Aortic aneurysm dr jeevraj
- 3. Aortic aneurysm • Aortic aneurysm is a localized or diffuse dilation of an aorta with a diameter at least 50% greater than the normal size of the aorta • Aneurysm is the second most frequent disease of the aorta after atherosclerosis • The strongest predictor of AAA formation is positive family history • Smoking is the most important modifiable risk factor in the formation, progression, and rupture risk of AAA • The male to female ratio is approximately 2:1, although women have a higher incidence of aneurysm rupture. • mean age for diagnosis in sixth decade of life
- 4. Type • Abdominal Aortic aneurysm • Thoracic aneurysms • Thoraco-Abdominal Aortic aneurysm • • 45% of thoracic aneurysms involved the ascending aorta, 10% the arch, 35% the descending aorta, and 10% the thoracoabdominal aorta
- 5. Classification by shape Fusiform aneurysms are more common, associated with atherosclerotic or collagen vascular disease, and usually affect a longer segment of the aorta, producing a dilation of the entire circumference of the vessel wall. Saccular aneurysms are more localized, confined to an isolated segment of the aorta, and produce a localized outpouching of the vessel wall Aortic arch aneurysms are commonly saccular Fusiform aneurysms have a higher operative mortality than saccular aneurysms
- 6. ETIOLOGY atherosclerosis, cystic medial necrosis, syphilitic aortitis Marfan’s Type IV Ehlers-Danlos Infection (syphillis) Arteritis (giant cell, Takayasu, Behcet’s)
- 7. Risk Factors – Smoking – COPD – HTN – Male gender – Older age – High BMI – Abnormal aortic valve (e.g., bicuspid valve) – Family history
- 8. pathophysiology • The number of collagen and elastic fibres is reduced within the aneurysmal segment of the aorta vascular wall strength is further compromised by several factors (i) local elastin resorption caused by increased elastase activity; (ii) localized wall inflammatory changes; (iii) increased protease activity; (iv) mural thrombus formation in the arterial wall and plasminogen activation
- 10. Ruptured AAA Die outside Hospital Die In Hospital Survive with major complications Survive with minor or no complication • Triad of Abd. or back pain Hypotension Pulsatile Abd. mass
- 11. Aortic growth in thoracic aortic aneurysms • Familial TAAs grow faster, up to 2.1 mm/year (combined ascending and descending TAA). • Syndromic TAA growth rates also vary. • In patients with Marfan syndrome, the TAA growth is on average at 0.5–1 mm/year, whereas TAAs in patients with Loeys-Dietz syndrome (LDS) can grow even faster than 10 mm/year, resulting in death at a mean age of 26 years. • TAAs of the descending aorta grow faster (at 3 mm/year) than those in ascending aorta (1 mm/year)
- 12. Complications of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms • Aortic rupture • Aortic regurgitation • Tracheobronchial and esophageal compression • Right pulmonary artery or right ventricular outflow tractobstruction • Systemic embolism from mural thrombus
- 13. Risk of aortic dissection • There is a rapid increase in the risk of dissection or rupture when the aortic diameter is 60 mm for the ascending aorta and 70 mm for the descending aorta. • Although dissection may occur in patients with a small aorta, the individual risk is very low
- 14. In Marfan syndrome, aortic enlargement is generally maximal at the sinuses of Valsalva, responsible for annulo-aortic ectasia. In patients with BAV, three enlargement patterns are described Level of the sinuses of Valsalva, Supracoronary ascending aorta, The sinotubular junction level (cylindrical shape).
- 15. Natural History 0 5 10 15 20 25 <2.75 cm/m2 2.75-4.25 cm/m2 >4.25 cm/m2 Aortic Size Index (ASI) AnnualRiskofRupture ASI = aortic dia (cm)/body surface area (m2)
- 16. Natural History
- 17. SYMPTOMS • Most of aortic ANEURSYMS may be clinically silent. • Anterior chest pain secondary to compression of • (1) Coronary arteries • (2) Sensory mediastinal nerves • Chronic back pain may occur descending aortic aneurysms • CHF symptoms secondary to aortic annular enlargement • (1) Widened pulse pressure • (2) Diastolic murmur • Facial and upper trunk venous congestion secondary to superior vena cava compression • Blood pressure usually elevated chronically
- 18. Conti . Acute deep, aching or throbbing chest or abdominal pain that can spread to the back, buttocks, groin or legs, suggestive of AD or other AAS, and best described as ‘feeling of rupture’. Cough, shortness of breath, or difficult or painful swallowing in large TAAs. Constant or intermittent abdominal pain or discomfort, a pulsating feeling in the abdomen, or feeling of fullness after minimal food intake in large AAAs. Stroke, transient ischaemic attack, or claudication secondary to aortic atherosclerosis. Hoarseness due to left laryngeal nerve palsy in rapidly progressing lesions
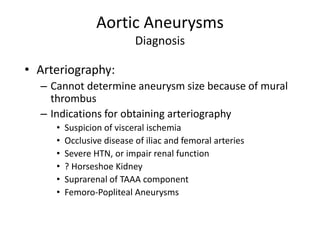
- 19. Aortic Aneurysms Diagnosis • Arteriography: – Cannot determine aneurysm size because of mural thrombus – Indications for obtaining arteriography • Suspicion of visceral ischemia • Occlusive disease of iliac and femoral arteries • Severe HTN, or impair renal function • ? Horseshoe Kidney • Suprarenal of TAAA component • Femoro-Popliteal Aneurysms
