04 Functional Programming in Python
- 1. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Instructor: Ebad ullah Qureshi Email: ebadullah.qureshi@rutgers.edu N2E Coding Club Python Workshop Functional Programming
- 2. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Time Conversion – Problem 2 Given a time in 12-hour AM/PM format, convert it to military (24-hour) time. Note: Midnight is 12:00:00AM on a 12-hour clock, and 00:00:00 on a 24-hour clock. Noon is 12:00:00PM on a 12-hour clock, and 12:00:00 on a 24-hour clock. Input Format A single string containing a time in 12-hour clock format (i.e.: hh:mm:ssAM or hh:mm:ssPM), where 01≤hh≤12 and 00≤mm,ss≤59. Constraints All input times are valid, example, 07:05:45PM. Output Format Convert and print the given time in -hour format, where 00≤hh≤23, example, 19:05:45. Testing Test your program for 07:05:45AM, 12:05:45AM, 07:05:45PM, and 12:05:45PM.
- 3. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi 3 Time Conversion – Starting out # Getting input time12 = input("Enter time in hh:mm:ssAM or hh:mm:ssPM “) # time12 and time24 have common minutes and seconds [:mm:ss] time24 = time12[2:8] # str12 format: hh:mm:ssAM or hh:mm:ssPM am_or_pm = time12[8] # Slicing hours hour = time12[0:2]
- 4. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi 4 Time Conversion – Conditional Block if am_or_pm == 'A': # for str12 01:00AM to 11:59AM if hour != '12': time24 = hour + time24 # for str12 12:00AM to 12:59AM else: time24 = "00" + time24 else: # for str12 01:00PM to 11:59PM if hour != '12': hr = int(hour) + 12 time24 = str(hr) + time24 # for str12 12:00PM to 12:59PM else: time24 = hour + time24
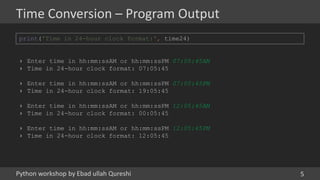
- 5. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Time Conversion – Program Output 5 print('Time in 24-hour clock format:', time24) › Enter time in hh:mm:ssAM or hh:mm:ssPM 07:05:45AM › Time in 24-hour clock format: 07:05:45 › Enter time in hh:mm:ssAM or hh:mm:ssPM 07:05:45PM › Time in 24-hour clock format: 19:05:45 › Enter time in hh:mm:ssAM or hh:mm:ssPM 12:05:45AM › Time in 24-hour clock format: 00:05:45 › Enter time in hh:mm:ssAM or hh:mm:ssPM 12:05:45PM › Time in 24-hour clock format: 12:05:45
- 6. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi 6 Introducing Functions I • In the previous problem, the program ran 4 times to test 4 inputs and it was dependent upon the user’s valid input • A time_conversion function would be very helpful here • The user’s input can be validated separately from the function so that the function always receives a valid input and the function can be reused as many times to test various inputs • A function is a block of organized, reusable code that is used to perform a single, related action • Functions provide better modularity for your application and a high degree of code reusing
- 7. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi 7 Introducing Functions II # Previous Examples of functions you’ve already seen print('Hello world') range(5, 17, 2) len('python') • The words in front of the parentheses are function names • The values inside the parenthesis are function arguments
- 8. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Defining and Calling a Function 8 # defining a function def hello(): print('hello world') # calling the function hello() › hello world
- 9. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Arguments and Return Statement 9 def add(num1, num2): # num1 and num 2 are arguments return num1 + num2 # result is returned # Function Calling total = add(7, 9) print(total) › 16 Function returning the sum of 2 numbers
- 10. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Flexible Number of Arguments 10 def add_numbers(*args): total = 0 for num in args: total += num return total print(add_numbers(5, 6, 8, 4, 2)) print(add_numbers(234, 543)) print(add_numbers(34, 56, 78, 5, 5.67, 2.45, 5*4)) › 25 › 777 › 201.11999999999998 Function to return the sum of numbers passed as argument
- 11. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi More about arguments 11 def cool_function(a, b=4, c=10): # b and c are default value arguments print('a is', a, 'b is', b, 'c is', c) cool_function(38, 49) # a&b are passed c takes its default value cool_function(54, c=74) # c is keyword argument, b is default argument cool_function(c=72, a=23)# a&c are keyword arguments, b is default argument data = [45, 35, 67] # a = data[0], b = data[1], c = data[2] cool_function(*data) # * unpacks the list and passes it to the function › a is 38 b is 49 c is 10 › a is 54 b is 4 c is 74 › a is 23 b is 4 c is 72 › a is 45 b is 35 c is 67
- 12. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi 12 Time Conversion – Function def time_conversion(time12): time24 = time12[2:8] am_or_pm = time12[8] hour = time12[0:2] if am_or_pm == 'A': if hour != '12': time24 = hour + time24 else: time24 = "00" + time24 else: if hour != '12': hr = int(hour) + 12 time24 = str(hr) + time24 else: time24 = hour + time24 return time24
