305 Chapter 2
- 1. 2 Chapter Information Systems in the Enterprise
- 2. OBJECTIVES Evaluate the role played by the major types of systems in a business and their relationship to each other Describe the information systems supporting the major business functions: sales and marketing, manufacturing and production, finance and accounting, and human resources Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise
- 3. Analyze the relationship between organizations, information systems, and business processes Explain how enterprise applications promote business process integration and improve organizational performance Assess the challenges posed by information systems in the enterprise and management solutions Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise OBJECTIVES (continued)
- 4. Challenge: monthly changes in fashions; Mango has 731 stores in 72 countries Solutions. Inventory replenishment system tracks all sales and matches stores with inventory. Design teams meet weekly to adjust to trends. Distribution system allocates bar-coded items to specific stores based on store/product mix. Reduces time to market, increases agility Increases accuracy of decision making Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Mango Case: Fast Fashion, Hot Systems
- 5. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Types of Information Systems Figure 2-1
- 6. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Different Kinds of Systems Operational-level systems: support operational managers, keeping track of the elementary activities and transactions Management-level systems: serve the monitoring, controlling, decision-making, and administrative activities Strategic-level systems: help senior management tackle and address strategic issues Three main categories of information systems serve different organizational levels:
- 7. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Major Types of Systems Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) Management Information Systems (MIS) Decision-Support Systems (DSS) Executive Support Systems (ESS)
- 8. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS The Four Major Types of Information Systems Figure 2-2
- 9. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) Basic business systems that serve the operational level A computerized system that performs and records the daily routine transactions necessary to the conduct of the business
- 10. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS A Symbolic Representation for a Payroll TPS Figure 2-3
- 11. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Typical Applications of TPS Figure 2-4
- 12. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Management Information Systems (MIS) Management level Inputs: High volume transaction level data Processing: Simple models Outputs: Summary reports Users: Middle managers Example: Annual budgeting
- 13. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Management Information Systems (MIS) (continued) Figure 2-5
- 14. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Management Information Systems (MIS) (continued) A sample MIS report Figure 2-6
- 15. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Decision-Support Systems (DSS) Management level Inputs: Transaction level data Processing: Interactive Outputs: Decision analysis Users: Professionals, staff Example: Contract cost analysis
- 16. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Decision-Support Systems (DSS) (Continued) Voyage-estimating decision-support system Figure 2-7
- 17. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS (ESS): Inputs: Aggregate data Processing: Interactive Outputs: Projections Users: Senior managers Example: 5 year operating plan
- 18. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Model of a Typical Executive Support System Figure 2-8
- 19. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS (ESS) (Continued) Top Level Management Designed to the individual senior manager Ties CEO to all levels Very expensive to keep up Extensive support staff
- 20. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Relationship of Systems to One Another Interrelationships among systems Figure 2-9
- 21. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Relationship of Systems to One Another In contemporary digital firms, the different types of systems are closely linked to one another. This is the ideal. In traditional firms these systems tend to be isolated from one another, and information does not flow seamlessly from one end of the organization to the other. Efficiency and business value tend to suffer greatly in these traditional firms
- 22. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise SYSTEMS FROM A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE Sales and Marketing Systems Major functions of systems: Sales management, market research, promotion, pricing, new products Major application systems: Sales order info system, market research system, pricing system
- 23. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise SYSTEMS FROM A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE Sales and Marketing Systems Table 2-2 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION ORGANIZATIONAL LEVEL Order processing Enter, process, and track orders Operational Pricing analysis Determine prices for products and services Management Sales trend forecasting Prepare 5-year sales forecasts Strategic
- 24. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise SYSTEMS FROM A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE Manufacturing and Production Systems Major functions of systems: Scheduling, purchasing, shipping, receiving, engineering, operations Major application systems: Materials resource planning systems, purchase order control systems, engineering systems, quality control systems
- 25. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise SYSTEMS FROM A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE Manufacturing and Production Systems SYSTEM DESCRIPTION ORGANIZATIONAL LEVEL Machine control Control the actions of machines and equipment Operational Production planning Decide when and how many products should be produced Management Facilities location Decide where to locate new production facilities Strategic
- 26. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Overview of an Inventory System SYSTEMS FROM A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE Figure 2-10
- 27. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise SYSTEMS FROM A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE Financing and Accounting Systems Major functions of systems: Budgeting, general ledger, billing, cost accounting Major application systems: General ledger, accounts receivable, accounts payable, budgeting, funds management systems
- 28. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise SYSTEMS FROM A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE Financing & Accounting Systems (Continued) Table 2-4 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION ORGANIZATION-AL LEVEL Accounts receivable Tracks money owed the firm Operational Budgeting Prepares short-term budgets Management Profit planning Plans long-term profits Strategic
- 29. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise SYSTEMS FROM A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE Human Resource Systems Major functions of systems: Personnel records, benefits, compensation, labor relations, training Major application systems: Payroll, employee records, benefit systems, career path systems, personnel training systems
- 30. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise SYSTEMS FROM A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE Human Resource Systems (Continued) Table 2-5 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION ORGANIZATIONAL LEVEL Training and development Tracks employee training, skills, and performance appraisals Operational Compensation analysis Monitors the range and distribution of employee wages, salaries, and benefits Management Human resources planning Plans the long-term labor force needs of the organization Strategic
- 31. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Human Resource Systems (Continued) An Employee Recordkeeping System SYSTEMS FROM A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE Figure 2-11
