Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques
- 1. Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques Claire Little, Bruce Edmonds Centre for Policy Modelling Manchester Metropolitan University Ed Fieldhouse, Laurence Lessard-Phillips Institute for Social Change University of Manchester
- 2. An “Inconvenient Truth” • That the universe is not arranged for our benefit (as researchers studying it) • in other words, that assumptions such as the following are likely to be wrong: – Our planet is the centre of the universe – Risky events follow a normal distribution – Humans act as if they followed a simple algorithm – Society can be understood using simple, universal prinicples – etc. etc. • In particular, the assumption that there will always (if you look hard enough) be models that are: – (a) simple enough for us to understand and – (b) adequate to what we want to model • …is wrong Complexity and Context-Dependency, Bruce Edmonds, ECCS, Lisbon, Sept 2010. slide-2
- 3. The Alternative • Thus consider the alternative, more realistic, situation where one is facing some phenomena where any model that is adequate (w.r.t. our goals) will be too complex for us to completely understand • Instead of indulging in wishful thinking this paper looks at ways forward under complexity • In other words, if we have a simulation model that is too complex to completely understand, how can we obtain some useful understanding of its properties… • …and hence use it to leverage some understanding/control over the target phenomena Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 3
- 4. The Broad Idea 1. Make relatively complex simulations based on available evidence (a “KIDS” approach) 2. Analyse this simulation in a number of ways, including… 3. Data mining output data in a more holistic manner over a broad “space” of settings 4. Look for patterns in the data that suggest (maybe context-dependent) hypotheses 5. These are candidates for simpler (but maybe partial) models of the simulation Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 4
- 5. The Model • To explore the complex mix of factors, structures and processes that affect whether people vote • An agent-based model, with demographics and dynamic social networks • Was formulated using a mixture of qualitative, survey data and others’ expert opinion/results Class Age Activities Ethnicity Etc. Level-of-Political-Interest A Household Discuss-politics-with person-23 blue expert=false neighbour-network year=10 month=3 Lots-family-discussions year=10 month=2 Etc. Memory An Agent’s Memory of Events Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 5
- 6. Overall Structure of Model Underlying data about population composition Demographics of people in households Social network formation and maintenance (homophily) Influence via social networks • Political discussions Voting Behaviour Input Output
- 7. Technique • Instead of initiating ‘thin’ analyses of the simulation behaviour (e.g. 1 or 2D parameter sweeps/correlation models against a few key output measures) • To sample a multi-dimensional space of settings and cluster on a multi-dimensional space of output indicators (in this case 9 parameter x 13 output measures) • Look at the patterns between clusters for indications as to hypotheses of behaviour • Then test these with targeted simulation experiments Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 7
- 8. More Holistic but Less Detailed 1. Many Runs, Randomly Sampling Parameter Values Multi-Dimensional Space of Parameter Settings 2. Analyse data set of result measures using data mining 3. Look for patterns that you might then check in a more systematic manner Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 8
- 9. Parameter ranges 3862 independent runs with parameters sampled from the following, uniform distributions: • density: [0.65, 0.95] • drop-activity-prob: [0.05, 0.15] • drop-friend-prob: [0, 0.01] • emmigration-rate: [0 ,0.03] • immigration-rate: [0, 0.02] • int-immigration-rate: [0, 0.02] • majority-prop: [0.55, 1] • prob-move-near: [0, 1] • prob-partner: [0.01, 0.03] Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 9
- 10. For each of these runs… • Measure many different indicators of the outputs (say at the end of the simulation) including: – Pop.size – population size – Av.age – average age – Av.adfriends – average number of friends (adults only) – Prop.maj – proportion of the majority population – Prop.adult – proportion that is adult – Prop.1stgen – proportion that are 1st generation immigrant – av.clust – average proportion of friends who are friends – av.sim.hh – average similarity within households – av.sim.fr – average similarity between friends – ncvs.ac – number of conversations over activity links – ncvs.sc – number of conversations over “school” links – Prop. Adults with highest level of political interest Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 10
