JavaScript Primer
- 1. JavaScript A Primer In Far Too Many Parts
- 2. History
- 3. Mocha April 1995 LiveScript JavaScript Brendan Eich CTO, Mozilla Corp.
- 4. JScript JavaScript ECMAScript ActionScript
- 5. Basics
- 6. Data Types • number • string • boolean • object • null • NaN • undefined
- 7. Strings • Are Objects, have methods
- 8. Strings "Foo" + "Bar"; //"FooBar" var str = "Lorem Ipsum Dolor Sit Amet"; str.toLowerCase(); //"lorem ipsum dolor sit amet" str.toUpperCase(); //"LOREM IPSUM DOLOR SIT AMET" str.split(" "); //["Lorem", "Ispum", "Dolor", "Sit", "Amet"] str.substring(6,9); //"Ips" new String("Lorem Ipsum Dolor Sit Amet") == str; //true
- 9. String to Number parseInt("56"); //56 parseInt("42.567"); //42 parseInt("asdf"); //NaN parseInt("5a6"); //5 parseFloat("24.68"); //24.68 parseFloat("asdf"); //NaN parseFloat("24a"); //24
- 10. Objects • “Dictionary” / “Associative Array” • Key: Value or 'Key': Value • Without ': A-Z0-9 only • Does not keep intrinsic ordering • Accessed keys using . (dot) or [] notation
- 11. Objects var object = { foo: 'value', 'complex key': 0, bar: { nested: true } }; object.foo; //'value' object.['complex key']; //0 object.bar.nested; //true object.bar['nested']; //true object['bar'].nested; //true object['bar']['nested']; //true
- 12. in or hasOwnProperty() • Tough call: • .hasOwnProperty() more consistent • in checks inherited properties • Used in for loop
- 13. in var test = { foo: 'value', bar: 'value', baz: 'value' } for (var key in test) { console.log(key + ": " + test[key]); } //PRINTS: //foo: value //bar: value //baz: value
- 14. Arrays • Special object • Numerical keys only • Keeps intrinsic ordering • Short ([]) and Long (new Array()) syntax
- 15. Arrays var arrayShort = [ 'one', 'two' ]; arrayShort[2] = 'three'; var arrayLong = new Array(); arrayLong[0] = 'one'; arrayLong[1] = 'two'; arrayLong[2] = 'three'; //arrayShort: ["one", "two", "three"] //arrayLong: ["one", "two", "three"]
- 16. Arrays var arr = [1,2,3,4,6]; arr.indexOf(2); //1 arr.join(':'); //"1:2:3:4:6" arr.pop(); //6 //[1,2,3,4] arr.push(7); //5 //[1,2,3,4,7] arr.reverse(); //[7,4,3,2,1] arr.shift(); //1 //[2,3,4,7] arr.unshift(8); //5 //[8,2,3,4,7] arr.slice(1); //[2,3,4,7] arr.slice(1,3); //[2,3] arr.slice(-3); //[3,4,7] arr.slice(-3,-1); //[3,4]
- 17. Arrays var arr1 = [1,2,3]; var arr2 = [3,4,5]; arr1.concat(arr2); //[1,2,3,3,4,5]
- 18. Functions • Are Objects as well • “Elevated” • You can use a named function before it is defined in code • Function definitions are elevated to the top
- 19. Functions function Foo() { //... } Foo(); //valid Bar(); //valid function Bar() { //... }
- 20. Functions function Foo() { } Foo.bar = "value"; 'bar' in Foo; //true Foo.bar == "value"; //true
- 21. Function Arguments • No way to assign default arguments • But arguments are not required • If an argument is not specified, it is set to undefined
- 22. arguments • A special variable found inside a function • A not-quite array object containing all the function arguments
- 23. arguments function sum() { var x = 0; for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; ++i) { x += arguments[i]; } return x; } sum(1, 2, 3); //6
- 24. typeof • Determines a variables type • Returns a string
- 25. typeof typeof true; //"boolean" typeof 12; //"number" typeof "string"; //"string" typeof []; //"object" typeof {}; //"object" typeof NaN; //"number" typeof null; //"object" typeof undefined; //"undefined" function Foo() {} typeof Foo; //"function"
- 26. Comparison • a == b / a != b • A and B compared by value alone • 1 == “1” evaluates to true • a === b / a !== b • A and B compared by value and by type • 1 === “1” evaluates to false