- 32. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Business Processes and Information Systems Business processes: Manner in which work is organized, coordinated, and focused to produce a valuable product or service Concrete work flows of material, information, and knowledge—sets of activities Unique ways to coordinate work, information, and knowledge Ways in which management chooses to coordinate work INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 33. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Business Processes and Information Systems (Continued) Information systems help organizations achieve great efficiencies by automating parts of processes IS also contributes to completely rethinking processes. Business processes typically span several different functional areas. INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 34. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Examples of Business Processes Manufacturing and production: Assembling product, checking quality, producing bills of materials Sales and marketing: Identifying customers, creating customer awareness, selling INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications Table 2.6
- 35. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Finance & accounting : Paying creditors, creating financial statements, managing cash accounts Human resources : Hiring employees, evaluating performance, enrolling employees in benefits plans INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications Examples of Business Processes (Continued) Table 2.6 continued
- 36. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Business Processes and Information Systems Cross-Functional Business Processes: Transcend boundary between sales, marketing, manufacturing, and research and development Group employees from different functional specialties to a complete piece of work Example: Order Fulfillment Process INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 37. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise The Order Fulfillment Process INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications Figure 2-12
- 38. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Systems for Enterprise-Wide Process Integration Enterprise applications: Designed to support organization-wide process coordination and integration INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 39. Consist of : Enterprise systems Supply chain management systems Customer relationship management systems Knowledge management systems Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Systems for Enterprise-Wide Process Integration (Continued) INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 40. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Enterprise Systems Enterprise systems, also known as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, provide a single information system for organization-wide coordination and integration of key business processes. Information that was previously fragmented in different systems can seamlessly flow throughout the firm so that it can be shared by business processes in manufacturing, accounting, human resources, and other areas. INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 41. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Enterprise Application Architecture INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications Figure 2-13
- 42. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Traditional “Silo” View of Information Systems Within the business: There are functions, each having its uses of information systems Outside the organization’s boundaries: There are customers and vendors Functions tend to work in isolation INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 43. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Traditional View of Systems INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications Figure 2-14
- 44. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Enterprise Systems INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications Figure 2-15
- 45. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Benefits of Enterprise Systems Help to unify the firm’s structure and organization: One organization Management: Firm wide knowledge-based management processes Technology: Unified platform Business: More efficient operations & customer-driven business processes INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 46. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Challenges of Enterprise Systems Difficult to build: Require fundamental changes in the way the business operates Technology: Require complex pieces of software and large investments of time, money, and expertise Centralized organizational coordination and decision making: Not the best way for the firms to operate INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 47. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Supply Chain Management (SCM) Close linkage and coordination of activities involved in buying, making, and moving a product Integrates supplier, manufacturer, distributor, and customer logistics time Reduces time, redundant effort, and inventory costs Network of organizations and business processes INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 48. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Helps in procurement of materials, transformation of raw materials into intermediate and finished products Helps in distribution of the finished products to customers Includes reverse logistics - returned items flow in the reverse direction from the buyer back to the seller Supply Chain Management (SCM) INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 49. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Haworth’s Supply Chain Management Systems INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications Figure 2-16
- 50. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Information from Supply Chain Management Systems helps firms: Decide when and what to produce, store, and move Rapidly communicate orders Track the status of orders Check inventory availability and monitor inventory levels INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 51. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Information from Supply Chain Management Systems helps firms: (Continued) Reduce inventory, transportation, and warehousing costs Track shipments Plan production based on actual customer demand Rapidly communicate changes in product design INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
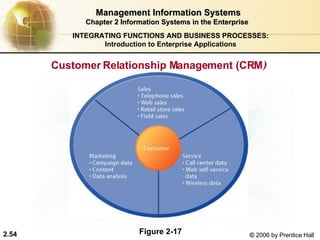
- 52. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Manages all ways used by firms to deal with existing and potential new customers Business and technology discipline Uses information system to coordinate entire business processes of a firm INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 53. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Customer Relationship Management (CRM) (Continued) Provides end- to- end customer care Provides a unified view of customer across the company Consolidates customer data from multiple sources and provides analytical tools for answering questions INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 54. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Customer Relationship Management (CRM ) INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications Figure 2-17
- 55. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Knowledge Management Systems Collects relevant knowledge and make it available wherever and whenever it is needed Support business processes and management decisions Also link the firm to external sources of knowledge Support processes for acquiring, storing, distributing, and applying knowledge INTEGRATING FUNCTIONS AND BUSINESS PROCESSES: Introduction to Enterprise Applications
- 56. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise There are extraordinary opportunities to use information systems to achieve business value, and increase profitability MANAGEMENT OPPORTUNITIES, CHALLENGES, AND SOLUTIONS Management Opportunities:
- 57. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Integration and the whole firm view: Given the different interests and perspectives within a firm, it is difficult to achieve consensus about the need for the "whole firm" viewpoint. Management and employee training: Training a large number of employees on many systems in a large organization involves commensurately large investments. MANAGEMENT OPPORTUNITIES, CHALLENGES, AND SOLUTIONS Management Challenges:
- 58. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise Accounting for the cost of systems and managing demands for systems: Given the large number of different types of systems in a firm, and the large number of people involved with using them, it is a complex task to understand which systems are truly necessary and productive with high returns on investment MANAGEMENT OPPORTUNITIES, CHALLENGES, AND SOLUTIONS Management Challenges: (Continued)
- 59. Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MANAGEMENT OPPORTUNITIES, CHALLENGES, AND SOLUTIONS Solution Guidelines: Inventory the firm’s information systems: Develop a list of firm-wide information requirements to give a 360-degree view of the most important information needs of the firm. Employee and management education: Ensure that you understand how much training is required. Account for the costs and benefits: Develop an accounting system for information services firm- wide.