17575602.ppt
- 1. PYTHON - VARIABLES AND OPERATORS 12th COMPUTER SCIENCE LESSON - 5 Padasalai.Net
- 2. Introduction • Python is a general purpose programming language • It is created by Guido Van Rossum from CWI (Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica) which is a National Research Institute for Mathematics and Computer Science in Netherlands. • The language was released in I991.
- 3. Key features of Python • It is a general purpose programming language which can be used for both scientific and non-scientific programming. • It is a platform independent programming language. • The programs written in Python are easily readable and understandable.
- 4. Programming in Python • Interactive mode • Script mode
- 5. Interactive mode Programming • In interactive mode Python code can be directly typed and the interpreter displays the result(s) immediately. Script mode Programming •A script is a text file containing the Python statements. •Python Scripts are reusable code
- 6. Creating Scripts in Python • FILE -> NEW • CTRL + N Saving Python Script • FILE -> SAVE • CTRL + S Executing Python Script • RUN -> RUN MODULE • F5 • For all error free code, the output will appear in the IDLE window of Python
- 7. Input and Output Functions • input() • print()
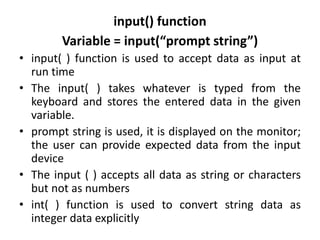
- 8. input() function Variable = input(“prompt string”) • input( ) function is used to accept data as input at run time • The input( ) takes whatever is typed from the keyboard and stores the entered data in the given variable. • prompt string is used, it is displayed on the monitor; the user can provide expected data from the input device • The input ( ) accepts all data as string or characters but not as numbers • int( ) function is used to convert string data as integer data explicitly
- 9. Print() function print(“String”) print(variable) print(“String”,variable) print(variable ,“String”, variable ,“String”) • The print() function is used to display result on the screen • Comma ( , ) is used as a separator in print ( ) to print more than one item.
- 10. Comments in Python • comments begin with hash symbol (#) • Comments may be single line or no multi-lines. Indentation •Python uses whitespace such as spaces and tabs to define program blocks •All statements within the block must be indented with same amount spaces.
- 11. Tokens • Python breaks each logical line into a sequence of elementary lexical components known as Tokens. 1. Identifiers 2. Keywords 3. Operators 4. Delimiters 5. Literals
- 12. Identifiers • An Identifier is a name used to identify a variable, function, class, module or object. • An identifier must start with an alphabet (A..Z or a..z) or underscore ( _ ). • Identifiers may contain digits (0 .. 9) • Python identifiers are case sensitive i.e. uppercase and lowercase letters are distinct. • Identifiers must not be a python keyword. • Python does not allow punctuation character such as %,$, @ etc., within identifiers.
- 13. Keywords • Keywords are special words used by Python interpreter to recognize the structure of program. • Identifiers must not be a python keyword.
- 14. Operators • In computer programming languages operators are special symbols which represent computations, conditional matching etc. • The value of an operator used is called operands. • Arithmetic operators • Relational or Comparative operators • Logical operators • Assignment operators • Conditional operator
- 15. Arithmetic operators • An arithmetic operator is a mathematical operator that takes two operands and performs a calculation on them.
- 16. Relational or Comparative operators • A Relational operator is also called as Comparative operator which checks the relationship between two operands.
- 17. Logical operators • Logical operators are used to perform logical operations on the given relational expressions.
- 18. Assignment operators • = is a simple assignment operator to assign values to variable.
- 19. Ternary operator • Ternary operator is also known as conditional operator that evaluate something based on a condition being true or false. • It simply allows testing a condition in a single line
- 20. Delimiters • Python uses the symbols and symbol combinations as delimiters in expressions, lists, dictionaries and strings
- 21. Literals • Literal is a raw data given in a variable or constant • Numeric • String • Boolean Numeric Literals – Numeric Literals consists of digits and are immutable String Literals – In Python a string literal is a sequence of characters surrounded by quotes. – Python supports single, double and triple quotes for a string. Boolean Literals – A Boolean literal can have any of the two values: True or False.
- 22. Escape Sequences • The backslash "" is a special character, also called the "escape" character. • It is used in representing certain whitespace characters
- 23. Python Data types • Number • String • Boolean • Tuples • lists • dictionaries
- 24. எந்த அளவு நீ உயர்ந்தவனாக வவண ் டும் என ் று நினனக்கிறாவயா அந்த அளவுக்கு கடுனமயான வ ாதனனகனள நீ கடந்து ச ல்ல வவண ் டும் CELL : 9524756933 MAIL : mrajivgandhibcomca@gmail.com