Targeted drug delivery
- 1. TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY Presented by:- CHRISTY P GEORGE M pharm, BHARATI VIDYAPEETH UNIVERSITY POONA COLLEGE OF PHARMACY,PUNE 1
- 2. CONTENTS I. OVERVIEW OF TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY II. III. IV. V. VI. VII. VIII. I. OVERVIEW OF TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY II. ACTIVE TARGETING III. PASSIVE TARGETING IV. MAGNETIC TARGETING V. ULTRASOUND BASED TARGETING VI. SITE SPECIFIC TARGETING I. BRAIN TARGETING II. COLON TARGETING VII.DISEASE BASED TARGETING I. TUMOR TARGETING VIII.CASE STUDY 2
- 3. DRUG TARGETING- OVERVIEWDRUG TARGETING- OVERVIEW “Targeting the drugs (and DDS) involves the improvement of the specificity of the system towards the pharmacologically relevant target in the body” Targeted drug delivery systems (TDDS) involve administration of the DDS to the patient, delivery of the DDS at the target (pathological) site , release of the active ingredients in/around the target, and avoiding nonspecific toxicity in normal cells. The concept of targeted drugs is not new, but dates back to 1906 when Ehrlich first postulated the ‘magic bullet’. 3
- 4. TARGETING AIMS AVOID TOXICITY OR ADVERSE REACTIONS OF THE DRUG/GENE ON NONSPECIFIC NORMAL CELLS AND FACILITATING ADMINISTRATION OF LOWER DOSES TO ACHIEVE THERAPEUTIC/DIAGNOSTIC BENEFITS FACILITATE THE THERAPEUTIC SUBSTANCE TO REACH THE SITE OF ACTION FROM THE SITE OF ADMINISTRATION WHERE THE TARGET SITE CAN BE ORGAN, TISSUE, CELL, OR ORGANELLES RELEASE THE THERAPEUTIC PAYLOAD IN ITS ACTIVE FORM IN AND AROUND SITE OF ACTION AT REQUIRED CONCENTRATION PROTECT THE DRUG OR GENE FROM THE DETRIMENTAL ENVIORNMENTAL EFFECTS LIKE PH OR ENZYMES 4
- 5. WHY TO TARGET ? • membrane bounding, biological instability, • Pharmaceutical drug instability in conventional dosage form solubility ,biopharmaceutical low absorption, high-membrane bounding, biological instability, pharmacokinetic / pharmacodynamic short half life, large volume of distribution, low specificity, clinical, low therapeutic index. 5
- 6. IDEAL CHARACTERISTICSIDEAL CHARACTERISTICS : biocompatible, biodegradable, and physicochemical stable invitro cells or tissues or organs and should have uniform capillary distribution. drug release. Drug release does not effect the drug action. Minimal drug leakage during transit. biodegradable or readily eliminated from the body without any problem and no carrier induced modulation of diseased state. system should be easy or reasonably simple, reproductive and cost effective. IDEAL CHARACTERISTICSIDEAL CHARACTERISTICS : It should be nontoxic, biocompatible, biodegradable, and physicochemical stable invivo and invitro. Restrict drug distribution to target cells or tissues or organs and should have uniform capillary distribution. Controllable and predicate rate of drug release. Drug release does not effect the drug action. Therapeutic amount of drug release. Minimal drug leakage during transit. Carriers used must be biodegradable or readily eliminated from the body without any problem and no carrier induced modulation of diseased state. The preparation of the delivery system should be easy or reasonably simple, reproductive and cost effective. ADVANTAGESADVANTAGES : • may be simplified. • Toxicity is reduced by delivering a drug to its target site, there by reducing harmful systemic effects. • smaller dose to produce the desire effect. • metabolism. • Enhancement of the absorption of target molecules such as peptides and particulates. • conventional drug delivery system. • concentration(controlled release). • cells that compare to normal cells ADVANTAGESADVANTAGES : • Drug administration protocols may be simplified. • Toxicity is reduced by delivering a drug to its target site, there by reducing harmful systemic effects. • Drug can be administered in a smaller dose to produce the desire effect. • Avoidance of hepatic first pass metabolism. • Enhancement of the absorption of target molecules such as peptides and particulates. • Dose is less compared to conventional drug delivery system. • No peak and valley plasma concentration(controlled release). • Selective targeting to infections cells that compare to normal cells. 6
- 7. APROACHES IN TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY ACTIVE TARGETING PASSIVE TARGETING DISEASE BASED STRATEGIES LOCATION BASED STRATEGIES LIGAND BASED LIGAND BASED EXTERNAL STIMULI EXTERNAL STIMULI LIKE:- •MAGNETIC FIELD •LIGHT •ULTRASOUND •TEMPERATURE CANCER DISEASES CANCER INFECTIOUS DISEASES BBB BBB COLON RETINA SKIN TARGETED PULMONARY INTRACELLULAR 7
