Causes of Financial Crises
- 2. On 15 September 2008, Lehman Brothers filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in a New York courtroom in the United States. Panic ensued. Uncertainty about its causes and contagious consequences brought many financial markets to a standstill.
- 3. A disturbance to financial markets, associated typically with falling asset prices and insolvency amongst debtors and intermediaries, which ramifies through the financial system, disrupting the market’s capacity to allocate capital.
- 4. Financial Crises in Developed / Emerging Countries • Financial crises have become more frequent and severe in both developed markets (DM) and emerging markets (EM) • Recent developed markets crises • US housing and sub-prime crisis in 2006-2008 • Global Financial Crisis (GFC) of 2008-2009 • Sovereign debt crises and economic crisis in the Eurozone (2010- 2013): Greece, Ireland, Portugal, Spain, Italy, Cyprus, Slovenia. + continuing Grexit Risk. • (Brexit: regarded by most as a shock rather than a crisis) • Recent emerging market crises: • Mexico (1994), East Asia (1997-98), Russia (1998), Turkey and Argentina (2001) • China’s 2015-16 financial market turmoil • Turkey 2017-17
- 5. Types of Financial Crisis • Currency crisis when a fixed exchange rate regime collapses or a currency goes into a free-fall e.g. in Turkey • Balance of Payments (BoP) or external debt crisis – when a country cannot attract the capital needed to finance a current account deficit – recent example Mongolia • Sovereign debt crisis – when a government cannot afford to pay the interest on their existing debts e.g. Greece • Banking crisis – when stability of banking system is low for example in Italy and Cyprus • Household debt crisis – for example in the UK and USA • Broad financial crisis that combines many elements of the above crises (Argentina in 2001)
- 6. Currency Crisis - Turkey • Political instability (failed coup in 2016) • Large current a/c deficit • Investors get nervous – capital flight intensifies • Country exposed to existing external debts • More expensive to repay when the value of the currency falls • Limited impact of central bank intervention • Higher interest rates risk causing a deep recession
- 7. External Debt Crisis - Mongolia • Resource rich country of 3 million • Super-fast growth during years of high commodity prices • But now vulnerable to global price shocks • China’s slowdown has hit Mongolian economy hard • Collapse in currency and tax revenues • Sought emergency external aid
- 8. Banking Crisis - Cyprus • Cypriot banks high exposure to over-leveraged local property companies. • Cyprus banks had also invested in Greek bonds – Greek bond haircut in 2012 imposed losses of around €4.5 billion on Cypriot banks • Risky expansion strategies – Cyprus banks had high interest rates causing large inflow of deposits from foreigners, mainly Russian, which gave the banks liquidity – these funds were invested poorly overseas 0.0% 5.0% 10.0% 15.0% 20.0% 25.0% 30.0% 35.0% 40.0% 45.0% 50.0% Non-perfomingloansratio
- 9. Cyprus – the first example of an emergency “bail-in” In 2013, the Bank of Cyprus used large deposits of above €100,000 to help fund its rescue deal, the first example of a “bail in” so that taxpayers would no longer carry the cost for failed banks. Large savings deposits were converted to capital and the Bank of Cyprus was kept afloat by €11.4bn in emergency central bank loans, a figure of more than 60 per cent of the country’s GDP in 2013.
- 10. Where will the next financial crisis come from? • The stock market • Car loans and credit card debt • House prices • Chinese economic slowdown • US Federal Reserve hiking rates
- 11. What are the key causes of financial crises? • Financial market failures 1. Irrational exuberance among agents (Shiller) 2. Increased complexity arising from financial innovation 3. Minsky hypothesis – stability breeds instability • Policy failures 1. Unintended consequences of financial deregulation 2. Banks too big to fail? Risky behaviour due to moral hazard? 3. Interest rates too low for too long (e.g. USA, EZ 2002-2007) 4. Large models of the economy which assume agents (businesses and consumers) always behave rationally 5. Failures of ratings agencies in pricing risk accurately • Structural changes in the global economy 1. Economic imbalances including global savings glut and low /zero real interest rates 2. Media and modern communications – immediate feedback
- 12. Credit Cycles and Excessively Low Policy Interest Rates Source: Haldane, www.bankofengland.co.uk/publications/Documents/speeches/2014/speech713.pdf
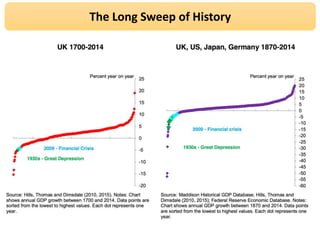
- 13. The Long Sweep of History
- 15. @tutor2ugeoff
Editor's Notes
- #2: The main financial assets are property, pensions, equities, unit trusts and cash.
- #3: What is a financial crisis? A disturbance to financial markets, associated typically with falling asset prices and insolvency amongst debtors and intermediaries, which ramifies through the financial system, disrupting the market’s capacity to allocate capital.
- #5: Emerging markets - The financial markets of developing countries.
- #8: Mongolia’s efforts to extricate itself highlight the dangers of the “resource curse” — the notion that countries blessed with tremendous natural resources find themselves at the mercy of wealth-destroying boom-bust cycles
- #9: Closing of Laiki Bank and the restructuring of the Bank of Cyprus, which entailed a haircut of 47.5% imposed on depositors.
- #12: Irrational exuberance: Investors still follow cycles of mania and crashes, rather than rationally calculating the probabilities of all relevant scenarios - and rather than considering the negative externalities of their transactions. Minsky Argues that capitalist financial systems are inherently unstable. Over periods of prolonged economic prosperity and high optimism about future prospects, financial institutions invest more in ever-riskier assets in search of higher returns, which can make the economic system more vulnerable in the case that default materializes.
- #13: For much of the period between 2001 and 2007, interest rates were exceptionally low – in nominal terms and, at times, in real terms too. Central banks across much of the developed world kept short-term interest rates low for so long because they feared a Japanese-style depression following the bursting of the dotcom bubble in 2000.