- 11. Dendrogram of hierarchical clustering of simulations Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 11
- 12. A heatmap of the hierarchical clustering Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 12
- 13. The within group sum of squares against the number of clusters for 10 randomly initialised runs using k-means Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 13
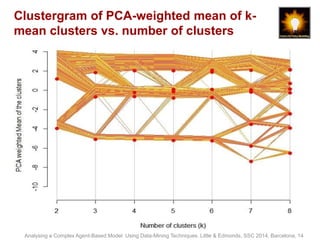
- 14. Clustergram of PCA-weighted mean of k-mean clusters vs. number of clusters Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 14
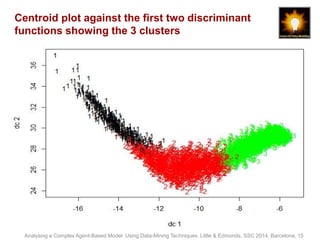
- 15. Centroid plot against the first two discriminant functions showing the 3 clusters Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 15
- 16. Details of the centroids of the 3 k-means clusters Attribute Cluster 1 (543 records) Cluster 2 (1333 records) Cluster 3 ( 1986 records) Pop.size 100 557 1750 Av.age 76 58 55 Av.adfriends 0.73 1.36 1.82 Prop.maj 74% 67% 65% Prop.adult 99% 94% 93.5% Prop.1stgen 8% 13% 14% av.clust 0.97 0.84 0.70 av.sim.hh 2.45 3.53 3.74 av.sim.fr 2.82 3.70 3.33 Rate ncvs.ac 1.3% 1.3% 0.0% Rate ncvs.sc 0.45% 0.20% 0.13% Prop. Adults 0.97% 1.6% 1.7% involved Within cluster sum of squares 6748.243 11288.460 7407.591 Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 16
- 17. the 3 clusters against the parameters: emigration rate, immigration rate, internal immigration rate Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 17
- 18. Pop Size Av. Age Multi-Dimensional Scatter Graphs Av Sim Hh Av Sim Fr Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 18
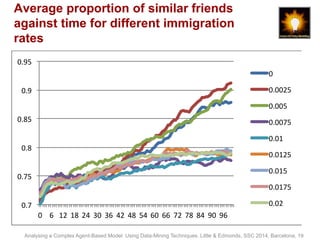
- 19. Average proportion of similar friends against time for different immigration rates 0.95 0.9 0.85 0.8 0.75 0.7 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54 60 66 72 78 84 90 96 0 0.0025 0.005 0.0075 0.01 0.0125 0.015 0.0175 0.02 Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 19
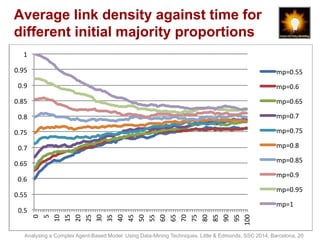
- 20. Average link density against time for different initial majority proportions 1 0.95 0.9 0.85 0.8 0.75 0.7 0.65 0.6 0.55 0.5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 mp=0.55 mp=0.6 mp=0.65 mp=0.7 mp=0.75 mp=0.8 mp=0.85 mp=0.9 mp=0.95 mp=1 Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 20
- 21. Conclusions • The particular results and insights in this model are not as important as the overall approach which… • …tries to get a more complex and holistic idea of the properties of a complex model • …which then might suggest simple hypotheses/models • …and thus “stage” abstraction a bit more gradually and carefully, being more aware of what is being abstracted away Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 21
- 22. Postscript: Emerging Principles • That evidence should not be ignored without a very, VERY good reason • That abstraction should be staged in gradual steps rather than “heroic” leaps • Be clear and explicit about your goals • Separate exploratory from analytic stages • Recognise that it is easy to fool ourselves and impose (wrong or limited) assumptions • Utilise any and all techniques that are applicable, but recognising their limitations Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 22
- 23. The End Claire Little: http:// Bruce Edmonds: http://bruce.edmonds.name Centre for Policy Modelling: http://cfpm.org Ed Fieldhouse: http:// Laurence Lessard-Phillips: http:// Institute for Social Change: http:// The SCID Project: http://www.scid-project.org These slides will be at: http://slideshare.com/BruceEdmonds The simulation will ‘soon’ be at: http://openabm.org as “The Voter Model”









![Parameter ranges
3862 independent runs with parameters sampled
from the following, uniform distributions:
• density: [0.65, 0.95]
• drop-activity-prob: [0.05, 0.15]
• drop-friend-prob: [0, 0.01]
• emmigration-rate: [0 ,0.03]
• immigration-rate: [0, 0.02]
• int-immigration-rate: [0, 0.02]
• majority-prop: [0.55, 1]
• prob-move-near: [0, 1]
• prob-partner: [0.01, 0.03]
Analysing a Complex Agent-Based Model Using Data-Mining Techniques. Little & Edmonds, SSC 2014, Barcelona, 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analysingacomplexagent-basedmodel-v2-140908050302-phpapp02/85/Analysing-a-Complex-Agent-Based-Model-Using-Data-Mining-Techniques-9-320.jpg)