Algorithms and computational complexity.ppt
- 1. 1 CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity
- 2. 2 Master Divide and Conquer Recurrence If T(n)=aT(n/b)+cnk for n>b then if a>bk then T(n) is if a<bk then T(n) is Q(nk) if a=bk then T(n) is Q(nk log n) Works even if it is n/b instead of n/b. ) ( log a b n Q
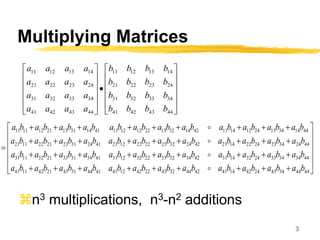
- 3. 3 Multiplying Matrices n3 multiplications, n3-n2 additions 44 43 42 41 34 33 32 31 24 23 22 21 14 13 12 11 44 43 42 41 34 33 32 31 24 23 22 21 14 13 12 11 b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a 44 44 34 43 24 42 14 41 42 44 32 43 22 42 12 41 41 44 31 43 21 42 11 41 44 34 34 33 24 32 14 31 42 34 32 33 22 32 12 31 41 34 31 33 21 32 11 31 44 24 34 23 24 22 14 21 42 24 32 23 22 22 12 21 41 24 31 23 21 22 11 21 44 14 34 13 24 12 14 11 42 14 32 13 22 12 12 11 41 14 31 13 21 12 11 11 b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a b a
- 7. 7 Multiplying Matrices T(n)=8T(n/2)+4(n/2)2=8T(n/2)+n2 8>22 so T(n) is A11 A12 A21 A11B12+A12B22 A22 A11B11+A12B21 B11 B12 B21 B22 A21B12+A22B22 A21B11+A22B21 = ) ( ) ( ) ( 3 log log n n n 8 a 2 b Q Q Q
- 8. 8 Strassen’s algorithm Strassen’s algorithm Multiply 2x2 matrices using 7 instead of 8 multiplications (and lots more than 4 additions) T(n)=7 T(n/2)+cn2 7>22 so T(n) is Q(n ) which is O(n2.81) Fastest algorithms theoretically use O(n2.376) time not practical but Strassen’s is practical provided calculations are exact and we stop recursion when matrix has size about 100 (maybe 10) log27
- 9. 9 The algorithm P1=A12(B11+B21) P2=A21(B12+B22) P3=(A11 - A12)B11 P4=(A22 - A21)B22 P5=(A22 - A12)(B21 - B22) P6=(A11 - A21)(B12 - B11) P7= (A21 - A12)(B11+B22) C11=P1+P3 C12=P2+P3+P6 - P7 C21= P1+P4+P5+P7 C22=P2+P4
- 10. 10 Proving Master recurrence T(n)=aT(n/b)+cnk a n Problem size n/b n/b2 b 1 # probs a2 a 1 ad T(1)=c
- 11. 11 Proving Master recurrence T(n)=aT(n/b)+cnk a n Problem size n/b n/b2 b 1 # probs a2 a 1 ad T(1)=c
- 12. 12 Proving Master recurrence T(n)=aT(n/b)+cnk a n Problem size n/b n/b2 b 1 # probs a2 a 1 ad cost cnk T(1)=c cank/bk ca2nk/b2k =cnk(a/bk)2 cnk(a/bk)d =cad
- 13. 13 Total Cost Geometric series ratio a/bk d+1=logbn +1 terms first term cnk, last term cad If a/bk=1, all terms are equal T(n) is Q(nk log n) If a/bk<1, first term is largest T(n) is Q(nk) If a/bk>1, last term is largest T(n) is Q(ad)=Q(a ) =Q(n ) (To see this take logb of both sides) logbn logba
- 14. 14 Quicksort Quicksort(X,left,right) if left < right split=Partition(X,left,right) Quicksort(X,left,split-1) Quicksort(X,split+1,right)
- 15. 15 Partition - two finger algorithm Partition(X,left,right) choose a random element to be a pivot and pull it out of the array, say at left end maintain two fingers starting at each end of the array slide them towards each other until you get a pair of elements where right finger has a smaller element and left finger has a bigger one (when compared to pivot) swap them and repeat until fingers meet put the pivot element where they meet
- 16. 16 Partition - two finger algorithm Partition(X,left,right) swap X[left],X[random(left,right)] pivot X[left]; L left; R right while L<R do while (X[L] pivot & L right) do L L+1 while (X[R] > pivot & R left) do R R-1 if L>R then swap X[L],X[R] swap X[left],X[R] return R
- 17. 17 In practice often choose pivot in fixed way as middle element for small arrays median of 1st, middle, and last for larger arrays median of 3 medians of 3 (9 elements in all) for largest arrays four finger algorithm is better also maintain two groups at each end of elements equal to the pivot • swap them all into middle at the end of Partition equal elements are bad cases for two fingers
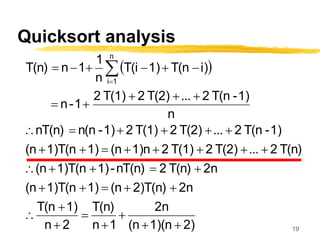
- 18. 18 Quicksort Analysis Partition does n-1 comparisons on a list of length n pivot is compared to each other element If pivot is ith largest then two subproblems are of size i-1 and n-i Pivot is equally likely to be any one of 1st through nth largest n 1 i i) T(n 1) T(i n 1 1 n T(n)














![16
Partition - two finger algorithm
Partition(X,left,right)
swap X[left],X[random(left,right)]
pivot X[left]; L left; R right
while L<R do
while (X[L] pivot & L right) do
L L+1
while (X[R] > pivot & R left) do
R R-1
if L>R then swap X[L],X[R]
swap X[left],X[R]
return R](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-240723184949-a3a5a923/85/Algorithms-and-computational-complexity-ppt-16-320.jpg)