100004568.ppt
- 1. Cutaneous Fungal Infections oDermatophytosis - "ringworm" disease of the nails, hair, and/or stratum corneum of the skin caused by fungi called dermatophytes. oDermatomycosis - more general name for any skin disease caused by a fungus.
- 3. DERMATOPHYTES • Microsporum - infections on skin and hair (M-N-No Nails) • Epidermophyton - infections on skin and nails (not the cause of TINEA CAPITIS) • Trichophyton - infections on skin, hair, and nails.
- 4. • Epidermophyton- E. floccosum • Microsporum- M.canis • M. gypseum • Trichophyton-T. rubrum • T. mentagrophytes • T. verrucosum • T.violaceum
- 5. Major sources of ringworm infection Warm damp areas (e.g., tropics, moisture accumulation in clothing and shoes). • Schools, military camps, prisons. • Animals (e.g., dogs, cats, cattle, poultry, etc.).
- 6. Clinical manifestations of ringworm infections are called different names on basis of location of infection sites • tinea capitis - ringworm infection of the head, scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes • tinea favosa - ringworm infection of the scalp (crusty hair) • tinea corporis - ringworm infection of the body (smooth skin)
- 7. • tinea cruris - ringworm infection of the groin (jock itch) • tinea unguium - ringworm infection of the nails • tinea barbae - ringworm infection of the beard • tinea manuum - ringworm infection of the hand • tinea pedis - ringworm infection of the foot (athlete's foot)
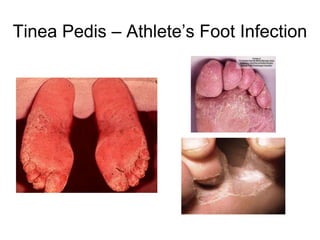
- 8. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF RINGWORM • tinea pedis - Athletes' foot infection • between toes or toe webs (releasing of clear fluid) - 4th and 5th toes are most common. • Soreness and itching of any part of the foot. • Fungi probably transmitted host to host through infected squames; flat, keratinised, dead cells shed from the outermost layer of a stratified squamous epithelium. • Three causal agents, T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, and Epidermophyton floccosum
- 9. Tinea Pedis – Athlete’s Foot Infection
- 10. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF RINGWORM • Allergic reactions are sometimes associated with tinea pedis and other ringworm infections. • dermatophytid - an "id" allergic reaction. • toxins get into blood stream and reaches a site other than the site of infection. • blistering occurs on fingers and hands. • treat the primary site of infection where the antigen is being produced. • treat secondary site - blisters.
- 12. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF RINGWORM • tinea corporis - body ringworm • Generally restricted to stratum corneum of the smooth skin. • Produces concentric or ring-like lesions on skin • Severe cases -raised and inflamed. • • All forms of tinea corporis caused by T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, T. tonsurans, M. canis, and M. audouinii... • Transmission - infected scales hyphae or arthroconidia on the skin. - direct contact between infected humans or animals, by fomites • Normally resolves itself in several months.
- 13. Tinea corporis – body ringworm
- 14. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF RINGWORM SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT • tinea cruris - ringworm of the groin and surrounding region • More common in men • Infection seen on scrotum and inner thigh, the penis is usually not infected. • Epidemics associated with grouping of people into tight quarters - athletic teams, troops, ship crews, inmates of institutions. • Several causes of tinea cruris include T. rubrum (does not normally survive long periods outside of host), E. flocossum (usually associate with epidemics because resistant arthroconidia in skin scales can survive for years on rugs, shower stalls, locker room floors), T. mentagrophytes
- 15. Tinea Cruris – Jock Itch
- 16. Tinea Unguium – Nail Infection
- 17. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF RINGWORM • tinea capitis - ringworm of the scalp, eyebrows and eyelashes • Cause- Microsporum and Trichophyton. • Fungus grows into hair follicle. • • Ectothrix infection - fragmentation of mycelium into conidia (called arthroconidia) around the hair shaft or just beneath the cuticle with destruction of the cuticle. Caused by M. audounii, M. canis • Endothrix infection - arthroconidia formation occurs by fragmentation of hyphae with the hair shaft with destruction of the cuticle. T. tonsurans (most common cause). • "Id" reaction may occur.
- 18. Ectothrix and Endothrix Fluorescing hair (under Wood's lamp) is seen in infection with some dermatophytes
- 19. • FAVUS • KERION. • GREY PATCH
- 21. Lab Diagnosis • Note the symptoms. • Woods Lamp examination • Sample- skin &nail scrappings (edge), plucked hair • Direct Microscopic examination of slides of skin scrapings, nail scrapings, and hair with10 % KOH • branching hyaline septate hyphae
- 22. CULTURE • SDA (with chloramphenicol & cycloheximide) • 25, 300 , 370 CX21 days • DTM=25oC- red • Hair Perforation test • Urease test
- 23. DERMATOPHYTES
- 24. Distribution of Conidia dermatophyte Macroconidia Microconidia Trichophyton Rare, thin walled Abundant Microsporum Numerous, thick walled, rough Rare Epidermophyton Numerous,smooth walled Absent
- 25. Microsporum canis Teleomorph: Arthroderma otae http://www.doctorfungus.org/thefungi/microsporum_canis.htm http://www.mycology.adelaide.edu.au/Fungal_Descriptions/Dermatophytes/Microsporum/Microsporum_canis.html
- 26. Microsporum canis Colony growth is rapid, downy to wooly, cream to yellow on the surface with a yellow to yellow- orange reverse. Microconidia are club-shaped but typically are absent. Macroconidia are fusoid, verrucose, and thick walled. They have a recurved apex and contain 5-15 cells. Lab tests: hair perforation test positive and urease positive. Infection in humans occurs on the scalp and glabrous skin. It is also a cause of ringworm in cats and dogs.
