Basic Computer information and Programming in C
- 1. Computational Physics Unit - V Special Lecture on Presented By Dr. Halapagol Pruthviraj Assistant Professor Government First Grade College Chitguppa, Dist. BIDAR
- 2. Introduction of Computer Block diagram of Computer Parts of Computer Basic of C Programming Language Session Outcomes
- 3. Introduction of Computer Nowadays, computers are an integral part of our lives. They are used in number of fields like. 1) For booking the tickets by airways. 2) For booking the tickets by Buses, railways. 3) Making the payment of telephone and electricity bills. 4) Deposit and withdrawal of money from banks. 5) Processing of business data. 6) Forecasting of weather conditions. 7) Diagnosis of diseases. 8) Searching for information on the Internet, etc.
- 4. Definition: Input Output Process What is a Computer? A computer is an electronic device that accepts data from the user, processes it, produces results, displays them to the users, and stores the results for future usage. In computer two thing are very important they are Data and Information Producing output Receiving Input Processing the information
- 5. A computer performs the following functions Receiving Input Processing the information Storing the information Producing output Functions of Computers
- 6. The characteristics of the computer system are as follows characteristics of the computer
- 7. Block Diagram of Computer Computer systems consist of three components as shown in below image: Central Processing Unit Input devices and Output devices. Input Unite Output Unite
- 8. Input devices of Computer Input devices help to get input or data from user. Some of input devices are
- 9. CPU of Computer Central Processing Unit The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is called "the brain of computer" as it controls operation of all parts of computer. It consists of two components: Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), and Control Unit.
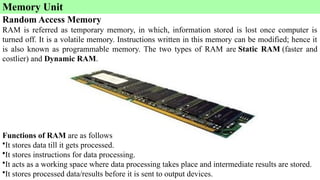
- 10. Memory Unit Random Access Memory RAM is referred as temporary memory, in which, information stored is lost once computer is turned off. It is a volatile memory. Instructions written in this memory can be modified; hence it is also known as programmable memory. The two types of RAM are Static RAM (faster and costlier) and Dynamic RAM. Functions of RAM are as follows •It stores data till it gets processed. •It stores instructions for data processing. •It acts as a working space where data processing takes place and intermediate results are stored. •It stores processed data/results before it is sent to output devices.
- 11. Memory Unit Read Only Memory ROM is referred as permanent memory, in which information stored is available even if computer is turned off. Instructions stored in this memory can only be read and cannot be modified. Mostly ROM has a start-up instruction which is executed every time when computer is switched on. Types of ROM are PROM (Programmable Read Only Memory), EPROM (Erasable PROM), EEPROM (Electrically Erasable PROM) and flash memory.
- 12. Secondary Memory Sometimes when data to be processed is large, it cannot fit in primary memory as it is limited, in such cases, we use supplement memory or secondary memory. Secondary memory helps to store information permanently and is non-volatile. Examples of secondary storage memory are compact disk, floppy disk, pen drive, external hard drive, etc. Memory Unit
- 13. Output unites of Computer Output devices help to display output to user. Some of output devices are
- 14. Basic of C Programming Language
- 15. ‘C’ is one of the most popular programming languages. It was developed by Dennis Ritchie It developed at AT & T’s Bell Laboratories at USA in 1972. It is an upgraded version ‘Basic Combined Programming Language’ (BCPL) and B. ‘C’ was developed along with the UNIX operating system. This operating system, which was also developed at Bell Laboratories. ‘ C ’ is running under a number of operating systems including MS-DOS. History of C Programming
- 16. Importance of C Programming o ‘C’ is a general purpose, structured programming language. o ‘C’ is powerful, efficient, compact and flexible. o ‘C’ is highly portable (i.e. It can be run in different operating systems environments). o ‘C’ is robust language whose rich set of built in functions and operators can be used to write any complex program. o ‘C’ has the ability to extend itself. We can continuously add our own functions to the existing library functions. o ‘C’ is well suited for writing system software as well as application software. o ‘C’ program are fast and efficient. o ‘C’ has rich set of operators.
- 17. • System Software • Operating system • Interpreters • Compilers • Assemblers • Editors Application of C Programming • Loaders • Linkers • Application Software • Data Base Management System (DBMS) • Basic Structure Of C Programs C is used to developed the system and application software. Some of the system and application software are listed below.
- 18. Basic Structure of C Programming /* Demo program on C */ #include <math.h> #define val 234 pi 23.142 main() { int a,b,c; clrscr(); printf(“Enter the two number”); scanf(“%d%d”,&a,&b); c=a+b; /* exp */ printf(“sum of two nu=%d”,c); getch(); }
- 19. Constant, Variables and Data types Constants Constants in C refer to fixed values that do not change during the execution of a program. Types of constant are as shown below. Constants Integer Constants Real constants Character constants String constants Numeric constants Non-Numeric constants num=123 val=-231 avg=0 um1=253444 Val=0.376 num=.57 Code=‘6’; ‘s’ ‘Wa’ ‘;’ ‘ ’ “Hello” “3566”
- 20. Data types Data Types The size and type of values that can be stored in variable is called as Data type. Data types in C under various categories are shown below.
- 21. A variable is an identifier that denotes a storage location used to store a data value. A variable may take different values at different times during the execution of the program. Variables The general form of declaration of a variable is: data_type variable1, variable2,……, variableN; Examples : int rollno, num1, num2; float average, val, per; double pi; char c1, c2;
- 22. Input and Output Statements In ‘C’ language, two types of Input / Output statements are available. They are Formatted Input / Output statements Unformatted Input / Output statements Formatted Input / Output statements printf( ); and scanf( ); Unformatted Input / Output statements gets( ); puts( ); getchar( ); putchar( ); getch( ); putch( );
- 23. C supports a rich set of operators. An operator is a symbol that tells the computer to perform certain mathematical or logical manipulations. C operators can be classified into a number of types are: Arithmetic operators + - * / % Relational operators < <= > >= == != Logical operators && || ! Assignment operators = Increment and decrement operators ++ and - - Conditional operators Exp1 ? Exp2 : Exp3 ; Bitwise operators & ! ^ ~ << >> Operators in C programming
- 25. Thank You