Basic of Data Structure - Data Structure - Notes
- 1. Definition • A Data structure consists of data objects, their properties are the set of legal operations which may be applied to elements of the data object. • A data structure is a set of domain D, a designated domain d € D, a set of functions F and a set of axioms A . the triple (D, F, A) denotes the data structure. D - denotes the data objects. F - denotes the set of operations that can be carried out on the data objects. A - describes the properties and rules of the operations. OR
- 2. Need of Data Structure • The data elements that are concerned with the problem. • The operations that will be performed on these data elements. • Methods of storing the data elements in memory to retain the logical relationship between them. • The programming language which suits the current requirements.
- 3. Abstract Data Types • The abstract datatype is special kind of datatype, whose behavior is defined by a set of values and set of operations. • The keyword “Abstract” is used as we can use these datatypes, we can perform different operations. • Programmer's own data types is termed as Abstract Data Type. OR
- 4. Advantage • Code is easier to understand (e.g., it is easier to see "high-level" steps being performed, not obscured by low-level code). • Implementations of ADTs can be changed (e.g., for efficiency) without requiring changes to the program that uses the ADTs. • ADTs can be reused in future programs.
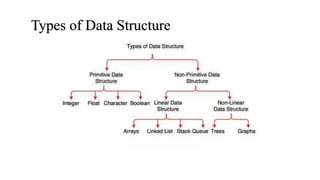
- 5. Types of Data Structure
- 6. Operation Perform of Data Structure • Insertion: Insertion means addition of a new data element in a data structure. • Deletion: Deletion means removal of a data element from a data structure if it is found. • Searching: Searching involves searching for the specified data element in a data structure. • Traversal: Traversal of a data structure means processing all the data elements present in it. • Sorting: Arranging data elements of a data structure in a specified order is called sorting. • Merging: Combining elements of two similar data structures to form a new data structure of the same type, is called merging.
- 7. Algorithm • The word Algorithm means “a process or set of rules to be followed in calculations or other problem-solving operations”. • Therefore Algorithm refers to a set of rules/instructions that step-by-step define how a work is to be executed upon in order to get the expected results. • An algorithm is a finite set of instructions that must be followed to solve a problem. OR
- 8. Advantage • It is a step-wise representation of a solution to a given problem, which makes it easy to understand. • An algorithm uses a definite procedure. • It is not dependent on any programming language, so it is easy to understand for anyone even without programming knowledge. • Every step in an algorithm has its own logical sequence so it is easy to debug. • By using algorithm, the problem is broken down into smaller pieces or steps hence, it is easier for programmer to convert it into an actual program.
- 9. Analysis of Algorithm Time Complexity Space Complexity Space complexity is the amount of memory it require for completion of an algorithm. Time complexity is the amount of frequency count. Algorithm analysis is an important part of computational complexity theory, which provides theoretical estimation for the required resources of an algorithm to solve a specific computational problem. Most algorithms are designed to work with inputs of arbitrary length. Analysis of algorithms is the determination of the amount of time and space resources required to execute it.
- 10. Best Case Average Case Worst Case Minimum time required for algorithm. Average time required for algorithm. Maximum time required for algorithm.