Lecture 08-inheritance-i
- 1. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Object Oriented Programming Riphah International University, Faisalabad Introduction to Inheritance Uzair Saeed
- 2. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Introduction • Probably most powerful feature of OOP • Concept similar to inheritance in real life • New classes are created from existing classes
- 3. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Introduction • New classes absorb all features of existing classes including their data and functions. Also enhance them by adding their own new features in form of new data members and new member functions
- 4. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Is-A vs Has-A relationship • Has-A relationship is composition type of relationship (Whole-Part relationship) – Car has an engine • Is-A relationship: also called association – Car is vehicle – Student is person • Implementation: – Composition: making member – Association: using inheritance
- 5. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Introduction • Existing classes are called base classes • New classes are called derived classes • Objects of derived classes are more specialized as compared to objects of their base classes • Inheritance provides us a mechanism of software reusability which is one of the most important principles of software engineering
- 6. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Inheriting Data and Functions • All data members and member functions of base class are inherited to derived class • Constructors, destructors and = operator are not inherited
- 7. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Some definitions in class hierarchy • Direct base class – Inherited explicitly (one level up hierarchy) • Indirect base class – Inherited two or more levels up hierarchy • Single inheritance – Inherits from one base class • Multiple inheritance – Inheritance from multiple classes
- 8. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Animals: Class’s hierarchy Mammal People Reptiles Dog Animal man woman John Mary . . . . . Classification Inheritance
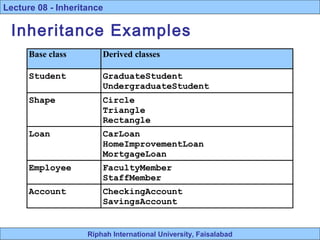
- 9. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Inheritance Examples Base class Derived classes Student GraduateStudent UndergraduateStudent Shape Circle Triangle Rectangle Loan CarLoan HomeImprovementLoan MortgageLoan Employee FacultyMember StaffMember Account CheckingAccount SavingsAccount
- 10. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Another example: University’s community member’s hierarchy Single inheritance CommunityMember Employee Student Administrator Teacher AdministratorTeacher StaffFaculty Alumnus Single inheritance Single inheritance Multiple inheritance
- 11. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Inheritance Concept 11 class Rectangle{ private: int numVertices; float *xCoord, *yCoord; public: void set(float *x, float *y, int nV); float area(); }; Rectangle Triangle Polygon class Polygon{ private: int numVertices; float *xCoord, *yCoord; public: void set(float *x, float *y, int nV); }; class Triangle{ private: int numVertices; float *xCoord, *yCoord; public: void set(float *x, float *y, int nV); float area();
- 12. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Inheritance Concept 12 Rectangle Triangle class Polygon{ protected: int numVertices; float *xCoord, float *yCoord; public: void set(float *x, float *y, int nV); }; class Rectangle : public Polygon{ public: float area(); }; class Rectangle{ protected: int numVertices; float *xCoord, float *yCoord; public: void set(float *x, float *y, int nV); float area(); }; Polygon
- 13. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Inheritance Concept 13 Rectangle Triangle class Polygon{ protected: int numVertices; float *xCoord, float *yCoord; public: void set(float *x, float *y, int nV); }; class Triangle : public Polygon{ public: float area(); }; class Triangle{ protected: int numVertices; float *xCoord, float *yCoord; public: void set(float *x, float *y, int nV); float area(); Polygon
- 14. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Inheritance Concept 14 Point Circle 3D-Point class Point{ protected: int x, y; public: void set (int a, int b); }; class Circle : public Point{ private: double r; }; class 3D-Point: public Point{ private: int z; }; x y x y r x y z
- 15. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Define a Class Hierarchy • Syntax: class DerivedClassName : access-level BaseClassName where – access-level specifies the type of derivation • private by default, or • public • Any class can serve as a base class – Thus a derived class can also be a base class 15
