Chapter17 140331233521-phpapp01
- 1. Chapter 17:Chapter 17: Aldehydes and KetonesAldehydes and Ketones R H O Functional Group: CarbonylFunctional Group: Carbonyl Aldehyde: RCHO,Aldehyde: RCHO, Ketone: RCOR’,Ketone: RCOR’, R R' O
- 2. Some 300 million sperm are released by the male during ejaculation, while the female usually produces one large egg at a time. Only one sperm cell can fertilize the egg. How does it find it? Magnification: ~2,500 Sperm are selected for fertilization by their ability to “smell” a nearby egg. The 11-carbon aldehyde bourgeonal, above, activates this ability, whereas the straight-chain 11-carbon aldehyde, undecanal, shuts it down. A little aldehyde at a crucialA little aldehyde at a crucial moment.......moment....... O H
- 3. NomenclatureNomenclature The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones hasThe carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones has prioritypriority over all other polar or functional groupsover all other polar or functional groups used so far, namelyused so far, namely RX, ROH, , ,RX, ROH, , , (But not COOH)(But not COOH) >>In addition:In addition:
- 4. Systematic NamingSystematic Naming (IUPAC)(IUPAC) AldehydesAldehydes AlkanAlkanee AlkanAlkanalal. Longest chain starts. Longest chain starts at carbonyl carbon, which is C1.at carbonyl carbon, which is C1. ExamplesExamples:: FormFormaldehydealdehyde AcetAcetaldehydealdehyde IUPAC-accepted common namesIUPAC-accepted common names
- 5. Cyclic aldehydes have the endingCyclic aldehydes have the ending -carbaldehyde-carbaldehyde after cycloalkane name.after cycloalkane name. The carbon attached to -CHO is C1.The carbon attached to -CHO is C1. Examples:Examples: TheThe unit as a substituent is calledunit as a substituent is called formylformyl.. Cis-2-Cis-2-mercaptomercaptocyclo-cyclo- hexanehexanecarbaldehydecarbaldehyde CHO 1 2 3 4 SH
- 6. KetonesKetones AlkAlkaneane AlkanAlkanone.one. Longest chainLongest chain incorporates carbonyl carbon and isincorporates carbonyl carbon and is numbered from terminus close to C=O.numbered from terminus close to C=O. Cyclic ketones areCyclic ketones are cycloalkanones;cycloalkanones; CC=O=O isis C1C1.. Examples:Examples: CisCis-2-ethenyl-3--2-ethenyl-3- methylcyclohexanonemethylcyclohexanone (if racemic) or 2(if racemic) or 2SS,3,3S-.S-. 2-Pentanone O H H
- 7. An aldehyde containing a ketoneAn aldehyde containing a ketone C=O is called anC=O is called an oxooxoalkanal.alkanal. Example:Example: Substituent name:Substituent name: alkanoylalkanoyl O R O CH3 acetylacetyl, but, but propanoylpropanoyl (IUPAC accepted common name)(IUPAC accepted common name) O CH3CH2
- 8. O O HO Complex Aldehydes andComplex Aldehydes and KetonesKetones 4-Acetylbenzenecarboxylic acid4-Acetylbenzenecarboxylic acid Br O H O TransTrans-4-bromo-2-oxo-3-butenal-4-bromo-2-oxo-3-butenal
- 9. StructureStructure OrbitalsOrbitals The carbonyl group contains aThe carbonyl group contains a shortshort,, strongstrong, and very, and very polarpolar bond.bond. ResonanceResonance PolarizationPolarization Molecular structureMolecular structure EPMEPM 175 kcal mol-1
- 10. Polarization affects the physicalPolarization affects the physical constants of aldehydes and ketonesconstants of aldehydes and ketones -- Boiling points relatively high-- Boiling points relatively high -- Smaller members (acetaldehyde,-- Smaller members (acetaldehyde, acetone) are completely miscible withacetone) are completely miscible with waterwater
- 11. 11 H NMR: Carbonyl group isH NMR: Carbonyl group is deshieldingdeshielding UniquelyUniquely deshieldeddeshielded by polarization andby polarization and double bond effectdouble bond effect J ~ 2Hz
- 12. 1313 C NMRC NMR R R' O ~ 200 ppm~ 200 ppm
- 13. IRIR υυC OC O ~~ ---- = 1690-1750 cm= 1690-1750 cm-1-1 Conjugation reduces , strain increases itConjugation reduces , strain increases itυυCOCO ~~