- 28. Microsporum gypseum Colony growth is rapid, downy, becoming powdery to granular, cream, tawny-buff, or pale cinnamon on the surface with a beige to red-brown reverse. Microconidia are moderately abundant and club-shaped. Macroconidia are abundant, ellipsoidal to fusiform, sometimes verrucose, and thin walled. They typically contain 3-6 cells. Lab tests: hair perforation test positive and urease positive. Infection in humans is found on the scalp and glabrous skin; it is more frequently isolated from the soil and from the fur of small rodents.
- 30. Epidermophyton floccosum Colony growth is slow, powdery, with a yellow to khaki surface color and chamois to brown reverse. Macroconidia are club shaped, with thin smooth walls and can be solitary or grouped in clusters. Chlamydospores are often produced in large numbers. Microconidia are absent. Lab tests: hair perforation test negative, urease positive, growth at 37°C. Infections are commonly cutaneous, especially of the groin or feet.
- 32. Trichophyton mentagrophytes Colony growth is moderately rapid, powdery to granular, white to cream colored on the surface with a yellowish, brown or red-brown reverse. Microconidia are numerous, unicellular, round to pyriform and found in grape like clusters. Spiral hyphae are often present. Macroconidia are multiseptate, club- shaped and often absent. Lab tests: hair perforation test positive, urease positive, growth at 37°C. Infection is typically found on the feet, hands, or groin, but can also be associated with inflammatory lesions of the scalp, nails, and beard.
- 34. Hair Perforation Test Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Hair perforation test is positive. Trichophyton rubrum, Hair perforation test is negative. Perforations
- 35. • Urease Test • T ment + • T rubrum -
- 36. TREATMENT • Mild- topical imidazole • Severe- Oral- Griseofulvin or Ketoconazole, itraconazole,fluconazole • Skin- 4-6 wks • Hair- 3-6 mths • Nails – 1 yr
- 37. Test Your Knowledge Answer View dermatophyte differentiation table View index slide Return to previously viewed slide View correct answer Each unknown slide has the following navigation buttons to help you:
- 38. Answer Unknown 1 Colony growth is rapid, downy to wooly, cream to yellow on the surface with a yellow to yellow- orange reverse.
- 39. Answer Unknown 2 Colony growth is moderately rapid, powdery to granular, white to cream colored on the surface with a yellowish, brown or red-brown reverse.
- 40. Answer Unknown 5 Colony growth is slow to moderate, downy, white on the surface with a red to brown reverse.
- 41. Answer Unknown 6 Colony growth is rapid, downy, becoming powdery to granular, cream, tawny- buff, or pale cinnamon on the surface with a beige to red-brown reverse.
- 43. DERMATOPHYTES • Trichophyton tonsurans • Anthropophilic and on hair causes endothrix. • Third most common cause of tinea capitis • Other leading causes of tinea capitis are M. audouinii (transmission is generally from child to child) and M. canis (transmission is from animal to human). • Colonies whitish and folded. • Colonies are yellowish-brown color on reverse of colony. • Microconidia are longer and larger than in T. rubrum. • Intercalary and terminal chlamydoconidia common in older cultures. • Macroconidia not common, irregular in form.
- 46. DERMATOPHYTES • Trichophyton violaceum • Attacks hair, scalp, skin and nails. • Nail infections are persistent. • Endothrix (black dot infection of scalp). • Found in humans, rarely in animals. • Disease has been reported in horses, cats, dogs, mice and pigeons. • Very slow growing in culture with a waxy appearance. • Colony deep violent in color, purplish pigment diffuses into media. • Rarely produces microconidia and macroconidia. • In culture this species requires thiamine for proper growth. • Hyphae coarser in appearance than seen in other dermatophytes. • Chlamydoconidia are seen in culture.
- 48. DERMATOPHYTES • Trichophyton verrucosum • Associated with cattle ("barn itch"). • Large-spored ectothrix. • Causes severer infections in humans on the scalp and beard. • Very slow growing, no pigment on reverse to yellow. • Grows best at 37 C. • On unenriched media - chains of chlamydoconidia and antler-like hyphae. • On thiamine-enriched media, produces many small microconidia and occasionally macroconidia are produced.
- 51. DERMATOPHYTES • Trichophyton schoenleinii • Endothrix infection of hair. • Causes tinea favosa (cup-shaped crusts on scalp called favus). • tinea favosa may lead to alopecia or permanent baldness. • Colonies waxy to suede-like; off white in color. • Colony may become convoluted from folds that develop • No conidia (micro- or macro-) even on enriched media . • Grows will at 37 C.
- 54. DERMATOPHYTES • Trichophyton ajelloi • Teleomorph - Arthroderma uncinatum. • Common soil dermatophilic fungus. • Rarely causes infection in man or animals (cattle, dogs, horses, squirrels). • Readily isolated from soil by hair baiting. • Cigar-shaped macroconidia with smooth ends.