Android Architecture design programming with java
- 1. Android Architecture • Android architecture contains different number of components to support any android device needs. • Android software contains an open-source Linux Kernel having collection of number of C/C++ libraries which are exposed through an application framework services. • Among all the components Linux Kernel provides main functionality of operating system functions to smartphones and Dalvik Virtual Machine (DVM) provide platform for running an android application. • The main components of android architecture are following:-Applications • Application Framework • Android Runtime • Platform Libraries • Linux Kernel
- 3. Applications • Applications is the top layer of android architecture. • The pre-installed applications like home, contacts, camera, gallery etc and third party applications downloaded from the play store like chat applications, games etc. will be installed on this layer only. • It runs within the Android run time with the help of the classes and services provided by the application framework.
- 4. Application framework • Application Framework provides several important classes which are used to create an Android application. • It provides a generic abstraction for hardware access and also helps in managing the user interface with application resources. • Generally, it provides the services with the help of which we can create a particular class and make that class helpful for the Applications creation. • It includes different types of services activity manager, notification manager, view system, package manager etc. which are helpful for the development of our application according to the prerequisite.
- 5. Application runtime • Android Runtime environment is one of the most important part of Android. It contains components like core libraries and the Dalvik virtual machine(DVM). • Mainly, it provides the base for the application framework and powers our application with the help of the core libraries. Like Java Virtual Machine (JVM), Dalvik Virtual Machine (DVM) is a register-based virtual machine and specially designed and optimized for android to ensure that a device can run multiple instances efficiently. • It depends on the layer Linux kernel for threading and low-level memory management. The core libraries enable us to implement android applications using the standard JAVA or Kotlin programming languages.
- 6. Platform libraries • The Platform Libraries includes various C/C++ core libraries and Java based libraries such as Media, Graphics, Surface Manager, OpenGL etc. to provide a support for android development.Media library provides support to play and record an audio and video formats. • Surface manager responsible for managing access to the display subsystem. • SGL and OpenGL both cross-language, cross-platform application program interface (API) are used for 2D and 3D computer graphics. • SQLite provides database support and FreeType provides font support. • Web-Kit This open source web browser engine provides all the functionality to display web content and to simplify page loading. • SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is security technology to establish an encrypted link between a web server and a web browser.
- 7. Linux Kernel • Linux Kernel is heart of the android architecture. It manages all the available drivers such as display drivers, camera drivers, Bluetooth drivers, audio drivers, memory drivers, etc. which are required during the runtime. The Linux Kernel will provide an abstraction layer between the device hardware and the other components of android architecture. It is responsible for management of memory, power, devices etc. The features of Linux kernel are:Security: The Linux kernel handles the security between the application and the system. • Memory Management: It efficiently handles the memory management thereby providing the freedom to develop our apps. • Process Management: It manages the process well, allocates resources to processes whenever they need them. • Network Stack: It effectively handles the network communication. • Driver Model: It ensures that the application works properly on the device and hardware manufacturers responsible for building their drivers into the Linux build.
- 8. Dalvik Virtual Machine | DVM • As we know the modern JVM is high performance and provides excellent memory management. But it needs to be optimized for low- powered handheld devices as well. • The Dalvik Virtual Machine (DVM) is an android virtual machine optimized for mobile devices. It optimizes the virtual machine for memory, battery life and performance. • Dalvik is a name of a town in Iceland. The Dalvik VM was written by Dan Bornstein. • The Dex compiler converts the class files into the .dex file that run on the Dalvik VM. Multiple class files are converted into one dex file.
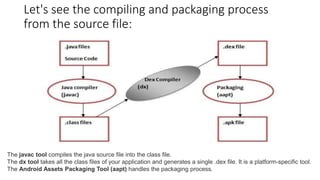
- 9. Let's see the compiling and packaging process from the source file: The javac tool compiles the java source file into the class file. The dx tool takes all the class files of your application and generates a single .dex file. It is a platform-specific tool. The Android Assets Packaging Tool (aapt) handles the packaging process.