- 14. H3C CH3 O H 11 H NMRH NMR 1313 C NMRC NMR IRIR
- 15. UVUV TheThe ππππ* and n* and nππ** transitions in acetonetransitions in acetone λλmaxmax (n(nππ*)*) = 275-295 nm= 275-295 nm Lone electronLone electron pairspairs :: ::
- 16. SynthesisSynthesis (A review of Chapter 8)(A review of Chapter 8) 1.1. OxidationOxidation of Alcoholsof Alcohols PrimaryPrimary aldehydesaldehydes SecondarySecondary ketonesketones UseUse chromium(VI)chromium(VI) reagentsreagents Selective: Will not oxidize alkene or alkyneSelective: Will not oxidize alkene or alkyne units. Especially mild is PCC:units. Especially mild is PCC: PyridinePyridinePyridinium chlorochromate :Pyridinium chlorochromate : “PCC”“PCC” NNHH ++ NN CrOCrO33ClCl --
- 17. Avoid water: CausesAvoid water: Causes overoxidationoveroxidation of primary alcoholsof primary alcohols ExamplesExamples::
- 18. 2.2. AllylicAllylic Oxidation:Oxidation: MnOMnO22 Selective: Will not attack ordinary alcoholsSelective: Will not attack ordinary alcohols Allylic H is reactiveAllylic H is reactive
- 19. 3.3. OzonolysisOzonolysis ofof alkenes:alkenes: OO33, then reducing agent, then reducing agent Oxidative cleavage of carbon-carbon doubleOxidative cleavage of carbon-carbon double bondsbonds
- 20. 4.4. HydrationHydration of alkynesof alkynes Hydration of the carbon–carbon triple bond yieldsHydration of the carbon–carbon triple bond yields enols that tautomerize to carbonyl compoundsenols that tautomerize to carbonyl compounds MarkovnikovMarkovnikov: Use Hg: Use Hg2+2+ , H, H22O, HO, H++ :: Anti-MarkovnikovAnti-Markovnikov: Use hydroboration-oxidation: Use hydroboration-oxidation
- 21. 5.5. Friedel-CraftsFriedel-Crafts alkanoylationalkanoylation ((Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution)Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution)
- 22. ReactionsReactions E.g., NaBH4, RLi, RMgX (H+ ) There are three regions of reactivity inThere are three regions of reactivity in aldehydes and ketonesaldehydes and ketones ReviewReview
- 23. Nucleophilic additions to carbonyls toNucleophilic additions to carbonyls to give alcoholsgive alcohols Addition reactions occur withAddition reactions occur with milder nucleophilesmilder nucleophiles, such, such as water, alcohols, amines, etc. To speed them up,as water, alcohols, amines, etc. To speed them up, acid oracid or base catalysisbase catalysis is required.is required.
- 24. Catalyzed IonicCatalyzed Ionic AdditionsAdditions Base CatalyzedBase Catalyzed Mechanisms:Mechanisms: Acid CatalyzedAcid Catalyzed Mechanisms:Mechanisms: X―Y = H―Nu X―Y = H―Nu
- 25. 1.1. Hydration:Hydration: Geminal DiolsGeminal Diols (Carbonyl Hydrates)(Carbonyl Hydrates) KK ~ 1~ 1 KK depends on “unhappiness” of C=Odepends on “unhappiness” of C=O polarization: Electron-withdrawingpolarization: Electron-withdrawing substituents activate, donors deactivate.substituents activate, donors deactivate.
- 27. ΔΔHH ° =° = -3.09-3.09 kcal molkcal mol-1-1 ,, ΔΔSS ° =° = -22.9-22.9 eu,eu, ΔΔGG ° =° = +3.74+3.74 kcal molkcal mol-1-1 ΔΔHH ° =° = -5.30-5.30 kcal molkcal mol-1-1 ,, ΔΔSS ° =° = -17.2-17.2 eu,eu, ΔΔGG ° =° = -0.18-0.18 kcal molkcal mol-1-1
- 28. 2. Addition of2. Addition of AlcoholsAlcohols (Not hemiketal:(Not hemiketal: IUPAC)IUPAC) Same as water, initially, to formSame as water, initially, to form hemiacetalshemiacetals K K K varies from < 1 to > 1, as with water. Depends on R. H+ or HO- H+ or HO-
- 29. IntramolecularIntramolecular variantvariant (important for(important for sugars, Chapter 24):sugars, Chapter 24): Best for 5- andBest for 5- and 6-membered rings.6-membered rings. Favored by entropyFavored by entropy relativerelative to intermolecular addition;to intermolecular addition; ΔΔGG ° =° = ΔΔHH ° - T° - TΔΔSS °° ΔΔSS ° is° is less negativeless negative forfor intramolecular reaction.intramolecular reaction. K >1!
