Case selection in endodontics
- 1. Good Morning
- 3. Contents Introduction Historical background Factors influencing treatment outcome Clinical features affecting Rx outcome 1
- 4. Radiographic features affecting treatment outcome Assessment of patient’s systemic status Role of radiographs Case difficulty assessment form Levels of difficulty 2
- 5. Factors affecting healing after endodontic treatment Endodontic treatment plan Indications for extraction 3
- 6. Single visit / mulitiple visit Periodontal considerations Surgical considerations Restorative and prosthetic considerations Conclusion 4
- 7. 6
- 9. Proper selection of cases avoids pitfalls during treatment and helps to ensure success 22%of failures – errors in case selection The Washington Study Ingle & Beveridge 7
- 10. 7
- 11. systematic manner problem solving approach treatment & evaluation 9
- 12. 10 Success / failure Advances in access cavity preparation Shaping & cleaning 3-d obturation
- 13. No treatment poor treatment wrong treatment 11
- 14. Historical background on treatment outcome Concept of success or failure - sterilization of root canal, hermetic seal 12
- 15. Hunter’s Focal infection theory Rosenow’s Elective localization Rickert & Dixon Hollow tube theory 13
- 16. Factors to be considered Sterilization – purest form, impossible Theories – highly speculative Hollow tube theory- disproved 1960 Dye leakage studies-static evaluation 14
- 17. 1950-1960- lack of apical seal Contemporary studies – root canal fillings leak over time Bacterial etiology together with inflammatory reactions 15
- 19. Factors – may influence the treatment outcome Pulpal status Procedural accidents Crown/root fractures Periodontal status Occlusal discrepancies Size of periradicular rarefaction 17
- 20. Pain threshold Level of canal obturation Time of post treatment evaluation Degree of canal calcification Accessory communications Presence of root resorption 18
- 21. Factors – definitely influence the outcome r/g interpretation Periradicular pathosis Root canal anatomy Thorough debridement Apical seal Disinfection and asepsis Systemic status Clinician’s skill 19
- 22. Treatment outcome based on clinical features Acceptable No tenderness Normal mobility No sinus tract, assc periodontal disease No swelling No subjective discomfort 20
- 23. Uncertain Sporadic vague symptoms Pressure sensation Low grade discomfort Discomfort when pressure applied by tongue Superimposed sinusitis Analgesics to relieve pain 21
- 24. Unacceptable Persistent subjective symptoms Recurrent sinus tract Predictable discomfort to percussion, palpation Irreparable tooth fracture Excessive mobility Inability to chew with tooth 22
- 25. Treatment outcome based on r/g features Acceptable Normal, slight thickened pdl space Elimination of previous r/l Normal lamina dura No evidence of resorption 3-D obturation of canal space 23
- 26. Uncertain Increased pdl space r/l of similar size, slight repair Irregularly thickened lamina dura Evidence of progressive resorption Voids in canal obturation overfilling 24
- 27. Unacceptable Increased width of PDL space >2mm Lack of osseous repair/ size of lesion Lack of new ld formation New osseous r/l Visible patent canal space Excessive overextension , voids in the apical area Definite progressive resorption 25
- 28. Assessment of systemic status 26
- 29. Cardiovascular disease AHA recommendation for endocarditis Prosthetic cardiac valves h/o infective endodcarditis Congenital heart diseases 27
- 30. Endocarditis prophylaxis not recommended Mitral valve prolapse Rheumatic heart disease Bicuspid valve disease Calcified aortic stenosis 28
- 31. Antibiotic prophylaxis regimen for dental procedures 29 REGIMEN FOR A DENTAL PROCEDURE Regimen Single dose 30-60min before Procedure Situation Agent Adults Children Oral Amoxicillin 2g 50 mg/kg Unable to take oral medication Ampicillin/ cefazolin/ ceftrioxone 2g IM/IV 1g IM/IV 50 mg/kg IM/IV 50 mg/kg IM/IV Allergic to penicillin /ampicillin - oral Cephalexin/ clindamycin/ azithromycin/ clarithromycin 2g 600mg 500 mg 50 mg 20mg 15mg Allergic to penicillin /ampicillin & unable to take oral medication Cefazolin/ ceftrioxone /clindamycin 1g IM/IV 600 mg IM/IV 50 mg/kg IM/IV 20mg/kg IM/IV
- 32. Pts on anticoagulants Identify reason Assess potential risk of altering drug regimen Lab tests(INR ,APTT) Possible complications Consult physician 30
