Whatisdigitalsignature
- 1. What is Digital Signature Building confidentiality and trust into networked transactions. Kishankant Yadav www.signyourdoc.com 9571333822
- 2. Encryption It is a technique of converting plain text into ciphertext and reconverting it into plain text.
- 3. Basic Techniques of Encryption • Transposition Cipher • Substitution Cipher • Product Cipher
- 4. Basic Techniques of Encryption- Transposition Cipher Encrypts by changing the order of characters in the text. • e.g. : Replace 1st character with 6th • 2nd with 7th • 3rd with 8th • 4th with 9th • 5th with 10th and so on
- 5. Basic Techniques of Encryption- Transposition Cipher WE WILL ATTACK ON BHAI ON SUNDAY LL ATWE WI ON BHTACK SUNDAAI ONY TRANSPOSETRANSPOSE
- 6. Basic Techniques of Encryption- Substitution Cipher Encrypts by replacing the characters in the text with characters in a “Key” on the basis of some rule. e.g. : • Key is “MANISH” and Rule is Replace all • A in the text with M • B with A • C with N • D with I • E with S • F with H • G with A and so on
- 7. Basic Techniques of Encryption- Substitution Cipher INDORE IS A GOOD CITY DKILQS DR M BLLI NDTY SUBSTITUTESUBSTITUTE
- 8. Basic Techniques of Encryption- Product Cipher Combination of Transposition and Substitution • Take a Key • replace the characters in the text with characters in the Key. • Transpose the result.
- 9. Basic Techniques of Encryption- Product Cipher INDORE IS A GOOD CITY DKILQS DR M BLLI NDTY SUBSTITUTESUBSTITUTE TRANSPOSETRANSPOSE S DR DKILQI NDTM BLLY
- 10. Elements of Encryption Encryption method Decryption methodPlain text Plain text Encryption key Decryption KeyCipher text • Encryption Algorithm (function used to encrypt or decrypt) • Encryption keys (information used to cipher)
- 11. Good Encryption System: Features • Short Key •Strong Algorithm •High work factor •Low error propagation
- 12. Encryption Building confidentiality and trust into networked transactions. CHANGING THE WAYCHANGING THE WAY OF DOING BUSINESSOF DOING BUSINESS
- 13. A MATTER OF TRUST • Building Trust: Direct trust relationship Using Encryption
- 14. Some every day transactions: Credit Card Contract Notarized Notarized Document Medical Records Why do we place trust in these transactions? • Authentication • Confidentiality • Integrity • Non-repudiation
- 15. Ways of Encryption Two ways of encryption Symmetric Key or Private Key Encryption Asymmetric Key or Public Key Encryption (abbreviated as PKI)
- 16. Symmetric Cryptosystem Also called private key infrastructure Cleartext Message Cipher Text Cleartext Message DES | RC4 DES | RC4Four score and seven years ago, our forefathers brought forth the proposition Four score and seven years ago, our forefathers brought forth the proposition sdfklj98a475$5 6jhgv98456vjnf 84576FGHH78 lfkghj- 506#6lkjg4#$5; lkn;t7;lsk%0
- 17. Symmetric Cryptosystem • Similar key is used for encryption and decryption • Both parties should know the same key Original Message Original Message Encrypted Message Encrypted Message Also called private key infrastructure Secured transmission of encryption key to other person is a problem.