- 20. CHEST XRAY • Loss of aortic contour • Mediastinal widening • Dilated descending thoracic aorta, • aortic calcifications • upward deviation of the left mainstem bronchus, and/or new left pleural effusion. • Deviation of the trachea to the right • Left hemothorax
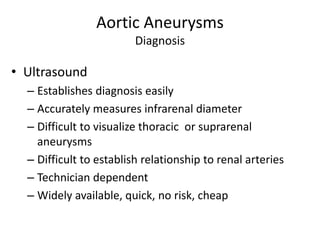
- 21. Aortic Aneurysms Diagnosis • Ultrasound – Establishes diagnosis easily – Accurately measures infrarenal diameter – Difficult to visualize thoracic or suprarenal aneurysms – Difficult to establish relationship to renal arteries – Technician dependent – Widely available, quick, no risk, cheap
- 22. Aortic Aneurysms CT Scan • Very reliable and reproducible • Can image entire aorta • Can visualize relation ship to visceral vessels • Longer to obtain and is more costly than U/S • Most useful • Requires contrast agent - renal toxicity
- 23. Aortic Aneurysms MRA Now widely available More expensive than CT No contrast agent required Spacial resolution less than CT Can visualize the whole extent of the aorta in multiple planes Ability to assess branch vessels, AI, and pericardial effusion • In the acute setting, MRI is limited because it is less accessible, it is • more difficult to monitor unstable patients during imaging, and it has • longer acquisition times than CT Limited applicability in pts with pacemakers or metallic clips
- 24. TEE TEE can image the thoracic aorta from the aortic valve to the distal ascending aorta and from the distal aortic arch to the proximal abdominal aorta. The distal ascending aorta and proximal aortic arch cannot be reliably imaged by TEE because the intervening trachea and left mainstem bronchus obstruct the acoustic window; this is known as the “blind spot” of TEE. The advantages of TEE include its portability, its real-time Interpretation, its compatibility at the bedside and in the OR, and its multiple imaging modalities for complete aortic and cardiac assessment. Its disadvantages include the requirement for sedation or general anesthesia and the risks for upper gastrointestinal injury.
- 25. Management strategies Non-surgical management and surveillance The main aim of medical therapy is to reduce shear stress on the diseased segment of the aorta by reducing blood pressure and cardiac contractility The most important medical management steps are as follows: (i) Smoking cessation can slow down aneurysmal growth by 15– 20% and decrease perioperative morbidity relating to wound healing and cardiorespiratory complications. (ii) Statins can minimize perioperative myocardial ischaemia (iii) According to recent recommendations, low-dose aspirin should be started when an AAA is diagnosed and continued indefinitely may alter aneurysmal growth .
- 26. • Control of both blood pressure and ejection velocity are the mainstays of hemodynamic optimization of the patient with an aortic lesion to prevent aneurysm rupture. • Aggressive control of blood pressure with vasodilators is likely to cause a reflex tachycardia and an increase in left ventricular change in pressure over change in time LV (dp/dt), thereby increasing ejection velocity and the sheer forces on the aortic lesion. • Simultaneous control of both blood pressure and ejection velocity is best obtained with a combination of beta-blockers and vasodilators
- 27. • In patients with Marfan syndrome, prophylactic use of beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, and angiotensin II receptor blocker seem to be able to reduce either the progression of the aortic dilation or the occurrence of complications • In chronic conditions, blood pressure should be controlled below 140/90 mm Hg, with lifestyle changes and use of antihypertensive drugs, if necessary
- 28. SCREENING • Data from the United Kingdom Multicentre Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Screening Study (MASS) have shown that for patients with AAA diameters greater than 55 mm measured by ultrasonography, the number needed to treat (NNT) with elective AAA repair to prevent one death from AAA over the following four years • The United Kingdom Small Aneurysm Trial showed that patients with AAA antero-posterior diameters of 40 to 54 mm measured by ultrasonography randomized to elective surgical treatment were more likely to die from an AAA- related cause than those randomized to best medical treatment and screening
- 29. surveillance
- 30. RECOMMENDATIONS FOR INTERVENTION IN AORTIC ANEURYSM
- 33. PRE OP EVALUATION • A preoperative history and examination reveals stridor, wheezing, cough, or tracheal deviation should raise suspicion of aortic impingement and possible tracheomalacia. • Unilateral vocal cord paralysis, which results from compression of the recurrent laryngeal nerve between the aorta and trachea, may present clinically as voice hoarseness. • Preoperative pulmonary function testing with flow–volume loop analysis will reveal an intrathoracic obstructive process in severe cases. • Radiographic studies may be useful in delineating the extent of airway compromise caused by aortic lesions.
