Pregnancymod Final Cut1
- 1. DENTAL MANAGEMENT IN PREGNANCY PRESENTED BY Feras Al-Halabi Abdulaziz Al-Abdulwahed Mohammed Al-Dhubaiban SUPERVISED BY: DR. Naveed Khawaja 13 - Jan- 2007
- 2. Why do we discuss pregnancy ? What is the definition of pregnancy ? Is there any changes during pregnancy ? and, will it affect dental treatment ? Is X-ray safe for a pregnant patient ? Can we prescribe drugs during pregnancy ? Amalgam and pregnancy, is there any concern ? How to manage pregnant women in dental chair ?
- 3. Why do we discuss pregnancy ? Dentist throughout their professional careers will face the responsibility of providing appropriate care for the pregnant women. Understanding the changes occurring in the pregnant patient is essential to deliver treatment with optimum safety to both mother & child.
- 4. Definition Pregnancy is the period of time between fertilization of the ovum (conception) & birth. Duration: 280 days = 40 weeks = 9 months. changes are : physical, physiological & psychological.
- 5. The Changes of Pregnancy The cardiovascular changes Respiratory changes Hematological change Renal changes Gastrointestinal changes Psychological Changes Oral Changes
- 6. The Cardiovascular Changes The main cardiovascular changes are : An increase in the total blood volume & cardiac output in late 2 nd & 3 rd trimester A decrease in blood pressure in 1 st trimester Dental Concern: Supine hypotensive syndrome Etiology Signs & symptoms Management
- 7. Respiratory Changes Main changes are: Dyspnea Hyperventilation An increase in tidal volume Dental concern: placing the patient in supine position may precipitate dyspnea
- 8. Hematological change Hematological changes are : An increase in : Plasma volume Red blood cells White blood cells All coagulation factors except factors XI and XIII Dental concern: The patient considered in hyper- coagulable state increasing the risk of thromboembolism.
- 9. Renal Changes Renal Changes are : Increased glomerular filtration rate (GFR). The increase in the renal plasma flow. Increase frequency of urination. Dental concern: It is advisable to ask the patient to void their bladder before dental procedure.
- 10. Gastrointestinal Changes Main Changes are : Nausea and vomiting Heartburn “Pyrosis” Dental concern: Avoid morning apointments. Advice the patient to avoid citris and fatty food. Prescribe fluoride mouth wash. Advice patient to avoid brushing.
- 11. Psychological Changes Main changes : Anxiety Emotional instability frequent changes in mood, ranging from happiness to depression. Dental concern: The dentist should minimize disturbances & noises adjust room temperature minimizing the irritability to the patient.
- 12. Oral Changes Pregnancy gingivitis Pregnancy tumor Tooth mobility Dental caries Facial pigmentation (melasma)
- 14. Effect of periodontal disease on the fetus : chronic periodontal disease during pregnancy increases the likelihood of preterm delivery by 4 to 7 fold. positive correlation between periodontal disease and low birth weight Pregnancy gingivitis
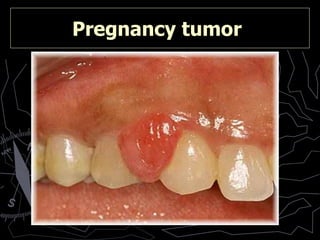
- 15. Pregnancy tumor
- 16. Tooth mobility
- 17. Dental caries
- 18. Effect of the caries on the fetus : A recent study has found a significant association between high levels of actinomyces naeslundii , an oral bacterium associated with dental caries, and low birth weight and preterm delivery Dental caries
- 20. Dental Radiographs for Pregnant Women Do we use radiographs In pregnant patients?