- 18. Asymmetric Cryptosystem Also called Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Improvement over Private Key System Provides all elements expected from a secure transaction : • Authentication • Confidentiality • Integrity • Non-repudiation Accordingly generates : • Signed message • Secret message • Signed and Secret message
- 19. Public Key System One half of a key pair is used to encrypt, the other half is used to decrypt. EncryptionEncryption Recipient’s Public Key Recipient’s Private Key DecryptionDecryption
- 20. Public Key Infrastructure(PKI) Uses a pair of keys. One part of pair is used for encryption Another part is used for decryption One part is kept private (called private key of a person) and another is made public (called public key of a person) Any key (public or private) can be used for encryption and then another is used for decryption Same key can not be used for encryption and decryption both. There has to be combination of both keys. Basic MethodologyBasic Methodology
- 21. Public Key Infrastructure(PKI) To generate a secret message Message is encrypted by sender with Receiver’s public key and It is decrypted by receiver with his private key. How messages are generatedHow messages are generated Original Message Encrypted Message Receiver’s public key Encrypted Message Original Message Receiver’s private key Encryption Decryption • ConfidentialityConfidentiality • IntegrityIntegrity It ensures :
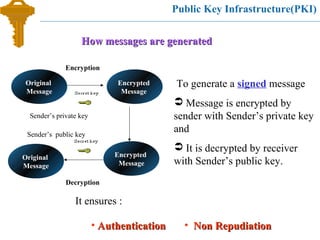
- 22. Public Key Infrastructure(PKI) To generate a signed message Message is encrypted by sender with Sender’s private key and It is decrypted by receiver with Sender’s public key. How messages are generatedHow messages are generated Original Message Encrypted Message Sender’s private key Encrypted Message Original Message Sender’s public key Encryption Decryption • AuthenticationAuthentication • Non RepudiationNon Repudiation It ensures :
- 23. Asymmetric Cryptosystem Original Message Encrypted Message I Sender’s private key Encrypted Message II Receiver’s public key Encrypted Message II Encrypted Message I Original Message Sender’s public key Receiver’s private key To generate a signed and secret message : Message is first encrypted by sender with Sender’s private key. This encrypted message is again encrypted with Receiver’s public key It is decrypted by receiver first with his private key and then with sender’s public key. How messages are generatedHow messages are generated It ensures : AuthenticationAuthentication Non RepudiationNon RepudiationIntegrityIntegrityConfidentialityConfidentiality
- 24. Digital Signatures • Digital signatures are hash code of a document encrypted with sender’s private key. • For sending the message, first hash code of message is generated. • This hash code is encrypted using sender’s private key. • The message is sent along with encrypted hash code. • At other end, receiver decrypts hash code with sender’s public key. • He also on his own calculates hash code of the message received. • Two hash codes should tally. AuthenticationAuthentication It ensures : Non RepudiationNon RepudiationIntegrityIntegrity Basic MethodologyBasic Methodology
- 25. Digital Signatures • In earlier process, message has been sent in clear text form thus confidentiality has not been achieved. • To overcome this problem, message and encrypted hash code may be encrypted by a symmetric key. • This symmetric key is also then encrypted with receiver’s public key. • All these i.e. Message and encrypted hash code which are now encrypted with symmetric key and symmetric key itself which is now encrypted with receiver’s public key, are sent to receiver. • Receiver first decrypt the symmetric key with his private key and then decrypt message and hash code with this symmetric key.
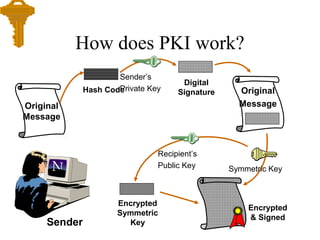
- 26. How does PKI work? Original Message Encrypted & Signed Sender’s Private KeyHash Code Digital Signature Symmetric Key Recipient’s Public Key Encrypted Symmetric KeySender Original Message
- 27. How does PKI work? Encrypted & Signed Symmetric KeyEncrypted Symmetric Key Recipient’s Private Key Original Message Hash Algorithm Hash CodeDigital Signature Sender’s Public Key Message verified Recipient
- 28. private Certificate ties a participant to public key The authenticity of the certificate is guaranteed by the digital signature generated using the CA’s private key. Validity Period Expires: 31 December 2022 Public Key: Signed: CA’s Signature Name: Prashant Mali Number: 2564567A ID Number & Name A Digital Certificate is a digitally signed document that associates a public key with a user. Digital Certificate
- 29. Key Lifecycle Management Key Generation Certificate Issuance Key Usage or Certificate Validation Key Expiry Key Update
- 30. Encryption Standard Data Encryption standard • A short key, strong algorithm system • Uses a 64 bit key, 56 bits for algorithm and 8 bits are parity RSA (Rivest, Shamir, Adalman) • Public key system. • Once private key is used to encrypt, it can be decrypted only using its public key and vice-versa.