- 34. PRE OP AIRWAY ASSESSMENT • The trachea is markedly deviated secondary to an aortic aneurysm. • The trachea and left mainstem bronchus may be compressed from an aortic aneurysm. • Left-sided double lumen endotracheal tubes may be difficult to place in these patients
- 35. Incidence of coexisting diseases in patients with aortic pathology presenting for surgery • Coronary artery disease 66% • Hypertension 42% • Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 23% • Peripheral vascular disease 22% • Cerebrovascular disease 14% • Diabetes mellitus 8% • Other aneurysms 4% • Chronic renal disease 3%
- 36. Cardiac Assessment • Because myocardial ischemia is an important predictor of perioperative outcome, it has featured prominently in the guidelines for thoracic aortic diseases. • Patients with evidence of myocardial ischemia should undergo further evaluation to determine the extent and severity of coronary artery disease (CAD; ACC/AHA Class I recommendation; level of evidence C). • If significant CAD is responsible for an acute coronary syndrome, then coronary revascularization is indicated before or concomitant with the thoracic aortic procedure (ACC/ AHA Class I recommendation; level of evidence C). • Concomitant coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is reasonable in patients who have not only stable but significant CAD, but who are also scheduled to undergo surgery for diseases of the ascending aorta or aortic arch, or both (ACC/AHA Class IIa recommendation; level of evidence C
- 37. Assessment of organ systems • 1. Neurologic. patient should be monitored closely for change in neurologic status, as this is an indication for immediate surgical intervention. Involvement of the artery of Adamkewitcz may lead to lower extremity paralysis, while propagation of a dissection into a cerebral vessel may lead to a change in mental status or stroke symptoms. • 2. Renal function. Urine output should be followed, as development of anuria or oliguria in the euvolemic setting is an indication for immediate surgical intervention. • 3. Gastrointestinal. Serial abdominal examinations should be performed, and blood gas analysis should be done routinely to assess changes in acid-base status. Ischemic bowel can cause significant metabolic acidosis
- 38. PRE OP MEDICINE • According to recent recommendations, patients should continue • taking b-blockers (if already taking these), aspirin, and statins before surgery. • Diuretics and ACE inhibitors should be considered on a case-by- case basis. • Decisions regarding continuation of clopidogrel and newer antiplatelet agents ( prasugrel, ticagrelor) through the perioperative period are more complex and depend on the indication for these agents; • Although there is an increased risk of perioperative bleeding, recent data suggest that continuation of clopidogrel may not increase transfusion requirements or the incidence of reoperation for bleeding after AAA repair
- 39. Bleeding and transfusion • Coagulopathy frequently encounterd • Many pt require Lt heart or full CPB during Sx, CPB may cause consuptive coagulopathy & enhanced fybrinolysis, thus ↑ing bl. Loss • DHCA may cause platelete dysfunction secondary to extream hypothermia • So prepare total of 8 to 10 units of PCV, FFP & PC • Blood scavenging & reprocessing • Antifibrinolytic therapy during aortic surgery is controversial but commonly used eg. Trenexamic acid, ƐACA,Aprotinin
- 40. Monitoring Minimum standard monitoring should be placed before induction of anaesthesia. A five-lead ECG is more sensitive in detecting myocardial ischaemia. Invasive arterial pressure monitoring should be established before but central venous access is usually secured after induction of anaesthesia. Urinary catheterization and temperature monitoring Neuromonitoring Different cardiac output monitoring strategies have their limitations and may respond slowly to haemodynamic changes with aortic cross-clamp application and release. Oesophageal Doppler uses flow velocity in the aorta to calculate cardiac output and is unreliable when the aorta is clamped. Pulse wave contour analysis cardiac output and other monitors are gaining popularity, but their use has not yet been fully evaluated in aortic surgery
- 41. ARTERIAL CANNULATION • A right radial arterial catheter is preferred for most cases. • If arterial cannulation of the right axillary, subclavian, or innominate artery is planned for CPB and ACP, bilateral radial arterial catheters often are required to measure cerebral and systemic perfusion pressures • Asc. Aortic lesion may involve the Innominate A., so Lt Radial or femoral line is inserted for direct BP monitoring. • If Rt. Axillary cannulation is used arterial pr measurement will be falsely elevated bec. Of increased flow. • In case of Descending aortic and thoracoabdominal aneurysms (TAA) Arterial monitoring lines are inserted in the right radial and femoral arteries to monitor proximal and distal pressures during the period of aortic cross-clamping. The femoral line is valuable when left-heart bypass techniques are used
- 42. Induction Anaesthesia is no different from that for conventional open heart sx The induction of general anesthesia requires careful hemodynamic monitoring with anticipation of changes because of anesthetic drugs and tracheal intubation. • Appropriate vasoactive drugs should be immediately available as required. • Avoid hypertension to increases forward flow in AR and minimizes the risk for aneurysm rupture. Concomitant vasodilator infusions often are discontinued before anesthetic induction. Because etomidate does not attenuate sympathetic responses with no direct effects on myocardial contractility, it may be preferred in the setting of hemodynamic instability. In elective cases, anesthetic induction can proceed with routine intravenous hypnotics, followed by narcotic titration for attenuation of the hypertensive responses to tracheal intubation and skin incision. General anesthetic maintenance is typically with a balanced technique with narcotic and inhalation agent , neuromuscular blockade is achieved by titration of a nondepolarizing muscle relaxant
- 43. Surgical repair in different type of aortic aneurysm • The type of surgical repair depends on aortic valve function and the aneurysm extent. • The most common aortic valve diseases associated with ascending aortic aneurysm are bicuspid aortic valve or AR caused by dilation of the aortic root. • If the aortic valve and aortic root are normal, a simple tube graft can be used to replace the ascending aorta. • If the aortic valve is diseased but the sinuses of Valsalva are normal, an aortic valve replacement combined with a tube graft for the ascending aorta without need for reimplantation of the coronary arteries can be performed; ACC/AHA class I recommendation; level of evidence C).