- 16. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Class Derivation 16 Point 3D-Point class Point{ protected: int x, y; public: void set (int a, int b); }; class 3D-Point : public Point{ private: double z; … … }; class Sphere : public 3D- Point{ private: double r; … … }; Sphere Point is the base class of 3D-Point, while 3D-Point is the base class of Sphere
- 17. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance What to inherit? • In principle, every member (but not private) of a base class is inherited by a derived class – just with different access permission 17
- 18. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Access Control Over the Members • Two levels of access control over class members – class definition – inheritance type 18 b a s e c la s s / s u p e rc la s s / p a re n t c la s s d e riv e d c la s s / s u b c la s s / c h ild c la s s derivefrom membersgoesto class Point{ protected: int x, y; public: void set(int a, int b); }; class Circle : public Point{ … … };
- 19. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Constructor Rules for Derived Classes The default constructor and the destructor of the base class are always called when a new object of a derived class is created or destroyed. 19 class A { public: A ( ) {cout<< “A:default”<<endl;} A (int a) {cout<<“A:parameter”<<endl;} }; class B : public A { public: B (int a) {cout<<“B”<<endl;} }; B test(1); A:default B output:
- 20. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Constructor Rules for Derived Classes You can also specify an constructor of the base class other than the default constructor 20 class A { public: A ( ) {cout<< “A:default”<<endl;} A (int a) {cout<<“A:parameter”<<endl;} }; class C : public A { public: C (int a) : A(a) {cout<<“C”<<endl;} }; C test(1); A:parameter C output: DerivedClassCon ( derivedClass args ) : BaseClassCon ( baseClass args ) { DerivedClass constructor body }
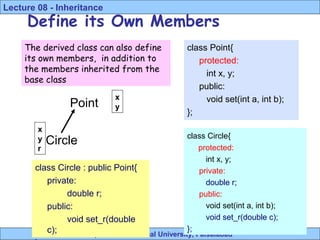
- 21. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Define its Own Members 21 Point Circle class Point{ protected: int x, y; public: void set(int a, int b); }; class Circle : public Point{ private: double r; public: void set_r(double c); x y x y r class Circle{ protected: int x, y; private: double r; public: void set(int a, int b); void set_r(double c); }; The derived class can also define its own members, in addition to the members inherited from the base class
- 22. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance Even more … • A derived class can override methods defined in its parent class. With overriding, – the method in the subclass has the identical signature to the method in the base class. – a subclass implements its own version of a base class method. 22 class A { protected: int x, y; public: void print () {cout<<“From A”<<endl;} }; class B : public A { public: void print () {cout<<“From B”<<endl;} };
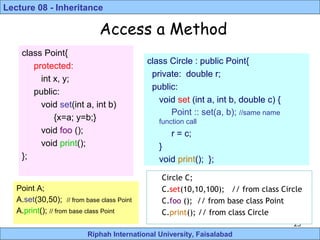
- 23. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance 23 class Point{ protected: int x, y; public: void set(int a, int b) {x=a; y=b;} void foo (); void print(); }; class Circle : public Point{ private: double r; public: void set (int a, int b, double c) { Point :: set(a, b); //same name function call r = c; } void print(); }; Access a Method Circle C; C.set(10,10,100); // from class Circle C.foo (); // from base class Point C.print(); // from class Circle Point A; A.set(30,50); // from base class Point A.print(); // from base class Point
- 24. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance point and circle classes class Point { protected: int x,y; public: Point(int ,int); void display(void); }; Point::Point(int a,int b) { x=a; y=b; } void Point::display(void) { cout<<"point = [" <<x<<","<<y<<"]"; }
- 25. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance class Circle : public Point { double radius; public: Circle(int ,int ,double ); void display(void); }; Circle::Circle(int a,int b,double c):Point(a,b) { radius = c; } void Circle::display(void) { Point::display(); cout<<" and radius = "<<radius; }
- 26. Riphah International University, Faisalabad Lecture 08 - Inheritance int main(void) { Circle c(3,4,2.5); c.display(); return 0; } Output: point=[3,4] and radius = 2.5




















![Riphah International University, Faisalabad
Lecture 08 - Inheritance
point and circle classes
class Point
{
protected:
int x,y;
public:
Point(int ,int);
void display(void);
};
Point::Point(int a,int b)
{
x=a;
y=b;
}
void Point::display(void)
{
cout<<"point = [" <<x<<","<<y<<"]";
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-08-inheritance-i-151005022330-lva1-app6892/85/Lecture-08-inheritance-i-24-320.jpg)

![Riphah International University, Faisalabad
Lecture 08 - Inheritance
int main(void)
{
Circle c(3,4,2.5);
c.display();
return 0;
}
Output:
point=[3,4] and radius = 2.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-08-inheritance-i-151005022330-lva1-app6892/85/Lecture-08-inheritance-i-26-320.jpg)