- 30. We can drive the hemiacetal stepWe can drive the hemiacetal step furtherfurther withwith more alcohol and withmore alcohol and with HH++ catalysis:catalysis: AcetalsAcetals Acetals are stable to:Acetals are stable to: BaseBase Oxidizing agentsOxidizing agents Nucleophiles (Grignards,Nucleophiles (Grignards, alkyllithiums, hydrides)alkyllithiums, hydrides) Acetals areAcetals are NOTNOT stable to:stable to: AcidAcid (A geminal diether)(A geminal diether) K >1! (isolated)
- 32. Cyclic Acetals:Cyclic Acetals: Protecting GroupsProtecting Groups o o CHCH33OHOH IntramolecularIntramolecular variantvariant (important for(important for sugars, Chapter 24).sugars, Chapter 24). Best for 5- and 6-memberedBest for 5- and 6-membered rings.rings. HO O H H+ , H2O Hydrolysis = Deprotection
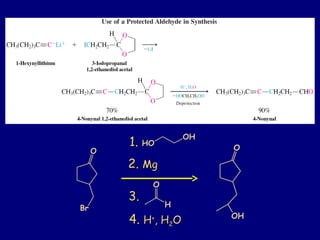
- 33. O OH O Br 1.1. HO OH 2.2. MgMg 3.3. 4.4. HH++ , H, H22OO O H
- 34. This is also a method toThis is also a method to protect diols:protect diols: O Br OH OH + H+ Br O O Mg BrMg O O O H+ OH OH HO
- 35. Thioacetals: Stable to acid!Thioacetals: Stable to acid! Application ofApplication of thioacetals:thioacetals: DesulfurizationDesulfurization Deprotection:Deprotection: Thioacetalization uses Lewis acid catalysis, e.g., ZnClThioacetalization uses Lewis acid catalysis, e.g., ZnCl22. Again, cyclic. Again, cyclic version particularly favorable.version particularly favorable. More applications: Chapter 23.More applications: Chapter 23.
- 36. 3.3. Amine AdditionsAmine Additions Example:Example: Ammonia and primary aminesAmmonia and primary amines add to the carbonyl functionadd to the carbonyl function and then dehydrate: Aand then dehydrate: A ““condensationcondensation” reaction.” reaction.
- 37. Mechanism:Mechanism: Hemiaminal DehydrationHemiaminal Dehydration Imine FormationImine Formation A condensationA condensation product (-Hproduct (-H22O)O) LipshutzLipshutz BBoysBBoys
- 38. IntramolecularIntramolecular reaction:reaction: Best for 5-Best for 5- and 6-membered rings.and 6-membered rings. O NH2 NCat.Cat. HH++ Teaser: AnTeaser: An 11 H NMRH NMR spectrum of an iminespectrum of an imine (downfield region)(downfield region)
- 39. Special IminesSpecial Imines + H+ H22N-OHN-OH (as H(as H33NN++ -OH Cl-OH Cl-- )) AnAn oximeoxime ++ SemicarbazideSemicarbazide SemicarbazoneSemicarbazone R R' O R R' N OH -H-H22OO R R' O N H NH2 O H2N R R' N H N O NH2 -H-H22OO R R' O ++ -H-H22OO HydrazoneHydrazone HydroxylamineHydroxylamine
- 40. Reaction of the carbonyl function withReaction of the carbonyl function with secondary aminessecondary amines gives hemiaminals ingives hemiaminals in which normal condensation is notwhich normal condensation is not possible: No H left on N. Therefore,possible: No H left on N. Therefore, water loss occurs to the “carbon side”water loss occurs to the “carbon side” to form anto form an enamineenamine.. EnamineEnamine FormationFormation
- 41. Mechanism:Mechanism: Enamines are useful, can be alkylated (Chapter 18-4).Enamines are useful, can be alkylated (Chapter 18-4).
- 42. Wolff-Kishner ReductionWolff-Kishner Reduction An Application ofAn Application of HydrazonesHydrazones Synthesis of a HydrazoneSynthesis of a Hydrazone Wolff-Kishner ReductionWolff-Kishner Reduction
- 43. Mechanism:Mechanism: Nitrogen eliminationNitrogen elimination In practice, the reaction is carried out without isolating the intermediate hydrazone. A diazaallylic anion
- 44. Use in alkylbenzene synthesis:Use in alkylbenzene synthesis: Br Br Br Br The Wolff-Kishner reduction is an alternative toThe Wolff-Kishner reduction is an alternative to the Clemmensen (rough, conc. acid) and thioacetal desulfurization methods (incompatible with cat. H2- sensitive groups) of deoxygenating aldehydes and ketones.