- 44. • If disease also involves the aortic valve and the aortic root, the patient requires aortic root replacement and aortic valve intervention. • If technically feasible, the aortic valve can be reimplanted with a modified David technique, which includes graft reconstruction of the aortic root with reimplantation of the coronary arteries (ACC/AHA Class I recommendation; level of evidence C). • If not feasible, aortic root replacement with a composite valve-graft conduit is indicated (Bentall procedure ACC/AHA Class I recommendation; level of evidence C).
- 45. Surgery in aortic arch aneurysm • For ascending aortic aneurysms that involve only the proximal aortic arch, partial arch replacement (hemiarch technique) is reasonable in which a tubular graft is interposed between the ascending aorta or aortic root and the underside of the aortic arch (ACC/AHA Class IIa recommendation; • Ascending aorta with hemiarch reconstruction often is performed using DHCA with or without ACP/RCP to make the distal anastomosis feasible without cross-clamping (“open technique”). • In patients who have isolated aortic arch aneurysms and who have a low operative risk, arch replacement is reasonable when the arch diameter exceeds 5.5 cm (ACC/AHA Class IIa recommendation; • Total aortic arch replacement is reasonable in aneurysms that involve the entire arch (ACC/AHA Class IIa recommendation • Ascending aortic aneurysms that extend through the aortic arch into the descending aorta can be repaired with the “elephant trunk” technique ACC/AHA Class IIa recommendation;
- 46. CANNULATION FOR CPB If the aneurysm ends in the proximal or midportion of the ascending aorta, the arterial cannula for CPB can be placed in the upper ascending aorta or proximal arch. Femoral artery cannulation is particularly useful in emergency situations with hemodynamically unstable pa tients. However, it creates retrograde flow in the abdominal and thoracic aorta, it is a potential cause of embolic stroke in patients with heavy atherosclerotic burden Most recommeded and newer approach is to cannulate the right axillary , or occasionally the right carotid, artery, allowing perfusion into the innominate artery and then into the aorta in an antegrade manner Most commonly venous drainage by right atrial dual-stage cannula, bicaval cannulae, . Femoral venous cannulation is routinely used in hemodynamically unstable patients who require pump support before sternotomy and is particularly useful in patients who are at risk of aortic injury during sternotomy. In patients undergoing reoperation and large ascending aortic aneurysms abutting the sternum
- 47. • During systemic cooling in aortic aneurysm surgery the heart will spontaneously fibrillate. At this time, a left ventricular VENT is inserted through the right superior pulmonary vein to decompress the left ventricle. This is especially important in patients who are prone to ventricular distention, such as those with aortic valve regurgitation. • To prevent this complication, the Vent is generally placed before systemic cooling begins. • If the patient has an incompetent aortic valve, as may be the case in an aortic dissection, manual compression of the distending heart may be necessary at this time • Other advantage of LV vent are to Minimizes preload, Prevents ventricular distention, Reduces myocardial rewarming, Prevents ejection of air, Facilitates exposure of the aortic valve.
- 48. MYOCARDIAL PROTECTION • Cardioplegia is achieved with the use of a cold hyperkalemic crystalloid or blood cardioplegic solution, which may be administered in one of several ways: (a) antegrade aortic root administration if the aorta can be cross- clamped and the aortic valve is competent, (b) direct coronary ostial administration after opening of the ascending aorta, or (c) retrograde administration through the coronary sinus. • When the aortic arch is included in the procedure and when cross- clamping of the ascending aorta is not possible because of excessive friability of the aortic tissues, DHCA is required.
- 49. TEE • Perioperative TEE can evaluate the aortic valve structure and function to guide and assess the surgical intervention (reimplantation,repair, replacement). • Furthermore, TEE can assess the diameters of the aortic root, ascending aorta, and aortic arch to guide intervention.. • In patients with AR, TEE can assist in the conduct of CPB by guiding placement of cannulae such as the retrograde cardioplegia cannula (coronary sinus) and by monitoring left ventricular (LV) volume to ensure that the LV drainage cannula keeps the ventricle collapsed.
- 50. Brain Protection for Aortic Arch Reconstruction • Deep systemic hypothermia • • Topical cerebral cooling • • Retrograde cerebral perfusion • • Selective antegrade cerebral perfusion • • Cerebral hyperthermia prevention during rewarming
- 51. DEEP HYPOTHERMIA AND CIRCULATORY ARREST • Deep hypothermia is the mainstay of any operation that requires opening the distal ascending aorta or transverse aortic arch where blood flow to the brain must be interrupted. • Although there may be controversy about the best method of cerebral perfusion during surgeries that involve the aortic arch, deep hypothermia alone will usually provide the surgeon with a safe arrest period of 30 minutes, provided the patient's brain is cooled to <20°C.