- 10. What is DVM(Dalvik Virtual Machine) • Dalvik Virtual Machine is a Register-Based virtual machine. It was designed and written by Dan Bornstein with contributions of other Google engineers as part of the Android mobile phone platform. • The Dalvik virtual machine was named after Bornstein after the fishing village “Dalvík” in Eyjafjörður, Iceland, where some of his ancestors used to live.
- 11. Working of DVM • The Java Compiler(javac) converts the Java Source Code into Java Byte-Code(.class). Then DEX Compiler converts this (.class) file into in Dalvik Byte Code i.e. “.dex” file.
- 12. Application • For Android, a new Virtual machine was developed by Google as stated above. It uses registers of the CPU to store the operands. So no requirement of any pushing and popping of instructions. Hence making execution faster. The instructions operate on virtual registers, being those virtual registers memory positions in the host device. Register-based models are good at optimizing and running on low memory. They can store common sub- expression results which can be used again in the future. This is not possible in a Stack-based model at all. Dalvik Virtual Machine uses its own byte-code and runs “.dex”(Dalvik Executable File) file. Advantages • DVM supports the Android operating system only. • In DVM executable is APK. • Execution is faster. • From Android 2.2 SDK Dalvik has it’s own JIT (Just In Time) compiler. • DVM has been designed so that a device can run multiple instances of the Virtual Machine effectively. • Applications are given their own instances. • Disadvantages • DVM supports only Android Operating System. • For DVM very few Re-Tools are available. • Requires more instructions than register machines to implement the same high-level code. • App Installation takes more time due to dex. • More internal storage is required.
- 13. Step 1: Create a new project • Open Android Studio. • In the Welcome to Android Studio dialog, click Start a new Android Studio project. • Select Basic Activity (not the default). ... • Give your application a name such as My First App. • Make sure the Language is set to Java. • Leave the defaults for the other fields. • Click Finish.
- 14. Android App / Project Folder Structure • To implement android apps, Android Studio is the official IDE (Integrated Development Environment) which is freely provided by Google for android app development. • Once we setup android development environment using android studio and if we create a sample application using android studio, our project folder structure will be like as shown below. In case if you are not aware of creating an application using an android studio please check this Android Hello World App.
- 15. Java Folder • This folder will contain all the java source code (.java) files which we’ll create during the application development, including JUnit test code. Whenever we create any new project/application, by default the class file MainActivity.java will create automatically under the package name “com.tutlane.helloworld” like as shown below.
- 16. res (Resources) Folder • It’s an important folder that will contain all non-code resources, such as bitmap images, UI strings, XML layouts like as shown below.
- 17. Drawable Folder (res/drawable) •It will contain the different types of images as per the requirement of application. It’s a best practice to add all the images in a drawable folder other than app/launcher icons for the application development.
- 18. Android Features Android is a powerful open-source operating system which provides a lot of great features, those are • It’s open-source and we can customize the OS based on our requirements. • It supports connectivity for GSM, CDMA, WIFI, NFC, Bluetooth, etc. for telephony or data transfer. It will allow us to make or receive a calls / SMS messages and we can send or retrieve data across mobile networks • By using WIFI technology we can pair with other devices using apps • Android has multiple APIs to support location-based services such as GPS • We can perform all data storage related activities by using lightweight database SQLite. • It has a wide range of media supports like AVI, MKV, FLV, MPEG4, etc. to play or record a variety of audio/video and having a different image format like JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, MP3, etc. • It has extensive support for multimedia hardware control to perform playback or recording using camera and microphone • It has an integrated open-source WebKit layout based web browser to support HTML5, CSS3 • It supports a multi-tasking, we can move from one task window to another and multiple applications can run simultaneously • It will give a chance to reuse the application components and the replacement of native applications. • We can access the hardware components like Camera, GPS, and Accelerometer • It has support for 2D/3D Graphics
- 19. Android Development Environment Setup Generally to build applications for Android we should have Java Development Kit (JDK), Android SDK, and a development environment. • The Android SDK is compatible with Windows, Mac, and Linux operating systems to build android applications based on our requirements. • We can set up an Android development environment using the following two ways • Setup Eclipse IDE Manually (Depreciated) • Android Studio Initially, Google supported a Manual Eclipse IDE Setup for android development environment by downloading required components like Eclipse IDE, Android SDK, Java Development Kit (JDK), etc. from official site. Afterward, Google introduced a component called Android Studio to make the environment setup process simple. • By using the Android Studio bundle we can easily set up android development environment in any operating system to implement android applications. • Android Studio is a combination of the following components to allow users to implement android applications. • Eclipse IDE • Android SDK • Android Virtual Device • Eclipse Plugin • By downloading Android Studio directly from the Google website to set up we can easily set up development environment. • Check the following article to know more details about setting up the android development environment to implement required apps using Android Studio.