- 13. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Time Conversion – Testing the Function 13 # calling the function print(time_conversion('07:05:45AM')) print(time_conversion('12:05:45AM')) print(time_conversion('07:05:45PM')) print(time_conversion('12:05:45PM')) › 07:05:45 › 00:05:45 › 19:05:45 › 12:05:45
- 14. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Python Modules 14 There are 3 main types of modules; 1. Those you write yourself 2. Those you install from external resources 3. Those that are preinstalled with Python The last type is called the standard library and has many useful functions
- 15. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Python Standard Library 15 • Python’s extensive standard library is one of its main strengths as a language • Some useful modules are; string re datetime math random os socket email json sys and much more
- 16. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Modules in Python Standard library 16 • Some of the Python Modules in the standard library are written in Python, and some are written in C • Most are available on all platforms, but some are windows or Unix specific • Many third-party Python modules are stored on the Python Package Index (PyPI) • Modules are installed using a program called pip • To install, go to the command line (command prompt on windows) and enter > pip install library_name • An alternate way to install is through the Project Interpreter on Pycharm • Some modules have prebuilt binaries that are normal executable files for Windows and let you install them with a GUI in the same way you would install other programs. • Use the modules in your program using the import keyword
- 17. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Gift Card Winners – Problem 17 import random # random.randint(a,b) generates a random number N such that a <= N <= b print(random.randint(1, 10)) › 7 As a General manager, you are responsible to give away a Gift Card to a raffle winner among your top 10 performers. Write a python script to generate a random number that would correspond to the winner of this week’s prize.
- 18. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Gift Card Winners – Alternate Solution 18 from random import randint # randint(a,b) generates a random number N such that a <= N <= b print(randint(1, 10)) › 4 • In the previous solution, the whole module was imported when we only required the randint() function • There is an alternate syntax for only importing functions that are required in the program
- 19. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Average of 10 random numbers – Problem 19 from statistics import mean as avg import random as r numbers = [] for _ in range(10): numbers.append(r.randint(1, 50)) print(numbers) print(avg(numbers)) › [47, 26, 34, 3, 8, 4, 43, 34, 44, 11] › 25.4 Generate a list of 10 random numbers between 1 and 50 inclusive and calculate its average. Achieve this by importing the random module and the mean function in the statistics module. Rename the random module r and the mean function avg
- 20. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Lambdas 20 # function to convert temperature in Kelvin to temperatures in degree celsius def kelvin_to_celsius(temperature): return temperature – 273 print(kelvin_to_celsius(298)) # lambda function result = (lambda temperature: temperature - 273)(250) print(result) › 25 › -23 • Alternate way of creating functions – lambda syntax • Functions created this way are known as anonymous and most commonly used when passing a simple function to another function
- 21. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi map() and filter() function 21 • The built-in functions map and filter are very useful higher order functions that operate on list (or other iterables • The function map takes a function and an iterable as arguments, and returns a new iterable with the function applied to each argument • The function filter filters an iterable by removing items that don’t match a predicate (function that returns a Boolean)
- 22. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi map() and filter() function 22 kelvin_temperatures = [298, 278, 305, 245, 0, 100, 300, 400] # convert all the temperatures in the above list into celsius celsius_temperatures = list(map(kelvin_to_celsius, kelvin_temperatures)) print(celsius_temperatures) # filtering out temperatures below freezing point temp_below_zero = list(filter(lambda x: x < 0, celsius_temperatures)) print(temp_below_zero) › [25, 5, 32, -28, -273, -173, 27, 127] › [-28, -273, -173]
- 23. Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi Instructor: Ebad ullah Qureshi Email: ebadullah.qureshi@rutgers.edu N2E Coding Club Python Workshop Thank You! Any Questions?


![Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi 3
Time Conversion – Starting out
# Getting input
time12 = input("Enter time in hh:mm:ssAM or hh:mm:ssPM “)
# time12 and time24 have common minutes and seconds [:mm:ss]
time24 = time12[2:8]
# str12 format: hh:mm:ssAM or hh:mm:ssPM
am_or_pm = time12[8]
# Slicing hours
hour = time12[0:2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-functionsmodules-190805031508/85/04-Functional-Programming-in-Python-3-320.jpg)






![Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi
More about arguments
11
def cool_function(a, b=4, c=10):
# b and c are default value arguments
print('a is', a, 'b is', b, 'c is', c)
cool_function(38, 49) # a&b are passed c takes its default value
cool_function(54, c=74) # c is keyword argument, b is default argument
cool_function(c=72, a=23)# a&c are keyword arguments, b is default argument
data = [45, 35, 67] # a = data[0], b = data[1], c = data[2]
cool_function(*data) # * unpacks the list and passes it to the function
› a is 38 b is 49 c is 10
› a is 54 b is 4 c is 74
› a is 23 b is 4 c is 72
› a is 45 b is 35 c is 67](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-functionsmodules-190805031508/85/04-Functional-Programming-in-Python-11-320.jpg)
![Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi 12
Time Conversion – Function
def time_conversion(time12):
time24 = time12[2:8]
am_or_pm = time12[8]
hour = time12[0:2]
if am_or_pm == 'A':
if hour != '12':
time24 = hour + time24
else:
time24 = "00" + time24
else:
if hour != '12':
hr = int(hour) + 12
time24 = str(hr) + time24
else:
time24 = hour + time24
return time24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-functionsmodules-190805031508/85/04-Functional-Programming-in-Python-12-320.jpg)






![Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi
Average of 10 random numbers – Problem
19
from statistics import mean as avg
import random as r
numbers = []
for _ in range(10):
numbers.append(r.randint(1, 50))
print(numbers)
print(avg(numbers))
› [47, 26, 34, 3, 8, 4, 43, 34, 44, 11]
› 25.4
Generate a list of 10 random numbers between 1 and 50 inclusive and calculate its average.
Achieve this by importing the random module and the mean function in the statistics module.
Rename the random module r and the mean function avg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-functionsmodules-190805031508/85/04-Functional-Programming-in-Python-19-320.jpg)


![Python workshop by Ebad ullah Qureshi
map() and filter() function
22
kelvin_temperatures = [298, 278, 305, 245, 0, 100, 300, 400]
# convert all the temperatures in the above list into celsius
celsius_temperatures = list(map(kelvin_to_celsius, kelvin_temperatures))
print(celsius_temperatures)
# filtering out temperatures below freezing point
temp_below_zero = list(filter(lambda x: x < 0, celsius_temperatures))
print(temp_below_zero)
› [25, 5, 32, -28, -273, -173, 27, 127]
› [-28, -273, -173]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-functionsmodules-190805031508/85/04-Functional-Programming-in-Python-22-320.jpg)