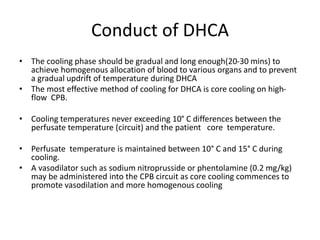
- 52. Conduct of DHCA • The cooling phase should be gradual and long enough(20-30 mins) to achieve homogenous allocation of blood to various organs and to prevent a gradual updrift of temperature during DHCA • The most effective method of cooling for DHCA is core cooling on high- flow CPB. • Cooling temperatures never exceeding 10° C differences between the perfusate temperature (circuit) and the patient core temperature. • Perfusate temperature is maintained between 10° C and 15° C during cooling. • A vasodilator such as sodium nitroprusside or phentolamine (0.2 mg/kg) may be administered into the CPB circuit as core cooling commences to promote vasodilation and more homogenous cooling
- 53. Organ protection during DHCA • Hypothermia • Pharmacological adjuncts • Perfusion strategies • Topical external cooling of the head • optimized acid-base management • pump prime modifications • leukocyte depletion • The degree of hemodilution • strategies of cooling and rewarming
- 54. α-stat vs pH-stat • pH-stat strategy results in greater cerebral blood flow, greater efficiency, and uniformity of brain cooling, and higher brain oxyhemoblobin saturation and less reduced cytochrome a,a3 signifying more oxygen at the mitochondrial level than α-stat blood gas management • However, other data suggest that cerebral metabolic recovery after DHCA may be better with the α-stat method than with the pH-stat mode • Some institute use crossover strategy in which a pH-stat approach is used during the first 10 minutes of cooling to provide maximal cerebral metabolic suppression, followed by an α-stat strategy to remove the severe acidosis that accumulates during profound hypothermia during pH-stat
- 55. Rewarming strategies There is no more than 10° C temperature differential between the core and perfusate temperatures. Patients should warm at the same rate at which they were cooled. Warming rate should never exceed 1° C core temperature increase per 3 minutes of bypass time. Use of vasodilators to facilitate distal perfusion Treat metabolic acidosis agressive Termination of warming should occur when the nasopharyngeal temperature is between 35° C and 36° C. This mild hypothermia provides additional cerebral protection in the early postoperative period.
- 56. Pharmacologic Neuroprotection There are no proven pharmacologic regimens that have demonstrated effectiveness for decreasing the risk or severity of neurologic injury in the setting of thoracic aortic operations. The agents that have been reported in aortic arch series include thiopental, propofol, steroids, magnesium sulfate, and lidocaine Furthermore, there is considerable variation in practice with these agents in aortic arch repair The technique of DHCA with pharmacologic adjuncts is a reasonable approach for neuroprotection during aortic arch surgery in the setting of an institutional protocol and adequate institutional experience (ACC/AHA Class IIa recommendation; level
- 57. Retrograde cerebral perfusion • RCP is performed by infusing cold oxygenated blood into the superior vena cava cannula at a temperature of 8° C to 14° C via CPB • The internal jugular venous pressure is maintained at less than 25 mm Hg to prevent cerebral edema • Patient is positioned in 10 degrees of Trendelenburg to Decrease the risk for cerebral air embolism and prevent trapping of air • Flow rates of 200 to 600 mL/min usually can be achieved
- 58. • Advantage are more homogeneous cerebral cooling; washout of air bubbles, embolic debris, and metabolic waste products; prevention of cerebral blood cell microaggregation; and delivery of oxygen and nutritional substrates to brain tissue • During RCP, only a minimal amount of blood (not more than 3% to 10%) is directed to the brain, whereas more than 90% is deviated through the azygos to the SVC or entrapped in the cerebral venous sinuses
- 59. Anterograde cerebral perfusion • Arterial CPB circuit flow can be delivered selectively to the cerebral circulation antegrade via the circle of Willis following cannulation of the innominate artery or right carotid artery • ACP may be unilateral or bilateral, there remains controversy about which ACP technique is superior. A recent literature Showed the period of safe ACP was significantly prolonged with bilateral ACP compared with unilateral ACP (30–50 minutes). The evidence favors bilateral ACP in the setting of aortic arch repair times longer than 60 minutes • The technique of DHCA with ACP is a reasonable approach for neuroprotection during aortic arch surgery in the setting of adequate institutional experience (ACC/AHA Class IIa recommendation; level of evidence B).
- 60. GOALS OF Anaesthetic management IN TAAA OPEN REPAIR • Anaesthetic management focuses on the Acute haemodynamic changes with aortic cross-clamping and unclamping, Maintaining organ perfusion and oxygenation Attenuating ischaemic reperfusion injury, Providing intra- and postoperative analgesia
- 61. Lung Isolation Techniques • Selective ventilation of the right lung with concomitant left lung Collapse during TAAA repair enhances surgical access and protects the right lung from left lung bleeding. • Collapse of the left lung typically is achieved when the left main bronchus is intubated either with a double-lumen endobronchial tube (DLT) or a bronchial blocker. • The advantages of a left DLT include the ability to apply selective continuous positive airway pressure to the left lung
- 62. analgesia A thoracic epidural catheter is usually placed before induction of anaesthesia at a level corresponding to the upper dermatomal level of the incision (usually T8– T10) for Postoperative analgesia Intraoperative analgesia can be provided using opioids or by using epidural analgesia; however, high doses of epidural local anaesthetics can cause profound hypotension after aortic crossclamp release due to sympathetic blockade. It is common practice to limit epidural local anaesthetic administration until after crossclamp release and haemostastis has been achieved.