- 33. Diabetes Well controlled diabetes- candidate for endodontic Rx Monitor fasting glucose level Ready availability of glucose 31
- 34. Pregnancy X ray exposure Antibiotics if any- penicillins, cephalosporins, macrolides – first line NSAIDs – not preferred Second trimester – safest for dental care 32
- 35. Malignancy Metastasize to jaws- breast, lung, thyroid, prostate Pts – chemotherapy, radiation- impaired healing responses 33
- 36. Oral infections and potential problems should be addressed before initiating radiation Rx of Symptomatic non vital teeth – 1 week before chemo/radiation Asymptomatic - delayed 34
- 37. Medication related osteonecrosis of the jaws(MRONJ) AAOMS 1. Current/ previous Rx with antiresorptive drug 2. Exposed necrotic bone in MF region 3. No h/o radiation therapy to jaws 35
- 38. Recommendations prior to endodontic treatment 1 min mouth rinse with CHX Avoid LA with vasoconstrictors Asepsis Avoid gingival damage Maintain apical patency Prevent overfilling Aggressive use of antibiotics - infection 36
- 39. HIV long term prognosis on endodontic therapy- unknown Minimize the possibility of transmission of infection – strict adherence to universal precautions 37
- 40. CD4+ cell count >350/mm3 – receive all indicated dental treatments <200/mm3- opportunistic infections , medicated with prophylatic drugs 38
- 41. Prescribing medication Oral manifestations of HIV – Consultation with pt’s physician – proir to complex procedures 39
- 42. End stage renal disease and dialysis Goal - slow progression of disease, improve quality of life of patient Consultation with physician 40
- 43. Aspirin, acetaminophen Amoxicillin, penicillin Endodontic Rx – scheduled usually after dialysis 41
- 44. Prosthetic implants Antibiotic prophylaxis – not routinely “High risk pts” 42
- 45. Behavioural & psychiatric disorders Drug interactions & side effects – tricyclic antidepressants, anxiolytics 43
- 46. Psychosocial evaluation Tooth- questionable prognosis Pts – should not dictate treatment Patient’s level of anxiety 44
- 47. Case selection – dictated by what is seen in the radiograph Extent of caries Periapical lesion Resorption Anatomy of root canal Fracture of tooth 45
- 48. Dilaceration Pulp stone Subgingival decay of tooth beneath crown Gemination Taurodontism 46
- 49. Patient Diagnostic Additional considerations & treatment considerations considerations 48 Case Difficulty Assessment Form AAE
- 50. 1. Pt considerations Medical history Anesthesia Pt disposition Mouth opening Gag reflex Emergency condition 49
- 51. 2. Diagnostic & Rx considerations Diagnosis r/g difficulties Position in the arch Tooth isolation Morphoogical aberrations of crown Canal morphology resorption 50
- 52. 3. Additional considerations h/o trauma h/o endodontic treatment Endo perio condition 51
- 53. Levels of difficulty -Minimal -Moderate - High 52
- 54. Use of case difficulty assessment form Items in minimal difficulty – point 1 Moderate – point 2 High- point value – 5 53
- 55. Decision to treat or refer < 20 points – dental student may treat under facult’s supervision 20-40 points – experienced n skilled dental student , with close supervision by faculty > 40 merits - case not treated by predoctural student 54
- 59. 1. Caries/ Decayed tooth 6
- 62. 6 Root caries
- 63. 6 Root caries
- 64. 6 Root caries
- 65. 6 Root caries involving the distal root
- 66. 6
- 67. 6 Management of periodontally compromised mandibular molar with Hemisectioning: A case report Bandu Napte, Srinidhi Surya Raghavendra Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, 28-Oct-2014
- 68. 2. Swelling 6
- 69. 6
- 70. 69 FIGURE 1. Anatomy of the fascial spaces in axial (A) and coronal (B) images. SMS: submandibular space; SLS: sublingual space; PPS: parapharyngeal space; CS: carotid space; MS: masticatory space. SMG: submandibular gland; GGM: genioglossus muscle; MHM: mylohyoid muscle; MM: masseter muscle; MPM: medial pterygoid muscle; LPM: lateral pterygoid muscle; TM: temporal muscle.
- 71. 6
- 73. 6
- 74. 6
- 76. 6 Pocket Dentistry Fastest Clinical Dentistry Insight Engine Chapter 30 – trauma
- 77. 6Restor Dent Endod. 2013 May;38(2):59-64 Sin-Yeon Cho and Euiseong Kim 6-year follow up case of horizontal root fracture. (a) Horizontal root fractures were found on teeth #11 and #21 at the first visit in 2006; (b) The tooth #11 became necrotic and Received non-surgical root canal therapy in 2007; (c) 3-year follow up radiograph in 2009; (d) 6-year follow up radiograph in 2012.
