o CALR mutation in 40%. o MPL W151L/K mutation in small subset. Teardrop-shaped RBCs in fibrotic phase. Myeloid predominance with intact maturation Some cases are triple negative. Variable basophilia. Blasts < 10 %. Mutation status linked to outcome and thrombosis risk. Cytopenias may develop with more advanced disease. Increased megakaryocytes with pyknotic and hyperlobated forms. Progressive osteosclerosis and myelofibrosis.
- 126. Blood Features BM Features Molecular/Genetics V. Chronic Neutrophilic Leukemia Sustained unexplained neutrophilia. Hypercellular BM. Must be BCR-ABL1 negative. May see toxic changes. Myeloid lineage predominates. CSF3R mutation in most cases; may be defining event. Absent basophilia. Intact maturation. Other CBC parameters generally unremarkable. Blasts <2%.
- 127. Blood Features BM Features Molecular/Genetics VI. Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia, NOS Sustained unexplained eosinophilia. Hypercellular BM. Must be BCR-ABL1 negative. Basophilia generally absent. Prominent eosinophils. Absence of PDGFRA, PDGFRB and FGFR1 required. Other CBC parameters generally unremarkable. Intact maturation, blasts <2%.