- 63. Heparin 75–150 units kg21 is given i.v. before aortic crossclamp application. Activated clotting time can be used to guide heparin therapy (2–3 times more than baseline). Cell salvage equipment should be used when available. Serial arterial blood gas samples are usually analysed to monitor respiratory and metabolic status. Facilities for the rapid infusion of warm fluids and blood should be available for immediate use. All efforts should be made to maintain normothermia; however, lower body warming during aortic cross- clamp application is discouraged
- 64. RECOMMENDATION FOR PERFUSION TECHNIQUE Descending thoracic aortic repairs Left heart bypass for high-risk patients (acute dissection, rupture, prior abdominal aortic aneurysm repair) Extent I and II thoracoabdominal repairs Left heart bypass during proximal anastomosis Selective perfusion of celiac axis and superior mesenteric artery during intercostal and visceral anastomoses Perfusion of renal arteries with 4°C crystalloid solution Extent III and IV thoracoabdominal repairs Perfusion of renal arteries with 4°C crystalloid solution
- 65. Open repair of TAAA typically is accomplished by one of three major PERFUSION techniques; (1) aortic cross-clamping, (2) aortic cross- clamping with a Gott shunt, (3) aortic cross-clamping with PLHB or partial CPB
- 66. Simple Aortic Cross-Clamp Technique • Its major Disadvantage is the concomitant vital organ ischemia below the aortic clamp. • Its further disadvantages include proximal aortic hypertension, Bleeding, and hemodynamic instability on reperfusion. • Proximal aortic hypertension may induce LV Ischemia. • Mild systemic hypothermia and selective spinal cooling protect against the ischemia associated with this technique. • Despite its physiologic consequences, this technique remains popular because it is simple and has proven clinical outcomes
- 67. Gott Shunt The Gott shunt allows passive shunting of blood from the proximal to distal aorta during aortic cross- clamping for thoracic aortic repair Blood flow from the proximal to distal aorta through the Gott shunt depends on proximal aortic pressure, shunt length and diameter, and distal aortic pressure. Monitoring the femoral arterial pressure facilitates assessment of distal aortic perfusion and shunt flow. The advantages of the Gott shunt are its simplicity, its low cost, and its requirement for only partial anticoagulation.
- 68. Partial Left-Heart Bypass • The control of both proximal and distal aortic perfusion during TAAA repair is achieved with PLHB. • This technique requires left atrial cannulation, usually via a left pulmonary vein • Oxygenated blood from the left atrium flows through the CPB circuit into the distal aorta or a major branch via the arterial Cannula. • The degree of heparinization for PLHB is minimal with heparin-coated circuits without an oxygenator. • Full systemic anticoagulation with ACT greater than 400 seconds is required for CPB circuits with membrane oxygenators and heat exchangers
- 69. • During PLHB, the proximal mean arterial pressure (MAP; radial artery) is generally maintained in the 80 to 90 mm Hg range. • Flow rates in the range of 1.5 to 2.5 L/min typically maintain a distal aortic MAP in the 60 to 70 mm Hg range, monitored via a femoral arterial catheter. • Sequential advancement of the aortic crossclamp during PLHB permits segmental aortic reconstruction with a decrease in end-organ ischemia. • The advantages of PLHB include control of aortic pressures and systemic temperature, reliable distal aortic perfusion, and selective antegrade perfusion of important branch vessels
- 70. Advantages of distal perfusion • Control of proximal hypertension • Decrease left ventricular afterload • Less hemodynamic perturbations with aortic clamping and unclamping • Decrease duration of mesenteric ischemia • Decrease risk for paraplegia from spinal cord ischemia • Ability to control systemic temperature with heat exchanger • Vascular access for rapid volume expansion • Ability to oxygenate blood with extracorporeal oxygenator • Capability to selectively perfuse mesenteric organs or aortic branch vessels • Maintain lower extremity SSEPs and MEPs for neurophysiologic monitoring
- 71. aortic cross-clamping The physiological effect of aortic cross-clamping during surgery varies with the level of the clamp in relation to the main aortic branches. Perfusion to the lower half of the body is therefore dependent on collateral circulation while the clamp is applied. Clamp application increases the afterload of the heart and a sudden increase in arterial pressure proximal to the clamp; this can be ttenuated with vasodilators [e.g. glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), sodium nitroprusside], opioids, or deepening of anaesthesia.
- 72. • Increased afterload and left ventricular end- diastolic volume both increase myocardial contractility and oxygen demand. • This increase in myocardial oxygen demand is usually met by an increase in coronary blood flow and oxygen supply, but can cause myocardial ischaemia • The mean arterial pressure should be maintained within the autoregulation limits of vital organs.
- 73. aortic cross-clamp release After aortic cross-clamp release, peripheral vascular resistance decreases by 70–80%, causing a decrease in arterial pressure. Hypotension can also be caused by blood sequestration in the lower half of the body, ischaemia–reperfusion injury, and the washout of anaerobic metabolites causing metabolic (lactic) acidosis. This can cause direct myocardial suppression and profound peripheral vasodilatation. Coronary blood flow and left ventricular end-diastolic volume also decrease (almost 50% from pre-clamp levels) after clamp release
- 74. MANAGEMENT OF AORTIC CROSSCLAMP RELEASE • Strategies to manage hypotension after aortic cross-clamp release include Discontinue vasodilator agents Gradual release of the clamp, Volume loading, Vasoconstrictors, or Positive inotropic drugs (e.g. ephedrine, termine phenylephrine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine). • It is important to be aware that vasoactive drugs should only be used after adequate volume repletion • TEE can adequately assist with LV volume assessment. • Acidosis may be treated with hyperventilation and bolus administration of sodium bicarbonate. • A continuous infusion of bicarbonate (0.05 mEq/kg/min) during cross- clamping may be more efficacious.
