6.1 refraction of light
- 2. CONTENT IN THIS CHAPTER
- 3. 6.1 REFRACTION OF LIGHT • SC1: 6.1.1 DESCRIBE REFRACTION OF LIGHT • SC2: 6.1.2 EXPLAIN REFRACTIVE INDEX, N. • SC3: 6.1.3 CONCEPTUALIZE SNELL'S LAW • SC4: 6.1.5 EXPLAIN REAL DEPTH AND APPARENT DEPTH. • SC5: 6.1.7 SOLVE AT LEAST ONE PROBLEM RELATED TO REFRACTION OF LIGHT.
- 4. Refraction of light is the change in velocity of light when travelling through mediums of different optical densities i r air glass Incident ray Refracted ray i r Emergent ray Ray of light travel from air (less dense) to glass (denser) i > r The speed of light decreases. The ray of light bend towards the normal Ray of light travel from glass (denser) to air (less dense). i < r The speed of light increases. The ray of light bend away from the normal
- 5. OPTICAL DENSITY VS PHYSICAL DENSITY Both are different parameters A material with greater optical density than water does not imply it has a greater physical density than water For example paraffin oil is optically denser than water but less dense than water Medium Refractive index, n Paraffin oil 1.44 Water 1.33 REFRACTIVE INDEX, n Refractive index, n is the ratio of speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in medium. n = Speed of light in vacuum Speed of light in medium = c v Where speed of light, c = 3.0 x 108 ms-1 No unit because it is ratio between two speeds Medium Refractive index Vacuum and air 1.00 Olive oil 1.46 Perspex 1.50 Crown glass 1.52
- 6. The speed of light in benzene is 2.0 x 108 ms-1. If the speed of light in vacuum is 3.0 x 108 ms-1, calculate the refractive index of benzene. Exercise n = 1.5
- 7. Snell’s law Law of Refraction There are two laws of refraction: 1) The incident ray, the refracted ray and normal meet at one point and are in the same plane 2) The value of sin 𝑖 sin 𝑟 is a constant, where i is the angle of incident while r is the angle of refraction. (Also known as Snell’s law) n1 sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2 When medium 1 is air ( n=1) and medium 2, n2 = n n = sin 𝑖 sin 𝑟 n = sin 𝑖 sin 𝑟 Derivation: https://youtu.be/4ccXzZt4ID8
- 8. 1. The figure below shows a light ray passing through a plastic block. The refractive index of the plastic block is 1.24. If the speed of light in vacuum is 3.0 x 108 ms-1 , find a) the speed of light in the plastic block b) the angle of refraction, r v = 2.42 x 108 ms-1 R = 34.8 2. The figures below show a ray of light travelling from air to glass at different angles of incidence. Calculate the refractive index of the glass. n = 1.46 n = 1.22
- 9. A light ray travels from optically less dense medium to an optically denser medium. Since θ1 > θ2 , i = θ1 r = θ2 Hence, n = sin 𝑖 sin 𝑟 = sin 𝜃1 sin 𝜃 A light ray travels from optically denser medium to an optically less dense medium. Since θ2 > θ1 , i = θ2 r = θ1 Hence, n = sin 𝑖 sin 𝑟 = sin 𝜃2 sin 𝜃1 Reversibility of light
- 10. Real depth AND Apparent depth Refraction of light gives us false impression of depth. Example of situation: 1) Water in a deep pool appears than it really is. 2) The image of the fish appear closer to the water surface n = 𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑒𝑝𝑡ℎ,𝐻 𝑎𝑝𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑑𝑒𝑝𝑎𝑡ℎ,ℎ
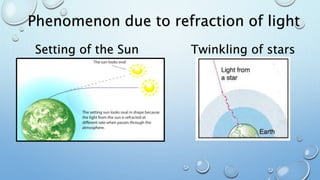
- 11. Phenomenon due to refraction of light Setting of the Sun Twinkling of stars
- 12. Exercise 1. Apparent depth of a coin in a glass of with water is 3.2 cm. If the refractive index of water is 1.33, calculate the actual depth of the coin. 2. In the figure below, a coin is placed at the bottom of a glass container of height 40 cm. The image of the coin is seen by an observer from the top of the container. If the refractive index of the glass block is 1.5, what is the height of x?