- 8. PASSIVE TARGETING (physiology based targeting) • Passive targeting is present naturally in the human body. Hormones, • • • Passive targeting is present naturally in the human body. Hormones, neurotransmitters, growth factors, etc. have a natural tendency to go and target the receptors at their sites of action, e.g., insulin and insulin receptors. This concept can be applied to the drugs too. • The accrual of drugs/drug-carrier systems at the intended site of action by the action of physicochemical and physiological factors is passive targeting. • Certain tissues under diseased conditions present opportunities in terms of modified physiologies which can be exploited by passively targeting nano carriers. 8
- 9. • E .g. of passive targeting:- The nano carriers phagocytes. This fact can be used to passively affect the RES (e.g., leishmaniasis and malaria) • E .g. of passive targeting:- The nano carriers are largely affected to clearance by the reticulo-endothelial system (RES) comprising of macrophages and mononuclear phagocytes. This fact can be used to passively target the macrophages and even lymph nodes and spleen to treat infections that affect the RES (e.g., leishmaniasis and malaria) 9
- 10. ACTIVE TARGETING • Modifications and functionalization on the drugs or drug carriers afford them affinity towards specific receptors/markers on cells, tissues or organs. • Factors considered in selecting moiety to be attached • Disease • Intended target organ • larger presence of targetable components on the target organ/cell than in normal cells e.g., transferrin receptors in tumor • Modifications on the drugs or drug carriers can involve the use of ligands such as peptides, antibodies, sugars, lectins, etc. • On administration to the body, the targeting moieties will enable the drug/drug-carriers to efficiently reach only the intended sites of action and avoid nonspecific accumulations and related side effects. 10
- 11. There are different approaches to actively target drugs to the site of action like ligands, immune reaction, external stimuli etc There are different approaches to actively target drugs to the site of action like ligands, immune reaction, external stimuli etc 11
- 12. LIGANDS IN DRUG TARGETING MCROMOLECULES o ANTIBODY o IMUNOTOXINS o OLIGONUCLEOTIDES o CD4 o INTERLUKINS AND INTERFERONS o TRANSFERRIN o FOLIC ACID AND FOLATE o INSULIN ENZYMES GLYCOPROTEINS AND GLYCOSYLATED PROTEINS PEG, POLY-LYSINE AND RELATED POLYMERS VESCICLES ESPECIALLY LIPOSOMES 12
- 13. 13 CONJUGATION Covalent Non- covalent Homo or hetro bifunctional cross linkers are used Mostly used in conjugation with liposome's Most commonly used for targeting purpose Less chances for changing of the properties Hydrophobic, electronic, immunospecific, interactions are utilized
- 14. 14
- 15. Characterization of ligand drug conjugates • Changes in shape-SEM, transmission electron, atomic force microscopy • Size- gel exclusion chromatography • Toxicity • Antigen binding capacity • Catalytic activity • Stability • In vivo or ex vivo studies- cell line studies in tumor cells 15 Depends on type of ligands used
- 16. STIMULI RESPONSIVE • External stimulus, such as magnetic fields and ultrasound, employed to perform imaging, to • • External stimulus, such as magnetic fields and ultrasound, acting on nano carriers, are employed to perform imaging, to target and release drugs from the nano carriers at the intended site of action. • It has various advantages like Real-time targeting, Targeting deep-seated tissues, Simultaneous imaging and therapy. 16
- 17. MAGNETICALLY MODULATED DRUG DELIVERY They are of different types Magnetic nano particles Magnetic microspheres Magnetic emulsions Magnetic resealed erythrocytes Magnetic implants 17
- 18. 18 Magnetic fields are believed to be harmless to biological systems. So targeted drug delivery can be attained by using magnetic carriers which can be guided with help of magnetic field in the biological system They provide advantages like Magnetic fields are believed to be harmless to biological systems. So targeted drug delivery can be attained by using magnetic carriers which can be guided with help of magnetic field in the biological system They provide advantages like Decreased dose Controlled drug release Adaptable to any part of the body Targeting Disadvantages Expensive Specialized magnets are required Magnetite and other materials used gets deposited in tissues
- 19. 19 MAGNETIC NANO PARTICLES Magnetic nano particles (MNP) as imaging agents for magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic drug targeting and hyperthermia treatment is well explored in the field of targeted drug delivery. The MNP can be either metallic or bimetallic or super paramagnetic iron oxide nano particles (SPION) SPION are widely studied for biomedical applications because of nontoxic nature, ability to be functionalized with different targeting coatings and can encapsulate drugs in reasonable quantity.