- 75. RENAL PROTECTION • The main cause of renal complications after AAA repair is the decrease in renal blood flow, decreased renal perfusion pressure (outside autoregulation) augmented by the increasing renal vascular resistance (by 30%) associated with aortic clamping. • Myoglobin release from ischaemic tissues may contribute to acute tubular necrosis by decreasing local nitric oxide release. • Acute kidney injury (AKI) may also be linked to ischaemic– perfusion injury, decreased renal cortical blood flow, prostaglandin imbalance, and increased activity of renin–angiotensin system. • Postoperative dialysis rates are similar in patients who have undergone either suprarenal or infra-renal aortic cross-clamping
- 76. • Rhabdomyolysis from lower extremity ischemia was recently identified as a mechanism for renal dysfunction after TAAA repair. • The maintenance of lower extremity perfusion bilaterally during distal aortic perfusion has been shown to ameliorate this rhabdomyolysis with a significant nephroprotective effect • intraoperative cold renal perfusion with blood or crystalloid is recommended as a reasonable intraoperative nephroprotective strategy during TAAA repair (ACC/AHA Class IIb recommendation; level of evidence C).
- 77. • The thoracic aortic guidelines recommend preoperative hydration and intraoperative mannitol administration as reasonable nephroprotective strategies in extensive distal open thoracic aortic repairs, including TAAA repair (ACC/AHA Class Iib recommendation; level of evidence C). • Several drugs (dopamine, N-acetyl cysteine, mannitol, furosemide) have been used in an attempt to protect against AKI, although none has been shown consistently to be beneficial, and all diuretics should be used only after adequate fluid replacement and volume loading. • Mannitol can increase renal blood flow during aortic cross- clamp; however, both mannitol and dopamine use fail to return GFR to baseline levels after operation
- 78. PARAPLEGIA IN TAAA REPAIR • Paraplegia after TAAA repair is a devastating complication. • most patients, one radicular arterial branch, known as the great radicular artery (of Adamkiewicz), provides a major portion of the blood supply to the midportion of the spinal cord. It may arise anywhere from T5 to below L1 • The temporary interruption of distal aortic perfusion and sacrifice of spinal segmental arteries during TAAA repair are central events in the pathogenesis of spinal cord ischemia and paraplegia •
- 79. Factors That Contribute to Paraplegia after Thoracic or Thoracoabdominal Aneurysm repair Duration of aortic cross-clamp Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm extent Hypotension or cardiogenic shock Emergency surgery Aortic rupture Presence of aortic dissection Sacrifice of intercostal or segmental artery branches Prior thoracic or abdominal aortic aneurysm repair Occlusive peripheral vascular disease Anemia
- 80. Techniques to Decrease the Risk for Intraoperative Spinal Cord Ischemia Distal aortic perfusion Arterial pressure augmentation Minimizing the ischemic time Mild systemic hypothermia Lumbar cerebrospinal fluid drainage Selective spinal cord cooling Segmental aortic reconstruction Intercostal artery preservation Pharmacologic neuroprotection Intraoperative motor- or somatosensory-evoked potential monitoring
- 81. Minimize Aortic Cross-clamp Time Distal aortic perfusion • Passive shunt (Gott) • Partial left heart bypass • Partial cardiopulmonary bypass Deliberate Hypothermia • Mild-to-moderate systemic hypothermia (32° C to 35° C) • Deep hypothermic circulatory arrest (14° C to 18° C) • Selective spinal cord hypothermia (epidural cooling, 25˚ C)
- 82. Increase Spinal Cord Perfusion Pressure • Reimplantation of critical intercostal and segmental arterial branches • Lumbar cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) drainage (CSF pressure ≤ 10 mm Hg) • Arterial pressure augmentation (mean arterial pressure ≥ 85 mm Hg)
- 83. spinal drain management • SCPP is estimated as the MAP minus the lumbar CSF pressure. • In general, the SCPP should be maintained greater than 70 mm Hg • 30% or more of all neurologic deficits are delayed in onset • spinal drains are commonly left in for 48 hours postoperatively and are replaced if neurologic deficits occur after the drain is removed. • maintain CSFP between 10 to 15 mm Hg in the postoperative setting, efforts must be made to avoid systemic hypotension and associated decreased spinal cord perfusion. •
- 84. Intraoperative Neurophysiologic Monitoring • Neurophysiologic monitoring of the spinal cord (SSEPs and/or MEPs) is recommended as a strategy for the diagnosis of spinal cord ischemia so as to allow immediate intraoperative neuroprotective interventions such as intercostal artery implantation, relative arterial hypertension, and CSF drainage (ACC/AHA Class IIb recommendation; level of evidence B). • Because SSEP monitors posterior spinal column integrity, MEPs have been advocated because they monitor the anterior spinal columns that are most common at risk during TAAA repair.
