Bone.pptx
- 1. BONE DR. SUNDIP CHARMODE ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMY AIIMS RAJKOT
- 2. OBJECTIVES • Definition of Bone • Classification and Description of Bone • Ossification of Bone • Blood supply of Bone • Clinical correlation of Bone
- 3. DEFINITION • Bone is mineralized, living, constantly changing connective tissue that forms majority of the skeleton. • It consists of an inter-cellular calcified matrix impregnated with collagen fibres and several types of cells.
- 4. CALCIFIED INTER-CELLULAR MATRIX • Organic component • Amorphous substance • Bone cells • Collagen fibres (Type -1) • Inorganic component • Calcium phosphate • Traces of other salts like Mg, Na, Cl, Fl, Citrate, etc.
- 5. COMPONENTS 1. Cells • Osteoblasts • Osteocytes • Osteoclasts 2. Matrix / Ground substance 3. Fibres
- 6. GROSS STRUCTURE • Outer Compact part • Inner Cancellous part • Periosteum • Endosteum • Medullary cavity • Nutrient foramen
- 9. PERIOSTEUM • It is a thick fibrous membrane covering the entire surface of bone except • Contains Osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts and osteoclasts. • Made up of two layers • Sharpey’s fibres
- 11. FUNCTIONS OF PERIOSTEUM • Protection • Maintain the shape • Nutrition • Provides attachment • Provides regenerative capability to the bone
- 12. ACCORDING TO POSITION • Axial bones : Skull bones, Vertebrae, Ribs, Sternum • Appendicular bones : • Upper limb - Pectoral girdle, free bones • Lower limb – Pelvic girdle, free bones
- 13. ACCORDING TO OSSIFICATION • Membranous bones • Cartilaginous bones • Membrano-cartilaginous bones
- 14. ACCORDING TO STRUCTURE • Macroscopically • Compact (dense) • Cancellous (spongy) • Microscopically • Woven • Lamellar
- 16. COMPACT / CORTICAL BONE • Dense, ivory like with no visible spaces on naked eye. • It comprises of • Lamellae of collagenous sheets • Haversian systems or osteons
- 18. CANCELLOUS / SPONGY BONE • It consists of interconnecting rods and plates of bone called Trabeculae enclosing large spaces filled with red bone marrow.
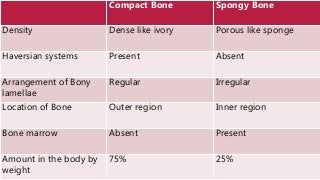
- 20. Compact Bone Spongy Bone Density Dense like ivory Porous like sponge Haversian systems Present Absent Arrangement of Bony lamellae Regular Irregular Location of Bone Outer region Inner region Bone marrow Absent Present Amount in the body by weight 75% 25%
- 21. WOVEN BONE • Collagen fibres and Bone crystals are arranged haphazardly. • Mechanically weak and flexible. • It is either immature or pathologic. • E.g. Fetal bone (initially), Callus, Paget’s disease.
- 23. LAMELLAR BONE • Here mineralized matrix is arranged in thin layer (lamellae). • Concentric – Compact bone • Branching and anastomosing – Cancellous bone • E.g. All adult bones are lamellar bones.
- 24. ACCORDING TO SHAPE • Long • Short • Irregular • Flat • Pneumatic • Sesamoid • Accessory
- 25. LONG BONE • Parts of Long bone • Centre's of ossification • Epiphysis • Epiphyseal cartilage – It is a plate of hyaline cartilage which intervenes between epiphysis and diaphysis.
- 27. EPIPHYSIS • Pressure epiphysis • Traction epiphysis • Atavistic epiphysis • Aberrant epiphysis
- 28. LAW OF UNION OF EPIPHYSIS / LAW OF OSSIFICATION • The law enunciates that the Epiphyseal Centre which appears first unites last with the diaphysis and vice-versa. • Fibula violates the law.
- 29. GROWING END OF LONG BONE
- 30. METAPHYSIS • It is the most actively growing area of long bone. • It is the most vascular part of long bone.
- 31. TYPES OF LONG BONE • Typical long bone • Miniature / short long bone • Modified long bone
- 32. SHORT BONE • Small in size • Cuboidal in shape • E.g. Tarsals and Carpals.
- 33. FLAT BONE • Flat and shallow plate like bones forming boundaries of body cavities. • They consist of two compact bone plates separated by spongy bone. • E.g. Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, Scapula, Sternum, Ribs etc.
- 34. IRREGULAR BONE • Highly irregular in shape • E.g. Hip bone, Vertebrae, Bones forming base of skull.
- 35. PNEUMATIC BONE • They are a variety of irregular bones containing air filled cavities which are lined by mucous membrane. • Called as Paranasal air sinuses. • E.g. Frontal, Maxilla, Sphenoid, Ethmoid, Mastoid. • Features:
- 36. SESAMOID BONE • Patella in Quadriceps Femoris • Fabella in Lateral head of Gastrocnemius • Pisiform in Flexor carpi ulnaris • Two bones beneath the head of first metacarpal – Flexor Hallucis brevis • One bone at Cuboid bone in Peroneus Longus • Rider’s bone in Adductor longus
- 38. SESAMOID BONE Functions Peculiarities Act as pulleys for muscle contraction Round or oval bones Alter the direction of the pull of muscles Develop in the tendon of the muscles Minimize the friction of tendon against the bone to prevent its attrition. Ossify after birth by multiple centres Devoid of periosteum Absence of haversian systems
- 39. ACCESSORY BONE • These bones are not usually found as a part of human skeleton. • Can exist as a normal variant in many people. • E.g. • Sutural or Wormian bones • Os Trigonium, Os Vesalianum, Patella cubiti
- 41. OSSIFICATION • Ossification means the process of formation of bone. • It involves differentiation of osteoblasts which secrete characteristic organic intercellular substance including collagen fibres. • Ossification is followed by calcification which is deposition of calcium crystals along and within collagen fibres.
- 42. BLOOD SUPPLY OF BONE • The long bone is supplied by Four sets of arteries : • Nutrient artery • Metaphyseal arteries • Periosteal arteries • Epiphyseal arteries
- 44. FUNCTIONS OF BONE • Provide rigid frame-work • Provide surface for attachment • Serve as lever for muscles • Protection of vital organs • Reservoir of calcium and phosphorus • Container for blood producing cells
- 45. CLINICAL CORRELATION • Fracture • Determination of skeletal age • Bone marrow transplant • Avascular necrosis • Osteoporosis • Epiphyseal fractures • Paget’s disease
- 46. THANK YOU