- 20. Optimizing the MNP as well as the external magnet is of prime importance because on application of magnetic field , they must be able to generate enough magnetic moments and magnetic gradient that the MNP can overcome the force of the blood-flow (rating from 0.05–50 cm/s) depending on the target area. The MNP have found several uses in thrombolytic therapy intravascular imaging and cardiovascular diseases, tumor imaging and treatment, as well as delivery across the blood–brain barrier 20
- 21. ULTRASOUND MEDIATED DRUG DELIVERY Ultrasound has been used previously for contrast imaging, and it is explored at length for use in drug delivery. Ultrasound mediated targeting can lead to disruption of the drug-loaded carriers (micro bubbles, micelles, etc.) causing drug release 21
- 22. Inverse Targeting : • In this type of targeting attempts are made to avoid passive uptake of colloidal carrier by RES (Reticulo Endothelial Systems) and hence the process is referred to as inverse targeting. • To achieve inverse targeting, RES normal function is suppressed by pre injecting large amount of blank colloidal carriers or macromolecules like dextran sulphate • This approach leads to saturation of RES and suppression of defence mechanism. This type of targeting is a effective approach to target drug(s) to non-RES organs. Dual Targeting : • In this targeting approach carrier molecule itself have their own therapeutic activity and thus increase the therapeutic effect of drug. • For example, a carrier molecule having its own antiviral activity can be loaded with antiviral drug and the net synergistic effect of drug conjugate was observed. Double Targeting : • Temporal and spatial methodologies are combined to target a carrier system, then targeting may be called double targeting. • Spatial placement relates to targeting drugs to specific organs, tissues, cells or even subcellular compartment. whereas temporal delivery refers to controlling the rate of drug delivery to target site 22
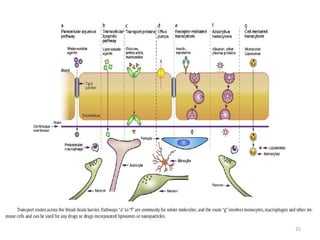
- 24. BRAIN TARGETING IS UNIQUE DUE TOBRAIN TARGETING IS UNIQUE DUE TO • Presence of blood brain barrier constituting tight junctions, pericytes, astrocytes and continuous basal membrane • Anatomically, the endothelial cells of the BBB are distinguished from those in the periphery by increased mitochondrial content, a lack of fenestrations, minimal pinocytotic activity, and the presence of tight junctions • endothelium is characterized by exhibiting a high transepithelial electrical resistance (1500–2000 Ωcm2) • The BBB makes the brain practically inaccessible for polar molecules and small ions. (transport proteins for the transport glucose and amino acids) • BBB is also an enzymatic barrier making drug delivery even more challenging as drugs are exposed to cytosolic and membrane-associated enzymes, such as γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, alkaline phosphatase, aromatic acid decarboxylase, dipeptidyl(amino)peptidase IV, and aminopeptidase A and N directed at metabolizing neuroactive agents 24
- 25. 25
- 26. 26
- 27. CHEMICAL DELIVERY PRODRUGS • crossing the bbb • excellent example of a drug that exploits an endogenous carrier is levodopa, a lipid insoluble precursor of dopamine, used for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. PRODRUGS •Produgs gets converted to active drug after crossing the bbb •An excellent example of a drug that exploits an endogenous carrier is levodopa, a lipid- insoluble precursor of dopamine, used for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. DRUG CONJUGATES Therapeutic compounds are able to cross the BBB after association or conjugation to specific ligands Recepter directed Insulin receptor Transferrin receptor Cationic derivatives BBB endothelium possesses anionic sites that attract cationic substances to the membrane surface Lipoidal derivatives 27
- 28. 28