- 85. Spinal Cord Hypothermia Although DHCA is effective, moderate systemic hypothermia is also reasonable for spinal cord protection during TAAA repair (ACC/AHA Class IIa recommendation; level of evidence B). Furthermore, topical spinal cord hypothermia is possible with cold saline epidural infusion to avoid ischemia during TAAA repair. Epidural cooling is recommended as an adjunctive technique for spinal cord protection during major distal thoracic aortic reconstructions (ACC/AHA Class IIb recommendation; level of evidence B). This technique give adjunctive benefit and the recent clinical development of a specialized countercurrent closed-lumen epidural catheter for epidural cooling during major distal aortic reconstructions
- 86. Pharmacologic Protection of the Spinal Cord • Pharmacologic spinal cord protection with agents such as high dose systemic glucocorticoids, mannitol, intrathecal papaverine, and anesthetic agents is recommended as an adjunctive technique in a multimodal neuroprotective protocol (ACC/AHA Class IIb recommendation; level of evidence B). • Additional neuroprotective agents that have been studied in this regard include lidocaine, naloxone, and magnesium
- 87. TEVAR • Thoracic endovascular aortic repair aims at excluding an aortic lesion (i.e. aneurysm or FL after AD) from the circulation by the Implantationof a membrane-covered stent- graft across the lesion, in order to prevent further enlargement and ultimate aortic rupture
- 88. INDICATION
- 89. TEVAR Anesthetic Protocol • Always GA for TEVAR • For EVAR General Anesthesia ,Regional Anesthesia (epidural alone or spinal or combined) or Local Anesth (local groin infiltration) with sedation • Assess risk of SCI • Consider spinal drain • Neuromonitoring • Arterial line The right radial artery is preferred for • blood pressure monitoring, given that the left subclav artery frequently may be covered and/or the left brac artery may be accessed as part of the procedure. • PAC monitoring may be helpful in the setting of signif
- 90. GA VS REGIONAL OR LOCAL • Risk‐adapted Outcome after Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair: Analysis of Anesthesia Types Based on EUROSTAR data • Ruppert et al. Journal of Endovascular Therapy, 2007. • between 1997 and 2004, 164 centers, 5557 patients • Patients were divided into low‐risk (ASA I or II.), high risk(ASA III or IV), LA, GA, RA into 6 groups. • Low‐risk group: 78.8% GA, 15.9% had RA, 5.3% LA • High‐risk group: 60.4 % GA, 33.7% RA, 5.9% LA
- 91. • Outcomes • • GA vs. RA or LA: • less systemic complications (cardiac, cerebral, pulmonary, renal, • hepatobiliary, sepsis) • • GA versus RA: less 30 days early death in the RA group • • Less ICU admission with local and regional (low risk and high risk )
- 92. • Observation from the IMPROVE trial (BJS 2014) • Prospective multicenter, observational study on Anesthesia type in 558 patients with a symptomatic or ruptured aneurysm ( EVAR ) • Lowest blood pressure (<70 MAP) was strongly and independently associated with 30‐days mortality • • EVAR with local anesthesia (adjusted to variables) alone had greatly reduced (4 fold) 30 days mortality
- 93. pre-procedural planning • Contrast-enhanced CT represents the imaging modality of choice for planning TEVAR, taking ,3 mm ‘slices’ of the proximal supra-aortic branches down to the femoral arteries RECOMMENDATION FOR TEVAR
- 94. TEE IN TEVAR • Intraoperative TEE is reasonable in thoracic aortic procedures, including endovascular interventions, in which it assists in hemodynamic monitoring, procedural guidance, and endoleak detection (ACC/AHA Class IIa recommendation; level of evidence
- 95. Complications • Immediate conversion to open surgery is required in approximately 0.6% of patients. • . • The rates of vascular injury after EVAR are low (approximately 0–3%), due to careful pre-procedural planning. • The incidence of stent-graft infection after EVAR is ,1%, with high mortality. • Graft migration • Embolisation
- 96. Classification of endoleaks. Endoleak is the most common complication of EVAR. Type I and Type III endoleaks demand correction (proximal cuff or extension), Type II endoleak may seal spontaneously in about 50% of cases
- 97. spinal cord ischemia after TEVAR or EVAR • perioperative hypotension (decreased SCPP), • prior abdominal/descending thoracic aortic procedures (compromised spinal collateral arterial network) • coverage of the entire descending thoracic aorta (significant loss of intercostal arteries
- 98. Spinal cord protection protocol • Place CSF drain the pre procedure • Record opening pressure, zero at RA level • If pressure exceeds 12 mmHg, pressure goal < 10mmHg • Limit CSF drain to less than 20 ml over 1st‐hr • Limit CSF drain to less than 40 ml over 4‐hours • If SSEP signal decrease drain 10 ml • MAP > 90 hgmm post‐TEVAR • Clamp drain after confirming bilateral lower extremity function • Remove drain after 24 hrs of clamping • Reopen/Drain if delayed paraparesis/paraplegia • If CSF turns bloody turn off drain
- 99. • THANK YOU
Editor's Notes
- #97: Type I: Leak at graft attachment site above, below, or between graft components (Ia: proximal attachment site; Ib: distal attachment site). Type II: Aneurysm sac filling retrogradely via single (IIa) or multiple branch vessels (IIb). Type III: Leak through mechanical defect in graft, mechanical failure of the stent-graft by junctional separation of the modular components (IIIa), or fractures or holes in the endograft (IIIb). Type IV: Leak through graft fabric as a result of graft porosity. Type V: Continued expansion of aneurysm sac without demonstrable leak on imaging (endotension, controversial



































































![aortic cross-clamping
The physiological effect of aortic cross-clamping during
surgery varies with the level of the clamp in relation to
the main aortic branches.
Perfusion to the lower half of the body is therefore
dependent on collateral circulation while the clamp is
applied.
Clamp application increases the afterload of the heart
and a sudden increase in arterial pressure proximal to
the clamp; this can be ttenuated with vasodilators [e.g.
glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), sodium nitroprusside],
opioids, or deepening of anaesthesia.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aorticaneurysmjeevraj-160822092058/85/Aortic-aneurysm-dr-jeevraj-71-320.jpg)



























