Anaesthesia machine
- 1. DR TULSI RAM SHRESTHA, KMCTH
- 2. CONTENTS ▪ History ▪ Introduction ▪ Essential safety features ▪ Pneumatic system ▪ High pressure system ▪ Intermediate pressure system ▪ Low pressure system ▪ Anaesthesia machine checkup
- 3. HISTORY ▪ 1846: Public demonstration of ether anaesthesia, WTG Morton ▪ 1917: Boyle’s machine, Henry Edmund Gaskin Boyle ▪ 1921: Waters to and fro absorption apparatus ▪ 1927: Flowmeter for CO2
- 4. ▪ 1930: Plunger of vaporizer; circle absorption system, Brian Sword ▪ 1933: Dry bobbin flow meters ▪ 1952: PISS by Woodbridge
- 5. THE ANAESTHESIA MACHINE ▪ Receives medical gases from a gas supply ▪ Controls the flow and reduces the pressure of gases to a safe level ▪ Vaporizes volatile anesthetics into final gas mixture ▪ Delivers gases to a breathing circuit connected to the patient’s airway
- 6. 1. Gas-specific connections to pipeline inlets (DISS) with pressure gauges, filter, and check valve 2. PISS for cylinders with pressure gauges, and at least one oxygen cylinder 3. Low oxygen pressure alarm 4. Minimum O2:N2O ratio controller device 5. Oxygen failure safety device ESSENTIAL SAFETY FEATURES
- 7. 6. O2 enters common manifold downstream to other gases 7. O2 concentration monitor and alarm 8. Automatically enabled essential alarms and monitors (eg, oxygen concentration) 9. Vaporizer interlock device 10.Capnography and anesthetic gas measurement 11.O2 flush mechanism
- 8. 12.Breathing circuit pressure monitor and alarm 13.Exhaled volume monitor 14.Pulse oximetry, BP, ECG monitoring 15.Mechanical ventilator 16.Backup battery 17.Scavenger system
- 10. HIGH PRESSURE SYSTEM ▪ Receives gases from high pressure E cylinders ▪ 2000 psig for O2 and air, 745 psig for N2O ▪ Handy in case of failure of hospital pipeline supply source
- 11. Hanger Yoke ▪ Orients and supports the cylinder ▪ Provides gas tight seal ▪ Ensures unidirectional gas flow ▪ Parts ▪ Body ▪ Retaining screw ▪ PISS pins ▪ Washer ▪ Filter
- 12. Pressure regulator ▪ Reduces high/ variable pressure from cylinder ▪ To lower/ constant pressure for use in anesthesia machine (40-45psig) ▪ Pressure at regulator outlet: set lower than pipeline pressure
- 13. Check valve ▪ Allows gas from cylinder to enter machine ▪ Minimizes transfer of gas from a cylinder at high pressure to one with lower pressure ▪ Helps exchange of empty cylinder with a full one ▪ Minimizes leakage from an open cylinder to the atmosphere if one cylinder is absent
- 14. INTERMEDIATE PRESSURE SYSTEM ▪ Receives gases from pressure regulator or pipeline inlet ▪ Pressure of 40-55 psig
- 15. Pipeline inlet connections ▪ For air, O2, N2O ▪ Fitted with threaded non interchangeable DISS connectors ▪ Contains filter, unidirectional check valve
- 16. Pipeline pressure gauges ▪ To monitor pipeline pressure ▪ Color coded ▪ 50-55 psig
- 17. Pneumatic safety systems O2 failure protection device ▪ When O2 pressure is normal->push the diaphragm and stem downward →opening valve ▪ When O2 pressure falls→Fail-safe valves shut off or proportionally decrease the flow of the other breathing gases ▪ If a gas other than O2 adequately pressurizes the O2 circuit as a result of hospital pipeline contamination, fail-safe valves will remain open. In such a case, only the inspired oxygen concentration monitor will help
- 18. O2 supply failure alarm ▪ Sensor with an audible and visual warning if O2 pressure drops below a minimum ▪ Cannot be silenced until the pressure is restored to the minimum value ▪ Dräger Fabius series machines are set to alarm at 20 psig
- 19. Oxygen flush valve ▪ Provides manual delivery of a high flow rate of 100% O2 ▪ High (35 to 75 L/m) flow directly to CGO ▪ Flow bypasses the anesthetic vaporizers ▪ Available even when machine is not turned on ▪ Pressure: 50 psig