- 29. COLLOIDAL DELIVERY LIPOSOMES Liposomes composed of a phospholipid that may act as a carrier for both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. The biophysical properties of liposomes, such as size and surface chemistry, may be varied in order to control distribution, including distribution to the brain LIPOSOMES Liposomes are composed of a phospholipid bilayer that may act as a carrier for both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. The biophysical properties of liposomes, such as size and surface chemistry, may be varied in order to control distribution, including distribution to the brain POLYMER NANOPARTICLES Manufactured from a wide range of materials such as poly(D,L co lactic acid), poly(methyl) (PMMA), poly(alkyl) , as well as from natural polymers such as chitosan and gelatin. These are able to prolong drug blood residence time and protect from enzymatic degradation POLYMER NANOPARTICLES Manufactured from a wide range of materials such as poly(D,L-lactide- co-glycolic acid), poly(L-lactic acid), poly(methyl)methacrylate (PMMA), poly(alkyl)cyanoacrylate, as well as from natural polymers such as chitosan, dextran, starch, albumin, and gelatin. These nanoparticles are able to prolong drug blood- residence time and protect drug from enzymatic degradation MONOCYTES They have unusual ability to cross bbb. infected brain cells have augmented population density of monocytes also can be used MONOCYTES They have unusual ability to cross bbb. infected brain cells have augmented population density of monocytes which also can be used 29
- 30. BIOLOGICBIOLOGIC PSEUDO NUTRIENTS They are polar small molecular structure mimicking nutrients that normally undergo carrier mediated transport through bbb e.g. hexoses, monocarboxylic acid PSEUDO NUTRIENTS They are polar small molecular structure mimicking nutrients that normally undergo carrier mediated transport through bbb e.g. hexoses, monocarboxylic acid CHIMERIC PEPTIDES In this aproach drug delivery to brain is by anchoring drug to a peptide or protien vector Some of the vectors used are Cationized albumin CHIMERIC PEPTIDES In this aproach drug delivery to brain is by anchoring drug to a peptide or protien vector Some of the vectors used are Cationized albumin ANTIBODY DIRECTED ENZYME PRODRUG THERAPY (1) an activating enzyme is specifically delivered to intended site of action with a targeting antibody (2) a subsequent administration of substrate prodrug ANTIBODY DIRECTED ENZYME PRODRUG THERAPY (1) an activating enzyme is specifically delivered to intended site of action with a targeting antibody (2) a subsequent administration of substrate prodrug 30
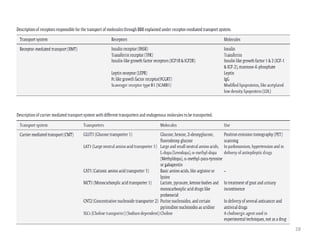
- 32. GIT: •Stomach •Small intestine •Large intestine Colon Rectum Anal canal Colon consists: • Cecum • Ascending colon • Transverse colon • Descending colon • Sigmoid colon ANATOMY OF COLON 32
- 33. Major metabolic processes occurring in the colon are hydrolysis and reduction Enzymes in Colon Reducing enzymes Hydrolytic enzymes Nitroreductase Esterases Azoreductase Amidases N-oxide reductase Glycosidases Sulphoxide reductase Glucuronidase Hydrogenase Sulfatase Azoreductases, which reduces azo-bonds selectively and Polysaccharidases which degrades the polysaccharides MICROBIAL FLORA IN COLON Bacterial count in the colon is much higher around 1011-1012 CFU/ml. 400 species of microorganisms are present Fundamentally anaerobic in nature. Predominant species: Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium and Eubacterium. 33
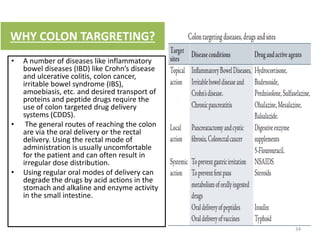
- 34. WHY COLON TARGRETING? • A number of diseases like inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, colon cancer, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), amoebiasis, etc. and desired transport of proteins and peptide drugs require the use of colon targeted drug delivery systems (CDDS). • The general routes of reaching the colon are via the oral delivery or the rectal delivery. Using the rectal mode of administration is usually uncomfortable for the patient and can often result in irregular dose distribution. • Using regular oral modes of delivery can degrade the drugs by acid actions in the stomach and alkaline and enzyme activity in the small intestine. 34
- 35. FACTORS GOVERNING COLONIC DELIVERY Gastrointestinal transit Small intestinal transit Colonic transit Gastric emptying Stomach and intestinal pH Colonic micro flora and enzymes 35
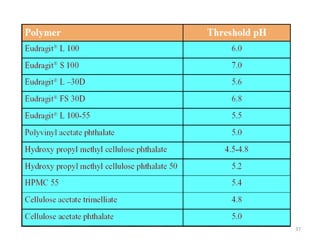
- 36. The most commonly used targeting mechanisms • The most commonly used targeting mechanisms are:- pH – dependent delivery Time - dependent delivery(Pulsincap device) Pressure- dependent delivery • Bacteria—dependent delivery(Sulfasalazine-In the colon, it degrades into 5-ASA APROACHES IN COLON TARGETING 36
- 37. 37
