Analytical Method of Wood Component presentation
- 1. By Audrey Zahra Analytical Method
- 6. The amount of the various wood components, viz cellulose, hemicelluloses, lignin, extractives and inorganics can vary widely depending on wood species. In addition, structural differences exist between the various types of wood tissue as well as between the individual cell wall layers. Irrespective of morphological differences, the gross composition of wood (or pulp) can Be determined by first applying a homogenization of the material, followed by solvent extraction to remove low molecular weight organics. Introduction Acid hydrolysis of the residue results in a precipitate consisting of highly condensed lignin (Klason lignin) and a solution of monomeric sugars. The latter are separated (by GC, HPLC or CE analysis) and quantified whereas the Klason lignin is determined gravimetrically. For the analysis of inorganics, present in the wood as carbonates, phosphates etc, combustion of the wood sample and gravimetric determination of the ash can be used. The individual components of the ash can be further analysed using e.g. inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS).
- 9. Periodate oxidation Wet chemical analyses of carbohydrates and polysaccharides were developed a long time ago and are still in use frequently although NMR methods can also be used. For the general detection of carbohydrate structures, an oxidation of the sample with periodate is convenient since periodate reacts with vicinal dihydroxy compounds. In the reaction, each hydroxyl group is converted to an aldehyde or, for glycerol structures, an additional formation of formic acid
- 10. The separation of the individual polysaccharides present in wood and other lignocellulosic material is not trivial due to the complex arrangement of polymers making up the cell wall with lignin acting as an incrusting material. The necessary increase in accessibility of the polysaccharides can be obtained by a selective oxidative degradation of the lignin with sodium chlorite under mild acid conditions
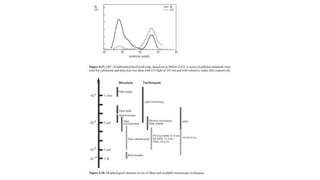
- 11. The further separation of the individual polysaccharide components present in wood can be done with holocellulose as the starting material. In the complicated separation scheme (Figure 9.4), strong alkali is used to dissolve the predominant portion of the xylan and galactoglucomannan leaving cellulose and glucomannan as a residue. The fact that sugar units like mannose having vicinal hydroxyl groups in a cis-configuration can form soluble borate complexes and insoluble barium salts (Figure9.5) can be used to further separate the individual hemicelluloses.
- 13. The composition, structure and morphology of the polysaccharides present in wood and pulps are of great importance since these to a major extent determine the properties of the resulting fibers. A simple quantification of the monomeric sugar units present in a wood or pulp sample can be done as outlined in Figure 9.1. After the acid hydrolysis, the mixture of sugars can be reduced with sodium borohydride to convert all reducing end-groups to the corresponding alcohol groups. Thereby, only one product from each pair of anomeric sugar units is obtained. After a subsequent acetylation, the mixture is analysed by gas chromatography (Figure 9.6). Other separation techniques are also frequently used such as HPLC or CE (capillary electrophoresis) With or without derivatization. Sugar compotition
- 14. An alternative method for the analysis of monomeric sugar units is based on acid hydrolysis in methanol (methanolysis). The reaction results in a conversion of the polysaccharides to the corresponding methylglucosides with a major advantage being a Much better preservation of the uronic acid groups. In the reaction, the latter are esterified and this promotes a more complete hydrolysis of otherwise resistant glucosidic linkages such as those between xylose and 4-Omethyl-glucuronic acid in xylans.
- 16. For the isolation of lignin from kraft pulp, methods based on acid and/or enzymatic hydrolysis of carbohydrate-carbohydrate and lignin-carbohydrate linkages are frequently employed whereas lignin from alkaline pulping liquors can be isolated by precipitation with acid.
- 17. The characteristic feature of a lignin (or lignan) is the presence of aromatic methoxyl groups. Except for the p-hydroxyphenyl units constituting part of compression wood and grass lignins, virtually all aromatic units contain at least one methoxyl group. This can be analysed By reacting the sample with hydriodic acid followed by gas chromatographic analysis of the methyl iodide that is formed
- 18. For the direct chemical analysis of isolated lignin or of lignin present in wood or pulps, degradation methods employing oxidation with potassium permanganate – hydrogen peroxide or ozone can be used. Among other methods, acid hydrolysis in the presence of ethanethiol, thioacidolysis, is the most important. The first of these reactions is outlined in Figure 9.12. In a four-step procedure, the lignin-containing sample is first alkylated to protect the phenolic hydroxyl groups. Oxidation in two steps with potassium permanganate and hydrogen peroxide converts all side-chains to aromatic carboxyl groups and these are finally esterified to provide derivatives suitable for gas chromatographic analysis.
- 32. Thank you