- 27. window, document • Built in, global, Objects • window • Provides access to the browser window • The “global” object: foo === window.foo • Things like window.location.href, etc • document • Provides access to the current DOM
- 28. Scoping
- 29. Global & Local • Functions are the only way to create new scopes • Variables defined with var are local • Variables defined without var are global • Global variables are members of window
- 30. Global & Local var outerScope = 10; var outerScope2 = 10; function Foo() { var outerScope = 20; var innerScope = 20; globalVariable = 30; outerScope2 = 40; } Foo(); alert(outerScope); //10 alert(outerScope2); //40 alert(innerScope); //error alert(globalVariable); //30
- 31. Lexical Scoping function Foo() { function Foo() { var baz = 1; var baz = 1; return Bar(); } function Bar() { return baz; function Bar() { } return baz; } return Bar(); } Foo(); //baz is not defined Foo(); //1
- 32. Closures
- 33. Closures • First-Class • Can assign functions to variables, pass as arguments and return as values • Anonymous • Not required to have a name • A function that “closes over” variables defined outside itself
- 34. Closures function Foo() { var count = 0; return function() { count = count + 1; return count; }; } var bar = Foo(); bar(); //1 bar(); //2 bar(); //3
- 35. Closures function createAdder(amount) { return function(input) { return input + amount; }; } var add2 = createAdder(2); add2(2); //4 add2(8); //10 var add3 = createAdder(3); add3(3); //6 add3(7); //10
- 36. Module Pattern (function(exports, undefined){ //ALL your code here var localVar = "bar" globalVar = "baz"; exports.foo = "bat"; })(window); alert(localVar); //error alert(globalVar); //"baz" alert(window.globalVar); //"baz" alert(foo); //"bat" alert(window.foo); //"bat" BEWARE: export (singular) is a reserved word in Safari
- 37. this
- 38. this • Trips everyone up • Special variable used within a function • Refers to the “contextual object” • Changes based on where a function executes
- 39. this var Foo = { bar: "bar", baz: function() { return this.bar; } }; Foo.baz(); //"bar" Foo.bar = "bat"; Foo.baz(); //"bat" var baz = Foo.baz; baz(); //undefined
- 40. this var Foo = { bar: "bar", baz: function() { return this.bar; } }; Foo.bat = function() { return this.bar + "bat"; }; Foo.bat(); //"barbat"
- 41. call & apply • Methods in the function prototype • Change the context in which a function executes!
- 42. call & apply var Foo = { bar: "bar", baz = function(param1, param2) { return this.bar + param1 + param2; } }; var Foo2 = { bar: "123" }; Foo.baz("baz", "bat"); //"barbazbat" Foo.baz.apply(Foo2, "baz", "bat"); //"123bazbat" Foo.baz.call(Foo2, ["baz", "bat"]); //"123bazbat"
- 43. Exceptions
- 44. Exceptions • All errors are thrown • Classic try...catch...finally blocks
- 45. Exceptions try { funcDoesNotExist(); } catch (e) { alert(e); //ReferenceError: funcDoesNotExist is not defined } finally { //Always Executes }
- 46. Exceptions function Foo() { throw new Error("Message"); } function Bar() { throw "Message"; } try { Foo(); } catch (e) { e.message == "Message"; //true } try { Bar(); } catch (e) { e == "Message"; //true }
- 47. Prototype
- 48. OOP... Kinda... • Almost no real difference between a dictionary and an object • Named Functions double as object constructors • Function objects contain a prototype dictionary that is copied to instance when using new
- 49. OOP... Kinda... Foo function Foo() { //The "Constructor" } ‣ bar Foo.bar = function() { //A "Static" Function ‣ prototype } ‣ baz Foo.prototype.baz = function() { ‣ constructor //A "Method" }; ‣ __proto__
- 50. new instance var instance = new Foo(); instance.baz(); //works instance.bar(); //error ‣ __proto__ Foo.bar(); //works ‣ baz Foo.baz(); //error ‣ constructor Foo.prototype.baz(); //works ‣ __proto__ ‣ ...