- 38. Evaluation In vitro models In vitro test for intactness of coating and carriers in simulated conditions of stomach and intestine step1 Drug release study in 0.1N HCL for 2 hours (mean gastric emptying) step 2 Drug release study in phosphate buffer for 3 hours (mean small intestine transit time) In vitro enzymatic degradation test Method 1: Drug release in buffer medium containing enzymes(e.g.pectinase, dextranase) or rat or guinea pig or rabbit fecal contents Amount of drug release in particular time directly proportional to the rate of degradation of polymer carrier. Method 2: Incubating carrier drug system in fermenter Suitable medium containing colonic bacteria (streptococcus faecium or B.ovatus) Amount of drug released at different time intervels determined Clinical evaluation is also performed 38
- 40. TUMOR CELL MICROENVIRONMENT Tumor is uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells characterized by mutations proteins Tumor is uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells characterized by mutations which help the cells to proliferate, avoid apoptosis and develop survival proteins compared with normal tissue tumor tissues has got significant differences vascular abnormalities and angiogenesis oxygenation, perfusion, pH and metabolic states 40
- 41. ANGOGENISIS Angiogenesis is defined as the formation of new blood vessels from existing ones. In the angiogenesis process, five phases can be distinguished: 1. endothelial cell activation, 2. basement membrane degradation, 3. endothelial cell migration, 4. vessel formation, and 5. angiogenic remodeling. VASCULAR ABNORMALITIES The abnormal vascular architecture plays a major role in drug targeting at tissue (1) Extensive angiogenesis and hyper vasculature (2) Lack of smooth-muscle layer, pericytes (3) Defective vascular architecture: fenestrations (4) No constant blood flow and direction (5) Inefficient lymphatic drainage that leads to enhanced retention in the interstitium of tumors (6) Slow venous return that leads to accumulation from the interstitium of tumor pH Tumors exhibit a lower extracellular pH than normal tissues. The low extracellular tumor pH mostly arises from the high glycolysis rate in hypoxic cancer cells The relatively basic intracellular compartment may in turn favor the ionization of the molecule, thereby promoting the cytosolic accumulation of the drug TARGRTING 41
- 42. 42
- 43. Many different targeted therapies have been approved for use in cancer treatment These are: (a) structural modifications for improving the physicochemical properties in accordance with structure–activity relationships (SAR) (b) conjugating homing ligands for predetermined bio-distribution patterns and (c) involvement of carrier based approaches PASSIVE METHODS Enhanced permeation and retention effects Phagocytosis of particulate carrier by mononuclear phagocytosis systems (MPS) Localization in the organs of reticuloendothelial System (RES) Low extracellular ph Relative micro-acidosis Mild hyperthermia ACTIVE METHODS antibodies ACTIVE METHODS Vitamin based Peptide based Lectin based Transferrin based Albumin based Monoclonal antibodies 43
- 44. Monoclonal antibodies • A great amount of work has been done with antibodies to target • • • • • A great amount of work has been done with antibodies to target drugs to specific cells, especially for cancer therapy. Theoretically, targeting with antibodies is ideal because antibody-antigen interactions are very specific • Monoclonal antibodies are monospecific antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell • Monoclonal antibodies have been produced which react with a wide range of human cancers, including carcinomas of the colon, rectum, breast, ovary, lung, pancreas, and bladder, malignant melanomas, bone and soft tissue sarcomas, and leukemia's. • Saccharides of the cell surface are important tumor associated and differentiation antigens • Monoclonals are useful in the detection of glycosylation changes and to study the biochemistry of these changes 44
- 45. 45 Transferrin receptor- Transferrin, a serum glycoprotein, transports iron through the blood and into cells by binding to the transferring receptor and subsequently being internalized via receptor-mediated endocytosis. The transferrin receptor is a vital protein involved in iron homeostasis and the regulation of cell growth. The high levels of expression of transferrin receptor in cancer cells, which may be up to 100-fold higher than the average expression of normal cells Folate receptor-binds to the vitamin folic acid and folate–drug conjugates or folate grafted nanocarriers with a high affinity and carries these bound molecules into the cells via receptor-mediated endocytosis. Folic acid is required in one carbon metabolic reactions and consequently, is essential for the synthesis of nucleotide bases. The alpha isoform, folate receptor-α is overexpressed on 40% of human cancers Lectins- proteins of non- immunological origin which are able to recognize and bind to carbohydrate moieties attached to glycoprotein's expressed on cell surface. Cancer cells often express different glycoproteins compared to normal cells. Peptides employed for tumor targeting could be either monomeric, homodimeric, heterodimeric oligomeric or tetrameric in nature. The tumor specific peptides could be broadly categorized into two categories, one targeting tumor cell surface while other targeting tumor vasculature