- 20. The Android project Folder structure • The Android project folder structure is a standardized format that the Android Studio uses to organize the application source code and resources. The folder structure consists of the following main components: • app – This folder contains the main source code and resources for your Android application. It includes Java source files, XML layout files, images, and other resources needed for the application. • gradle – This folder contains the Gradle build files that configure the build process for the project. Gradle is the build system used by Android Studio to compile and package the application. • build – This folder contains the output files generated by the build process. It includes the compiled Java code, resources, and the APK file that is installed on the Android device. • manifests – This folder contains the AndroidManifest.xml file, which is the configuration file for the Android application. It includes information about the application, such as its name, version number, and the activities it contains. • res – This folder contains the resources used by the Android application, such as images, layout files, and strings. It is further divided into subfolders based on resource type. • libs – This folder contains any third-party libraries or JAR files used by the application. • tests – This folder contains the source code and resources for the unit tests used to test the application. • assets – This folder contains any additional files needed by the application, such as database files, sound files, or video files. • app.iml – This file contains the configuration settings for the Android Studio project. The Android project folder structure is designed to be flexible and customizable, allowing developers to organize their application code and resources in a way that makes sense for their specific project.
- 21. Android Manifest file • Every app project must have an AndroidManifest.xml file, with precisely that name, at the root of the project source set. The manifest file describes essential information about your app to the Android build tools, the Android operating system, and Google Play. • Among many other things, the manifest file is required to declare the following: • The components of the app, including all activities, services, broadcast receivers, and content providers. Each component must define basic properties, such as the name of its Kotlin or Java class. • It can also declare capabilities, such as which device configurations it can handle, and intent filters that describe how the component can be started. Read more about app components in a following section. •The permissions that the app needs in order to access protected parts of the system or other apps. It also declares any permissions that other apps must have if they want to access content from this app. Read more about permissions in a following section. •The hardware and software features the app requires, which affects which devices can install the app from Google Play. Read more about device compatibility in a following section. If you're using Android Studio to build your app, the manifest file is created for you and most of the essential manifest elements are added as you build your app, especially when using code templates.
- 22. App components For each app component that you create in your app, declare a corresponding XML element in the manifest file: •<activity> for each subclass of Activity •<service> for each subclass of Service •<receiver> for each subclass of BroadcastReceiver •<provider> for each subclass of ContentProvider If you subclass any of these components without declaring it in the manifest file, the system can't start it.
- 23. Fundamentals of testing Android apps Benefits of testing • Testing is an integral part of the app development process. By running tests against your app consistently, you can verify your app's correctness, functional behavior, and usability before you release it publicly. • You can manually test your app by navigating through it. You might use different devices and emulators, change the system language, and try to generate every user error or traverse every user flow. • However, manual testing scales poorly, and it can be easy to overlook regressions in your app's behavior. Automated testing involves using tools that perform tests for you, which is faster, more repeatable, and generally gives you more actionable feedback about your app earlier in the development process.
- 24. Developer workflow basics • The workflow to develop an app for Android is conceptually the same as for other app platforms. However, to efficiently build a well- designed app for Android, you need some specialized tools. • This page provides an overview of the process to build an Android app and includes links to more information about Android Studio tools for each phase of development.