- 51. new instance instance.bat = function() { /* ... */ } ‣ bat instance.bat(); //works ‣ __proto__ Foo.bat(); //error ‣ baz Foo.prototype.bat(); //error ‣ constructor ‣ __proto__ ‣ ...
- 52. Overriding Prototype function Foo(baz) { this.baz = baz; } Foo.prototype.bar = function() { return this.baz; }; var foo1 = new Foo(1); var foo2 = new Foo(2); foo1.bar(); //1 foo2.bar(); //2 Foo.prototype.bar = function() { return this.baz * 2; }; foo1.bar(); //2 foo2.bar(); //4
- 53. Asynchronous
- 54. Asynchronous • setTimeout, setInterval allow you to have code executing asynchronously while other code executes
- 55. setInterval var id = setInterval(function() { //Code to execute every 1000 milliseconds }, 1000); //clearInterval(id); to stop
- 56. setTimeout var id = setTimeout(function() { //Code to execute after 1000 milliseconds have passed }, 1000); //clearTimeout(id); to cancel
- 57. Nifty Trick setTimeout(function() { //Code to run in parallel //while the code after is //executed. }, 1); //Code here will execute immediately //without waiting on the above
- 58. DOM
- 59. DOM • Document Object Model • API to interact with the HTML/XHTML document
- 61. DOM var paragraph = document.createElement('p'); var content = document.createTextNode("Lorem Ipsum"); paragraph.appendChild(content); paragraph.classList.add('my-class'); document.getElementsByTagName('body')[0].appendChild(paragraph);
- 63. JSON
- 64. 2001 JSON Douglas Crockford Awesome
- 65. JSON • JavaScript Object Notation • Serialization format that is basically JavaScript code minus comments • Can be eval()’ed • Minimal overhead compared to XML • No advanced parsers needed
- 66. JSON {"menu": { <menu id="file" value="File"> "id": "file", <popup> "value": "File", <menuitem value="New" "popup": { onclick="CreateNewDoc()" /> "menuitem": [ <menuitem value="Open" {"value": "New", onclick="OpenDoc()" /> "onclick": "CreateNewDoc()"}, <menuitem value="Close" {"value": "Open", onclick="CloseDoc()" /> "onclick": "OpenDoc()"}, </popup> {"value": "Close", </menu> "onclick": "CloseDoc()"} ] } }}
- 67. jQuery
- 68. January 2006 jQuery John Resig Author, jQuery
- 69. jQuery • Cross-browser JavaScript library • Simplifies and normalizes DOM, AJAX, etc. • Centers around using extended CSS selectors to grab an element(s)
- 70. jQuery $("div").addClass("special"); Find all div tags Add class special
- 71. jQuery $("#foo") <div id="foo"></div> .html("<strong>bar</strong> baz"); <div id="foo"> <strong>bar</strong> baz </div>
- 72. jQuery $('img.preview').hide(); $('.button').click(function(){ •Hide all images with }); $('img.preview').show(); the class preview •When element with the class button is clicked, show all images with the class preview
- 73. Animation $('.button').click(function(){ $('img.preview') When .button is clicked, .fadeOut(600, function() { fade out img.preview $(this).remove(); }); over 600 milliseconds }); and then remove it from the DOM
- 74. Events • jQuery wraps an event handling system • Handles browser events, AJAX events, and custom events
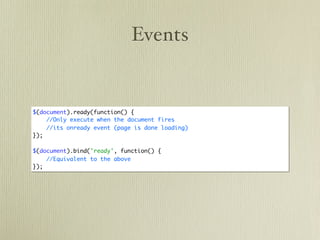
- 75. Events $(document).ready(function() { //Only execute when the document fires //its onready event (page is done loading) }); $(document).bind('ready', function() { //Equivalent to the above });
- 76. Events $('img').hover(function(){ //Do something when user hovers over //any img tag });
- 77. AJAX • Asynchronous JavaScript And XML • Though never use XML, use JSON • jQuery has an AJAX library • Wraps all the different browser quirks • IE is weird
- 78. AJAX $.ajax({ url: "test.php", success: function(data){ $('div.status').addClass("done") .html(data); } });
- 80. Tools
- 82. Firefox FireBug