- 47. 47
- 48. CASE STUDY 48
- 49. Liprosomes loading paclitaxel for brain-targeting delivery by intravenous administration: In vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation Bo Tang, Guihua Fang, Ying Gao, Yi Liu, Gang Cheng , School of Pharmacy, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, China Objective:- In this study, a lipid–protein nanocomplex (liprosome) was evaluated for its potential use for brain-targeting drug delivery. Liprosome was fabricated with the desolvation–ultrasonication method and characterized in terms of particle size, size distribution, zeta potential, morphology, crystal state of the drug, and in vitro release. The in vivo distribution of paclitaxel loading lipid–protein nanocomplex (PTX-liprosome) and Taxol were compared after i.v. administration in mice Preparation of the PTX-liprosome Liprosomes are nanocomplexes formed by combination of protien(bovine serum albumin) and lipid(egg yolk lecithin).A desolvation–ultrasonication technique was used to prepare the PTX-liprosome. Anhydrous ethanol was used as a solvent for PTX and PL 100 M. Briefly, BSA (0.20 g) was dissolved in 5 mL of deionized water with magnetic stirring. PTX (0.01 g) and PL 100 M (0.10 g) were dissolved in 0.3 mL of anhydrous ethanol, respectively. Then, the PTX ethanol solution was added dropwise to the BSA solution with magnetic stirring, and the PL 100 M ethanol solution was also added dropwise to the PTX-BSA solution with magnetic stiring. The resultant mixture was further ultrasonicated at 300 W for 3 min using a probe sonicator in an ice bath with a 3 s pulse-on period and a 3 s pulse-off period. After sonication, anhydrous ethanol was evaporated under vacuum using a rotator RE-2000 49
- 50. Rational behind the study • Therapeutic efficacy of PTX against brain cancer has been disappointing • From literature it was found that Polymeric nano particles are an effective • Compared to synthetic polymeric nano carriers, natural nano carriers have degradability and biocompatibility. Of these, proteins have also been used extensively as carriers for drug delivery particularly human serum albumin • • In addition, albumin nano particles preferentially accumulate at malignant • • Therapeutic efficacy of PTX against brain cancer has been disappointing because of drug-resistance and poor penetration across the BBB • From literature it was found that Polymeric nano particles are an effective carrier system for drug transport across the BBB • Compared to synthetic polymeric nano carriers, natural nano carriers have attracted much interest because of their decreased cytotoxicity, higher degradability and biocompatibility. Of these, proteins have also been used extensively as carriers for drug delivery particularly human serum albumin (HSA) • HSA contains regions for binding many organic and inorganic molecules, and these domains are characterized by deep hydro- phobic pockets with a negative charge. • In addition, albumin nano particles preferentially accumulate at malignant and inflamed tissues because of passive targeting due to the enhanced permeability and retention effect and the active targeting mediated by gp60 receptor-mediated transcytosis • On the basis of these observations PTX was prepared as liprosomes 50
- 51. Sl no Characterization of liprosomes Method of analysis 1 Size distribution and zeta potential The size distribution and polydispersity index (P.I.) of liprosome were measured by dynamic light scattering using a NicompTM 380 submicron particle sizer (Particle Sizing System, Santa Barbara, CA, USA). The zeta potential of the liprosomes was measured by electrophoretic light scattering using the same device. 2 Particle morphology The morphology of liprosome was assessed using TEM (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) at 90 kV. 3 X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) To identify the surface properties of the PTX-liprosome, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was conducted on an ESCALAB 250 4 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) The thermal properties of the PTX-liprosome were determined with a differential scanning calorimeter (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) 51