- 21. Dental Radiographs for Pregnant Women Full month series, 1 X 10 -5 (18 intraoral D film, lead apron) Panoramic film 15 X 10 -5 Daily radiation (cosmic) 4 X 10 -4 Skull 4 X 10 -3 Chest 8 X 10 -3 Radiographs Exposure in Gy
- 22. Although, the practitioner must use the necessary precautions, such as the use of : High-speed film Filtration, Collimation Lead aprons . greatly reduce exposure and the use of digital radiography Dental Radiographs for Pregnant Women
- 23. & the use of digital radiography will greatly reduce the exposure
- 24. What About Teratogenicity ? Depends on fetal age and the dose of radiation. Fetus age : 0-18 weeks Dose of radiation : 0.01Gy , The chance of teratogenicity is about 0.1% Although the chance of teratogenicity is minimal, the radiographic examination should be limited to the effected tooth
- 25. Dental drug prescription & pregnancy
- 26. Category A includes drugs that have been studied in humans and have evidence supporting their safe use. Category B drugs show no evidence of risk in humans. Category C includes drugs for which teratogenic risk cannot be ruled out. Category D includes drugs that have demonstrated risks in humans. Category X includes agents that have been shown to be harmful to the mother or fetus. Dental drug prescription & pregnancy
- 27. common drugs used : Lidocaine “xylocaine” B Aspirin C “ D in the 3 rd trimester ” Acetaminophen “Panadol” B Ibuprophen B delayed labor “ D in the 3 rd trimester ” Amoxcillin B Clindamycin B Metronidazole B Dental drug prescription & pregnancy
- 28. Dental Amalgam & Pregnancy Amalgam restorations release vaporized mercury during function. Mercury is known to cause congenital malformations The amount of mercury absorbed from amalgam restorations (2.0-5.0µg per day) is minimal, not clinically significant to the dental patients, and well below the toxic level )
- 29. The U.S.Public Health Service and Health Canada advice dentists that amalgam restorations should not be removed from or placed into a pregnant patient. This statement reflect the need for more research and not related to the potential effect of amalgam on the fetus. Dental Amalgam & Pregnancy
- 30. Dental Management of Pregnant Patient Goals : To develop efficient & effective treatment & compatible with the patient’s physical & emotional ability to undergo and respond well to dental care. Maintain the safety & well-being of the developing fetus or newborn.
- 31. Patient assessment Preventive strategies Therapeutic strategies Dental Management of Pregnant Patient
- 32. Therapeutic strategies Classification of dental treatments : Emergency treatment Non emergency but necessary treatment Elective treatment Timing of dental treatments : First trimester (conception to 14th week) Second trimester (14th to 28th week) Third trimester (29th week until childbirth)
- 33. Timing of dental treatments 1 st trimester (conception to 14th week) Educate the patient about maternal oral changes during pregnancy. Emphasize strict oral hygiene instructions and thereby plaque control. Limit dental treatment to periodontal prophylaxis and emergency treatments only. Avoid routine radiographs. Use selectively and when needed morning appointments should be avoided.
- 34. 2 nd trimester (14th to 28th week) Oral hygiene, instruction, and plaque control. Scaling, polishing, and curettage may be performed if necessary. Control of active oral diseases, if any. Elective dental care is safe. But it is best to deferred until after parturition. Avoid routine radiographs. Use selectively and when needed Timing of dental treatments
- 35. 3 rd trimester (29th week until childbirth) Oral hygiene, instruction, and plaque control. Scaling, polishing, and curettage may be performed if necessary. Avoid elective dental care during the second half of the third trimester. Avoid routine radiographs. Use selectively and when needed. Timing of dental treatments
- 36. Points to be considered Consultation with the patient’s physician should be undertaken. Keep appointment times short. Intermission in the middle of a sitting could be a great help, since the pregnant patient feels discomfort remaining in one position too long. It is advisable to ask the patient to void the bladder just prior to starting the dental procedure. Emergency treatment should be performed regardless to the pregnancy stage. The dentist should adapt conversation and instructions to her receptiveness. Also, it is recommended to minimize disturbance, interruptions and noises Finally remember It is important to remember that treatment is being rendered to 2 patients: mother and fetus .
- 37. Conclusion In the 1st trimester rapid cell division and active organogenesis occur; also the patient may suffer from nausea and vomiting so it is advisable to limit dental treatment to emergency and periodontal prophylaxis. The 2nd trimester is considered the safest period for providing dental care because organogenesis is completed and the fetus has not grown to a potentially uncomfortable size. Lastly, in the 3rd trimester the pregnant patient experience increasing fatigue and finds it increasingly difficult to assume and maintain a comfortable position. So, limited dental treatment is advisable.
- 38. any