7. Recombinat DNa & Genomics 1.ppt
- 1. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genetic Engineering or Bioengineering • Genetic engineering refers to the purposeful manipulation of genetic material to alter the characteristics of an organism in a desired way. • There are five techniques of genetic engineering: genetic fusion, protoplast fusion, gene amplification, recombinant DNA technology, and the creation of hybridomas
- 2. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Application of GE
- 3. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 4. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Tools or basic elements of GE • The tools of genetic engineering include: specialized enzymes, e.g. RE gel electrophoresis, DNA sequencing machines, RNA primers and gene probes Recombinant DNA Technology and Genomics
- 5. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. What Can You Do with a Cloned Gene? Applications of Recombinant DNA Technology
- 6. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genomics and Bioinformatics: Hot New Areas of Biotechnology • Genomics – cloning, sequencing, and analyzing entire genomes – Shotgun sequencing or shotgun cloning • The entire genome is cloned and sequenced • Produces thousands of fragments to be sequenced • Individual genes are sorted out later through bioinformatics –Computer programs are used to align the sequenced fragments based on overlapping sequence pieces
- 7. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genomics and Bioinformatics: Hot New Areas of Biotechnology • Bioinformatics – An interdisciplinary field that applies computer science and information technology to promote an understanding of biological processes • Application of Bioinformatics – Databases to store, share, and obtain the maximum amount of information from protein and DNA sequences – GenBank
- 8. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. The Human Genome Project • Determining the human DNA sequence • Understanding the function of the human genetic code • Identifying all of the genes • Determining their functions • Understanding how and when genes are turned on and off throughout the lifetime of an individual Original idea was:
- 9. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. The Human Genome Project Project goals were to: Identify all the approximately 20,000-25,000 genes in human DNA, Determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA, Store this information in databases, Improve tools for data analysis, Transfer related technologies to the private sector, and Address the ethical, legal, and social issues (ELSI) that may arise from the project.
- 10. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genomics and Bioinformatics: Hot New Areas of Biotechnology • The Human Genome Project –April 14, 2003, map of the human genome was completed –Consists of 20,000 to 25,000 protein- coding genes
- 11. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. The Human Genome Project Completed in 2003, the Human Genome Project (HGP) was a 13-year project coordinated by the U.S. Department of Energy and the National Institutes of Health. During the early years of the HGP, the Wellcome Trust (U.K.) became a major partner; additional contributions came from Japan, France, Germany, China, and others.
- 12. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. APPLICATIONS One type of gene therapy procedure
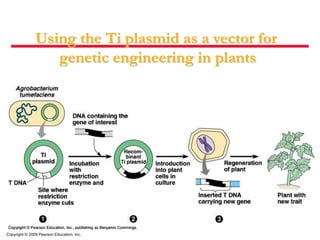
- 13. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Using the Ti plasmid as a vector for genetic engineering in plants
- 14. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Farming With Borrowed Genes
- 15. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. The Era of “omics” • The Human Genome Project – Started an “omics” revolution – The ability to obtain the entire genetic sequences of organisms has spawned(coined) new terms that refer to the “total picture” of some aspect of a cell or organism. • Proteomics • Metabolomics • Glycomics • Interatomics • Transcriptomics • Nutrigenomics
- 16. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. omics… genomics: The systematic study of an organism’s genes and their functions. Proteomics: The study of an organism’s complement of proteins (its “proteome”) and functions mediated by the proteins. metagenomics (also called “community genomics”) :The study of all the genomes in a particular ecological niche, as opposed to individual genomes from single species.
- 17. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. -’Omics’… • metabolomics : The study of the complete complement of small chemicals present in a cell at any given time. Provides a snapshot of the physiological state of the cell and the end products of its metabolism.
- 18. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 19. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Comparative Genomics – Mapping and sequencing genomes from a number of model organisms – Allows researchers to study gene structure and function in these organisms in ways designed to understand gene structure and function in other species including humans • Stone Age Genomics (paleogenomics) – Analyzing “ancient” DNA