- 78. 6 Figure 1: (a) The initial radiograph was showing the horizontal root fracture. (b)The periapical radiograph of the teeth was taken 3 months later. (c) Six month follow-up radiograph. (d) One-year follow-up radiograph. (e) Two-year follow-up radiograph Year : 2013 | Volume : 1 | Issue : 1 | Page : 19-23 Treatments of horizontal root fractures: Four case reports Ebru Kucukyilmaz, Murat Selim Botsali Journal of Pediatric dentistry
- 79. 6 Figure 4a. Schematic of class III fracture: incomplete vertical fracture involving the attachment apparatus. Figure 4b. Pretreatment radiograph of mandibular first molar demonstrating a class III fracture. Figure 4c. The mesial root has been amputated and the fracture is observed. Figure 4d. A 10-year recall of hemisection and restoration. Courtesy: Dentistry Today
- 80. 6 No treatment – the gingival tissue can be retracted during crown preparation Gingivectomy using electrosurgery - Crown lengthening including osseous recontouring Sub-epithelial connective tissue graft Mesial root amputation ?? Reattachment with RMGIC followed by crown placement / extraction ??
- 81. 6
- 83. crown – assessing the occlusion 6
- 84. 5. Sensitivity 6
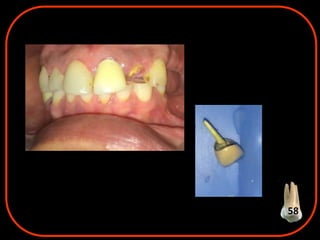
- 85. 6. Dislodged crown, post 58
- 86. 58
- 87. 58
- 88. 58
- 89. 58 Fracture of post Root perforation by post
- 90. 58 Courtesy : Dental hypothesis , systemic review Year : 2015 | Volume : 6 | Issue : 4 | Page : 141-145
- 91. Reasons for extraction Symptomatic tooth with non negotiable canals/ iatrogenic errors whose surgical management – not possible Failed rct not amenable to retreatment 58
- 92. Irreparable fracture of tooth Extensive periodontal breakdown 59
- 93. Single visit vs multiple visit Rx 6 No:of roots, time Severity of pt’s symptoms Clinician’s skill
- 94. 61 Single visit vs multiple visit Rx Post treatment obturation discomfort Post treatment flare up Radiologic success Healing rate JOE 2008 Figini, Lodi, et al IEJ 2008, Sathorn et al JOE 2008 , Figini et al JOE 2011 , Su, Wang et al
- 95. Periodontal considerations Assessing pulp vitality, extent of periodontal defect Combined lesions – guarded prognosis 62
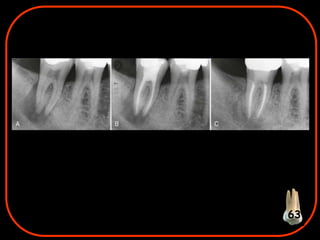
- 96. Understanding pathogenesis Sensibility testing Periodontal probing r/g assessment Evaluation of dental history 63
- 97. 63
- 98. Surgical considerations Lesions – non odontogenic Biopsy – definitive means , osseous pathosis Retreatment - approach ? Apical surgery – failed nsrct Cause should be corrected first 64
- 99. Endodontic surgery – primary procedure - Non surgical treatment is not possible 65
- 100. Pts with preoperative pain – lower healing rate // pts without pain Periodontal condition – interproximal bone levels, marginal bone loss Isolated endodontic lesion – better prognosis than endoperio lesion 66
- 101. Advent of microscope, endoscope , ultrasonics, retrograde filling instruments –improved surgery CBCT – 3-D image of tooth , pathosis, localizing mandibular canal, maxillary sinus 67
- 102. Restorative & Prosthodontic considerations Subosseous root caries Poor crown root ratio Extensive periodontal defects Malaligned teeth To be identified before Rx 68
- 103. Reduced coronal tooth structure beneath a full crown – difficult access & lack of idea about pulp chamber When possible , remove restorations before starting endodontic Rx Quality of coronal restoration – imp as the root filling 69
- 104. Conclusion Thus, according to Torabinejad and Goodacre, the decision to retain or remove teeth should be based on Thorough assessment of risk factors affecting long term prognosis of endodontic treatment 70
- 105. The clinician should consider Patient related factors Tooth and periodontium related factors Treatment related factors 71
- 106. The use of rotary instruments, ultrasonics, microscopy as well as new materials Made it possible to predictably reatin teeth that previously would have been extracted 72
- 107. In addition, even teeth that have failed following nsrct can often be retreated using non surgical or surgical approach. 73
- 108. 74 References
- 109. THANK YOU…