![Strings
"Foo" + "Bar"; //"FooBar"
var str = "Lorem Ipsum Dolor Sit Amet";
str.toLowerCase(); //"lorem ipsum dolor sit amet"
str.toUpperCase(); //"LOREM IPSUM DOLOR SIT AMET"
str.split(" "); //["Lorem", "Ispum", "Dolor", "Sit", "Amet"]
str.substring(6,9); //"Ips"
new String("Lorem Ipsum Dolor Sit Amet") == str; //true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-Primer-8-320.jpg)

![Objects
• “Dictionary” / “Associative Array”
• Key: Value or 'Key': Value
• Without ': A-Z0-9 only
• Does not keep intrinsic ordering
• Accessed keys using . (dot) or [] notation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-Primer-10-320.jpg)
![Objects
var object = {
foo: 'value',
'complex key': 0,
bar: {
nested: true
}
};
object.foo; //'value'
object.['complex key']; //0
object.bar.nested; //true
object.bar['nested']; //true
object['bar'].nested; //true
object['bar']['nested']; //true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-Primer-11-320.jpg)

![in
var test = {
foo: 'value',
bar: 'value',
baz: 'value'
}
for (var key in test) {
console.log(key + ": " + test[key]);
}
//PRINTS:
//foo: value
//bar: value
//baz: value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-Primer-13-320.jpg)
![Arrays
• Special object
• Numerical keys only
• Keeps intrinsic ordering
• Short ([]) and Long (new Array()) syntax](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-Primer-14-320.jpg)
![Arrays
var arrayShort = [
'one',
'two'
];
arrayShort[2] = 'three';
var arrayLong = new Array();
arrayLong[0] = 'one';
arrayLong[1] = 'two';
arrayLong[2] = 'three';
//arrayShort: ["one", "two", "three"]
//arrayLong: ["one", "two", "three"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-Primer-15-320.jpg)
![Arrays
var arr = [1,2,3,4,6];
arr.indexOf(2); //1
arr.join(':'); //"1:2:3:4:6"
arr.pop(); //6
//[1,2,3,4]
arr.push(7); //5
//[1,2,3,4,7]
arr.reverse(); //[7,4,3,2,1]
arr.shift(); //1
//[2,3,4,7]
arr.unshift(8); //5
//[8,2,3,4,7]
arr.slice(1); //[2,3,4,7]
arr.slice(1,3); //[2,3]
arr.slice(-3); //[3,4,7]
arr.slice(-3,-1); //[3,4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-Primer-16-320.jpg)
![Arrays
var arr1 = [1,2,3];
var arr2 = [3,4,5];
arr1.concat(arr2); //[1,2,3,3,4,5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-Primer-17-320.jpg)





![arguments
function sum() {
var x = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; ++i) {
x += arguments[i];
}
return x;
}
sum(1, 2, 3); //6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-Primer-23-320.jpg)

![typeof
typeof true; //"boolean"
typeof 12; //"number"
typeof "string"; //"string"
typeof []; //"object"
typeof {}; //"object"
typeof NaN; //"number"
typeof null; //"object"
typeof undefined; //"undefined"
function Foo() {}
typeof Foo; //"function"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-Primer-25-320.jpg)
















![call & apply
var Foo = {
bar: "bar",
baz = function(param1, param2) {
return this.bar + param1 + param2;
}
};
var Foo2 = {
bar: "123"
};
Foo.baz("baz", "bat"); //"barbazbat"
Foo.baz.apply(Foo2, "baz", "bat"); //"123bazbat"
Foo.baz.call(Foo2, ["baz", "bat"]); //"123bazbat"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-Primer-42-320.jpg)


















![DOM
var paragraph = document.createElement('p');
var content = document.createTextNode("Lorem Ipsum");
paragraph.appendChild(content);
paragraph.classList.add('my-class');
document.getElementsByTagName('body')[0].appendChild(paragraph);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-Primer-61-320.jpg)




![JSON
{"menu": { <menu id="file" value="File">
"id": "file", <popup>
"value": "File", <menuitem value="New"
"popup": { onclick="CreateNewDoc()" />
"menuitem": [ <menuitem value="Open"
{"value": "New", onclick="OpenDoc()" />
"onclick": "CreateNewDoc()"}, <menuitem value="Close"
{"value": "Open", onclick="CloseDoc()" />
"onclick": "OpenDoc()"}, </popup>
{"value": "Close", </menu>
"onclick": "CloseDoc()"}
]
}
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptprimer-110901135606-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-Primer-66-320.jpg)