- 52. 5 X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) The physical state of PTX in the PTX- liprosome was further determined with an X-ray diffractometer (Geigerflex, Rigaku Co., Japan). 6 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) The intermolecular interactions of PTX, BSA, and PL 100 M were investigated with a FTIR system (Bruker IFS-55, Bruker, Switzerland) using the KBr disk method. Sl no Charaterisation METHOD 1 Determination of PTX concentration The PTX concentrations were determined using a modified HPLC method on a HPLC system (LC-10Avp SHIMAZU, Japan), which was equipped with a UV–vis detector (SPD-10Avp SHIMAZU, Japan) and a Diamonsil C18 reversed phase column 2 Entrapment efficiency (EE) and loading capacity (LC) To release the PTX from PTX-liprosome, acetonitrile was added to precipitate BSA by bath sonication for 5 min. After centrifugation at 12,000 rpm for 10 min, 20 mL of the supernatant was injected into an HPLC system to determine the drug content in the liprosome 52
- 53. 3 In vitro drug release The release behavior of PTX from the PTX-liprosome suspen-sions was studied in vitro using a dialysis method with phosphate buffered saline (PBS, 0.01 M, pH 7.4) containing 0.5% w/v Tween 80 4 In vitro hemolysis assay To evaluate the hemolytic potential of the PTX-liprosome, an in vitro hemolysis test was performed. All of the experiments were performed using the venous blood from the ear vein of a healthy rabbit IN VIVO ANALYSIS EXPERIMENTAL PROCESS:- Sixty-four mice were divided randomly into two groups receiving Taxol and PTX-liprosome suspensions via lateral tail vein injections at 20 mg PTX/kg body weight. At 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 h after administration, four mice from each group were anesthetized with diethyl ether, 0.5 mL of blood was collected into a heparinized centrifuge tube from the retrobulbar venous plexus of the mice. The animals were then sacrificed, and the heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, and brain were removed. The blood was centrifuged (4000 rpm, 10 min) to obtain the plasma samples. The tissue samples were washed with physiological saline and dried on filter paper. The plasma and tissue samples were stored at 20 C until analysis by hplc technique 53
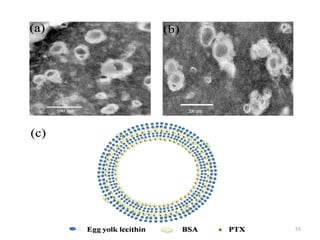
- 54. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Preparation and physical properties The amount of BSA strongly affected the EE of the PTX- liprosome. Significant increase in the EE at the BSA of 0.20 g was observed whereas a concomitant decrease in the EE at the BSA of 0.30 g was noted. increased particle size, whereas proportionate decrease in the EE was observed with increase in the drug amount The optimal PTX-liprosome has a high entrapment efficiency (>90%), small particle size (approximately 113 nm), and narrow distribution Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) liprosome displays a typical multilayer structure with a spherical shape. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) These results suggest that the PL 100 M formed the majority of the surface layers of the PTX-liprosome and that the PTX and BSA conjugate was inside the PTX-liprosome. 54
- 55. 55
- 56. FTIR analy sis FTIR was used to evaluate the intermolecular interactions between PTX, BSA, PL 100 M. The spectra of PTX, BSA, PL 100 M, blank liprosome, and PTX-liprosome. Hydrogen bonds are formed between amide groups in BSA and hydroxyl groups in PTX. hydrogen bonds are also formed between carbonyl groups in the PTX and hydroxyl groups of the amino acids in BSA existence of electrostatic interactions between the CN+(CH3)3 group of PL 100 M and surface COO group of BSA DSC DSC analysis was conducted for PTX, BSA, PL 100 M, blank liprosome, and PTX- liprosome. DSC thermogram of PTX endothermic peak at 223.8 C and one exothermic peak at 244.3 C, which were attributed to the melting and decomposition of PTX, respectively. Compared to the PTX, the endothermic peak of PTX in the PTX- liprosome disappeared, indicating a significant conversion from the crystalline state to an amorphous or molecular state in the PTX-liprosome during preparation. The DSC thermogram of BSA showed a denaturation peak at 97.5 C and a melting temperature at approximately 220 C (Kang et al., 2009). However, the denaturation peak is significantly shifted to a lower temperature in the blank liprosome (85.8 C) and PTX-liprosome (87.8 C), indicating interaction forces among PTX, BSA, and PL 100 M. 56
