1.3 Object Oriented Programming Paradigm, Basic Concepts of Object-Oriented Programming.pdf
- 1. Sanjivani Rural Education Society’s Sanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon-423 603 (An Autonomous Institute, Affiliated to Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune) NAAC ‘A’Grade Accredited, ISO 9001:2015 Certified Department of Computer Engineering (NBA Accredited) Subject- Object Oriented Programming (CO212) Unit 1 – Fundamentals of OOP Topic – 1.3 Object Oriented Programming Paradigm, Basic Concepts of Object-Oriented Programming Prof.V.N.Nirgude Assistant Professor E-mail : nirgudevikascomp@sanjivani.org.in Contact No: 9975240215
- 2. OOP paradigm DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 2 In OOP paradigm, • Emphasis is on objects rather than procedure. • Programs are divided into entities known as classes of objects. • Data Structures are designed such that they characterize objects. • Functions that operate on data are tied together in a class. • Data is hidden and cannot be accessed by external functions. • Objects communicate with each other through functions. • New data and functions can be easily added whenever necessary. • Follows bottom up approach in program design.
- 3. Organization of Data and Functions in OOP DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 3
- 4. Basic Concepts in OOP DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 4 • Object • Class • Message Passing • Abstraction • Encapsulation • Inheritance • Polymorphism • Dynamic Binding
- 5. Object • Object is a basic run-time entity of a class. •Object is also called as an instance of a class. •It may represent a person, a place or any item that the program must handle. • Example Representation of an object DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 5
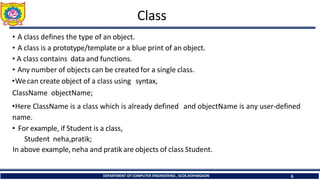
- 6. Class DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 6 • A class defines the type of an object. • A class is a prototype/template or a blue print of an object. • A class contains data and functions. • Any number of objects can be created for a single class. •Wecan create object of a class using syntax, ClassName objectName; •Here ClassName is a class which is already defined and objectName is any user-defined name. • For example, if Student is a class, Student neha,pratik; In above example, neha and pratik are objects of class Student.
- 7. Message Passing •A message passing is a request for execution of a procedure or to invoke a function in the receiving object that generates the desiredresult. •Message passing involves specifying the name of the object, the name of the function i.e. message or the information to be sent. • Objects can communicate with each other by passing messages same as people pass messages to each other. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 7
- 8. Abstraction DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 8 features as a list of relies on the •Abstraction refers to the representation of necessary without including details. •Classes use the concept of abstraction and are defined abstract data and functions to operate on these attributes. • Data abstraction is a programming technique that separation of interface and implementation.
- 9. Abstraction • When you press a key on your keyboard the character appears on the screen, you need to know only this, but How exactly it works electronically, is not needed. • Another Example is when you use the remote control of your TV, you do not bother about how pressing a key in the remote changes the channel on the TV. Youjust know that pressing the + volume button will increase the volume. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 9
- 10. Encapsulation • In simple words, “Encapsulation is a process of members and member functions into a single unit”. binding data DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 10
- 11. Encapsulation •The data is not accessible to the outside world, and only those functions which are wrapped in the class can access it. • This insulation of the data from direct access by the outside program is called data hiding or information hiding. • A Class is the best example of encapsulation. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 11
- 12. Inheritance •Inheritance is the process by which object of one class acquire the properties of another class. •In OOP, the concept of inheritance provides the idea of reusability. •This means that we can add additional features to an existing class without modifying it. •Through effective use of inheritance, you can save a lot of time in your programming and also reduce error. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 12
- 13. Polymorphism •Polymorphism is a Greek term which means than one form. •In polymorphism an operation may show different instances. the ability to take more different behavior in DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 13
- 14. Polymorphism •For example, + is used to make sum of two numbers as well as it is used to combine two strings. • This is known as operator overloading because same operator may behave differently on different instances. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 14
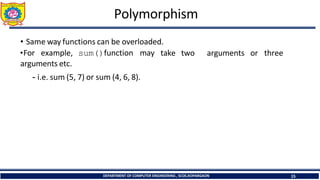
- 15. Polymorphism DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 15 • Same way functions can be overloaded. •For example, sum()function may arguments etc. - i.e. sum (5, 7) or sum (4, 6, 8). take two arguments or three
- 16. Dynamic Binding DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 16 •Dynamic Binding is the process of linking of the code associated with a procedure call at the run-time”. • Dynamic binding means that the code associated with a given procedure call is not known until the time of the call at run time.
- 17. Thank You.. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING , SCOE,KOPARGAON 17