- 20. Auxiliary O2 flowmeter ▪ Administer O2 in case of electric failure ▪ Allows the use of low-flow oxygen for devices independent of the patient’s breathing circuit ▪ Accessible even when the machine is not turned on
- 21. Second stage pressure regulator ▪ Located downstream from the gas supply sources ▪ Constant pressure to the flow control valves regardless of potential fluctuations in hospital pipeline pressures ▪ Lower levels than the pipeline supply, usually between 14 and 35 psig
- 22. LOW PRESSURE SYSTEM ▪ Begins at flow control valves and ends at machine outlet ▪ Flow control valves, flowmeters or flow sensors, vaporizer manifold, and anesthetic vaporizers ▪ Most vulnerable section to leaks within the gas supply system
- 23. Flow adjustment control ▪ Regulates flow of gases to flowmeter ▪ Clockwise: decrease gas flow ▪ Anticlock wise: increase gas flow ▪ Inlet pressure is determined by pressure characteristics of intermediate-pressure segment ▪ Flow control knob ▪ Different texture, diameter, color coded, name of gas engraved ▪ O2: fluted, larger
- 24. Flowmeter ▪ Variable orifice vertical glass tube with indicator (Thorpe’s tube) ▪ Upward force resulting from gas flow equals the downward force on the float resulting from gravity at a given flow rate ▪ Height of indicator: measure of gas flow ▪ Widest diameter : flow to be read
- 26. ▪ Flow rate depend on ▪ Pressure drop across the constriction ▪ Size of annular opening ▪ Physical properties of gas ▪ Calibrated at atmospheric pressure, room temperature
- 27. Flow indicator sequence ▪ Where O2 and other gases are delivered by their respective flow indicators into a common manifold, the O2 should be delivered downstream of all other gases. ▪ In the event of a flowmeter leak, a potentially dangerous arrangement exists when N2O located in downstream position (A and B). ▪ A safer configuration exists when O2 located in downstream position (C & D). ▪ Hypoxic mixture less likely because all O2 flow is advanced by N2O (the principle known as the Eger flow sequence)
- 28. Proportioning system ▪ No matter how high N2O is turned up, or how low the O2 flow is made when N2O is running ▪ The machine will automatically limit the amount of N2O flow→ hypoxemic gas will not be delivered ▪ Protects against delivery of a mixture with an oxygen concentration below 21% oxygen (v/v%)
- 29. Outlet check valve ▪ One way check valve located between vaporizer and CGO ▪ Prevent backflow into the vaporizer during positive-pressure ventilation
- 30. Common Gas Outlet ▪ Receives gas mixture from machine and delivers to breathing circuit ▪ Fresh gas outlet, critical role in adding new gas of fixed and known composition to the circle system
- 31. Oxygen (inspired) analyzers ▪ Polarographic (Clark electrode) ▪ Galvanic (fuel cell) ▪ Paramagnetic
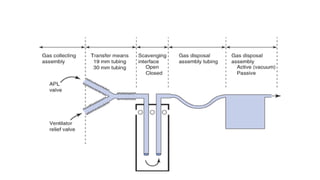
- 32. Waste gas scavengers ▪ Dispose gases that have been vented from breathing circuit by APL valve ▪ Safe level ▪ Room concentration of N2O:25ppm ▪ Halogenated agents:2ppm
- 35. High pressure system ▪ Check O2 cylinder supply ▪ Open cylinder, verify at least half full (1000 psig) ▪ Close cylinder ▪ Check central pipeline supplies ▪ Check hoses are connected ▪ Pipeline gauge: 50psig
- 36. Low pressure system ▪ Close flow control valves, turn off vaporizers ▪ Check fill level, tighten filler caps ▪ Perform leak check ▪ Test flowmeters
- 37. Breathing system ▪ Calibrate O2 monitor ▪ Check initial status breathing system ▪ Leak check ▪ Set all gas flows to zero ▪ Close APL valve , occlude Y piece ▪ Pressurize to about 30cm of H2O ▪ Ensure pressure remains fixed (at least 10 second) ▪ Open APL valve: pressure decrease
- 38. ▪Miller's Anaesthesia, 8th edn ▪Morgan and Mikhail’s Clinical Anesthesiology, 5th edn References