- 57. 57
- 58. XRPD XRPD was used to evaluate the dispersion of the drug within the liprosome. XRPD analysis was conducted for PTX, BSA, PL 100 M, blank liprosome and PTX-liprosome. Diffractograms revealed the crystalline nature of the PTX. Sharp diffraction peaks of the PTX disappeared in the diffracto- grams of the PTX-liprosome indicating molecules existed inside the PTX-liprosome in an amorphous or molecular state. Partial weak crystalline peaks were displayed between 5 and 10 in the diffractogram of the PL 100 M which is characteristic of some crystallinity. These peaks disappeared in the diffractograms of the blank liprosome and PTX-liprosome, suggesting an interaction between BSA and PL 100 M, such as electrostatic attraction, hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonds. These interaction forces are involved in the formation of liprosome and caused the partial amorphization of the lipid in the liprosome In vitro hemolysis assay Hemolytic activity of the PTX- liprosome was negligible (<5%), in the range of 20–240 mg/m 58
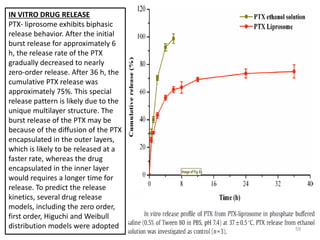
- 59. IN VITRO DRUG RELEASE PTX- liprosome exhibits biphasic release behavior. After the initial burst release for approximately 6 h, the release rate of the PTX gradually decreased to nearly zero-order release. After 36 h, the cumulative PTX release was approximately 75%. This special release pattern is likely due to the unique multilayer structure. The burst release of the PTX may be because of the diffusion of the PTX encapsulated in the outer layers, which is likely to be released at a faster rate, whereas the drug encapsulated in the inner layer would requires a longer time for release. To predict the release kinetics, several drug release models, including the zero order, first order, Higuchi and Weibull distribution models were adopted 59
- 60. Tissue distribution The tissue targeting efficiency was evaluated using the drug targeting index (DTI) described and the relative uptake rate (R). The values of R and DTI are defined as follows 60
- 62. The liprosome was determined after administration. The relative uptake rate (R) and drug targeting index (DTI) were used to evaluate the target efficiency of the PTX liprosome. tissues in descending order was brain > liver > plasma > spleen > kidney > heart > lung. The DTI of the tissues in a descending order was brain > liver > spleen > kidney > heart > lung. There is a similar trend for the values of R and DTI. The PTX clearly targets the brain ( 1.329, = 2.190), significantly increasing drug uptake by the brain tissue. The targeting efficiency of the PTX- liprosome was determined after administration. The relative uptake rate (R) and drug targeting index (DTI) were used to evaluate the target efficiency of the PTX- liprosome. The R values for the tissues in descending order was brain > liver > plasma > spleen > kidney > heart > lung. The DTI of the tissues in a descending order was brain > liver > spleen > kidney > heart > lung. There is a similar trend for the values of R and DTI. The PTX-liprosome clearly targets the brain (Rbrain = 1.329, DTIbrain = 2.190), significantly increasing drug uptake by the brain tissue. 62
- 63. CONCLUSION • Lipid–protein nano complex (liprosome) with a unique • • • • Lipid–protein nano complex (liprosome) with a unique spherical multilayer structure was fabricated using a desolvation–ultra sonication method. • The liprosome achieved excellent drug entrapment, a satisfactory particle size and a narrow size distribution. In vitro hemolysis assays demonstrated that the liprosome exhibited low cytotoxicity. • Compared to taxol, the prepared ptx-liprosome is an effective formulation for increasing drug distribution to brain tissue while reducing it in other organs. • Therefore, liprosome is a good drug delivery system for transporting drugs to the brain and for reducing toxic and side effects in other organs. 63
- 64. Reference • Targeted Delivery of Small and Macromolecular Drugs by Ajit S. Narang, Ram I. Mahato • Targeted Drug Delivery: Concepts and Design by Padma V. Devarajan , Sanyog Jain • Targeted and controlled drug delivery by S.P Vyas, R.K. Khar • Research papers 64