40ce.ppt
- 2. 2 Content • What is Modulation • Amplitude Modulation (AM) • Demodulation of AM signals • Calculation and Examples • Summary
- 3. 3 What is Modulation • Modulation – In the modulation process, some characteristic of a high-frequency carrier signal (bandpass), is changed according to the instantaneous amplitude of the information (baseband) signal. • Why Modulation – Suitable for signal transmission (distance…etc) – Multiple signals transmitted on the same channel – Capacitive or inductive devices require high frequency AC input (carrier) to operate. – Stability and noise rejection
- 4. 4 About Modulation • Application Examples – broadcasting of both audio and video signals. – Mobile radio communications, such as cell phone. • Basic Modulation Types – Amplitude Modulation: changes the amplitude. – Frequency Modulation: changes the frequency. – Phase Modulation: changes the phase.
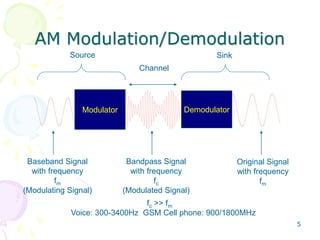
- 5. 5 AM Modulation/Demodulation Modulator Demodulator Baseband Signal with frequency fm (Modulating Signal) Bandpass Signal with frequency fc (Modulated Signal) Channel Original Signal with frequency fm Source Sink fc >> fm Voice: 300-3400Hz GSM Cell phone: 900/1800MHz
- 7. 7 Amplitude Modulation • The amplitude of high-carrier signal is varied according to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating message signal m(t). Carrier Signal: or Modulating Message Signal: or The AM Signal: cos(2 ) cos( ) ( ): cos(2 ) cos( ) ( ) [ ( )]cos(2 ) c c m m AM c c f t t m t f t t s t A m t f t
- 8. 8 Amplitude Modulation • The AM signal is generated using a multiplier. • All info is carried in the amplitude of the carrier, AM carrier signal has time-varying envelope. • In frequency domain the AM waveform are the lower-side frequency/band (fc - fm), the carrier frequency fc, the upper-side frequency/band (fc + fm).
- 9. 9 AM Modulation – Example • The information signal is usually not a single frequency but a range of frequencies (band). For example, frequencies from 20Hz to 15KHz. If we use a carrier of 1.4MHz, what will be the AM spectrum? • In frequency domain the AM waveform are the lower-side frequency/band (fc - fm), the carrier frequency fc, the upper-side frequency/band (fc + fm). Bandwidth: 2x(25K-20)Hz. frequency 1.4 MHz 1,385,000Hz to 1,399,980Hz 1,400,020Hz to 1,415,000Hz fc
- 10. 10 Modulation Index of AM Signal m c A k A ) 2 cos( ) ( t f A t m m m Carrier Signal: cos(2 ) DC: c C f t A For a sinusoidal message signal Modulation Index is defined as: Modulated Signal: ( ) [ cos(2 )]cos(2 ) [1 cos(2 )]cos(2 ) AM c m m c c m c S t A A f t f t A k f t f t Modulation index k is a measure of the extent to which a carrier voltage is varied by the modulating signal. When k=0 no modulation, when k=1 100% modulation, when k>1 over modulation.
- 11. 11 Modulation Index of AM Signal
- 12. CSULB May 22, 2006 12 Modulation Index of AM Signal
- 13. 13 Modulation Index of AM Signal
- 14. 14 High Percentage Modulation • It is important to use as high percentage of modulation as possible (k=1) while ensuring that over modulation (k>1) does not occur. • The sidebands contain the information and have maximum power at 100% modulation. • Useful equation Pt = Pc(1 + k2/2) Pt =Total transmitted power (sidebands and carrier) Pc = Carrier power





![7
Amplitude Modulation
• The amplitude of high-carrier signal is
varied according to the instantaneous
amplitude of the modulating message
signal m(t).
Carrier Signal: or
Modulating Message Signal: or
The AM Signal:
cos(2 ) cos( )
( ): cos(2 ) cos( )
( ) [ ( )]cos(2 )
c c
m m
AM c c
f t t
m t f t t
s t A m t f t
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/40ce-230526034418-73fe9cfa/85/40ce-ppt-7-320.jpg)


![10
Modulation Index of AM Signal
m
c
A
k
A
)
2
cos(
)
( t
f
A
t
m m
m
Carrier Signal: cos(2 ) DC:
c C
f t A
For a sinusoidal message signal
Modulation Index is defined as:
Modulated Signal: ( ) [ cos(2 )]cos(2 )
[1 cos(2 )]cos(2 )
AM c m m c
c m c
S t A A f t f t
A k f t f t
Modulation index k is a measure of the extent to
which a carrier voltage is varied by the modulating
signal. When k=0 no modulation, when k=1 100%
modulation, when k>1 over modulation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/40ce-230526034418-73fe9cfa/85/40ce-ppt-10-320.jpg)