- 45. 4. Addition of4. Addition of Non-Non- organometallicorganometallic CarbonCarbon NucleophilesNucleophiles a. Cyanide makesa. Cyanide makes cyanohydrinscyanohydrins To make HCN, but keep pH slightly basic MechanismMechanism NaNaOHOH Usefulness: A C-C bond formation and -CN is a versatile functional groupUsefulness: A C-C bond formation and -CN is a versatile functional group
- 46. b. Theb. The Wittig ReactionWittig Reaction Phosphonium salt synthesisPhosphonium salt synthesis Georg Wittig (1897–1987) NP 1979 Discovered during an investigation of SDiscovered during an investigation of SNN22 reactions of phosphines with haloalkanes.reactions of phosphines with haloalkanes. The charge on PThe charge on P acidifies the adjacentacidifies the adjacent C-H: DeprotonationC-H: Deprotonation gives a so-calledgives a so-called ylideylide
- 47. Other (weaker) bases OK, such as CHOther (weaker) bases OK, such as CH33OO-- , CH, CH33OH, generate the ylide inOH, generate the ylide in equilibrium concentrations sufficient for the next step: Attack onequilibrium concentrations sufficient for the next step: Attack on carbonyl carbon and formation of alkenes.carbonyl carbon and formation of alkenes. NucleophilicNucleophilic Valence shell expandedValence shell expanded WittigWittig
- 48. Driving force: Very strong bondDriving force: Very strong bond CompareCompare::
- 49. CHCH22=P(C=P(C66HH55))33 Can be made cis or trans selective.Can be made cis or trans selective. Steroid modificationSteroid modification O CH2 H H H O O H H H Resonance-stabilized, trans-selective
- 50. 5. Addition of Hydroxy Groups5. Addition of Hydroxy Groups Revisited:Revisited: Baeyer-VilligerBaeyer-Villiger OxidationOxidation Oxidation of ketones by peroxycarboxylicOxidation of ketones by peroxycarboxylic acids givesacids gives esters:esters: Mechanism:Mechanism: Adolf vonAdolf von BaeyerBaeyer (1835-1917)(1835-1917) NP 1905.NP 1905. Victor VilligerVictor Villiger LipshutzLipshutzCarusoCaruso
- 51. Familiar? Recall: Chapter 9-3Familiar? Recall: Chapter 9-3 And Chapter 12-8And Chapter 12-8 The transition state of the Baeyer-The transition state of the Baeyer- Villiger oxidation involves migration ofVilliger oxidation involves migration of R’R’ through a push-pull electronic relay:through a push-pull electronic relay:
Editor's Notes
- #3: Reassessing the role of progesterone in fertilization—compartmentalized calcium signalling in human spermatozoa? Claire V. Harper1,2 and Stephen J. Publicover1,3 1 School of Biosciences, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, UK 2 Present address: School of Biological Sciences, Biosciences Building, Crown Street, University of Liverpool, Liverpool L69 7ZB, UK 3 Corresponding author. E-mail: [email_address] Abstract Top Abstract Sperm responses to oocyte... Effect of progesterone on... Response of human spermatozoa... Generation of [Ca2+]i... Role of progesterone-induced... Compartmentalized [Ca2+]I... References Progesterone is present at micromolar concentrations in the vicinity of the oocyte. Human spermatozoa generate a biphasic rise in intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) and undergo the acrosome reaction upon progesterone stimulation, suggesting that the hormone acts as a secondary inducer or ‘primer’ of the acrosome reaction in association with the zona pellucida. However, the sensitivity of human spermatozoa to progesterone is such that many cells may undergo the acrosome reaction prematurely, compromising their ability to fertilize. We have shown that exposing human spermatozoa to a progesterone gradient, simulating the stimulus encountered as sperm approach the oocyte, results in a novel response. A slow rise in [Ca2+]i occurs, upon which, in many cells, [Ca2+]i oscillations are superimposed. Cells showing this pattern of response do not undergo the acrosome reaction, but instead show an alternating pattern of flagellar activity associated with peaks and troughs of [Ca2+]i. A Ca2+ store in the rear of the sperm head apparently generates this complex signal, functioning as an ‘[Ca2+]i oscillator’. We propose that: (i) the acrosome reaction and flagellar beat are regulated by separate Ca2+ stores; (ii) these stores are mobilized through different mechanisms by different agonists; and (iii) progesterone in vivo acts as a switch for the oscillator which regulates the flagellar beat mode. Key words: calcium/motility/oscillation/progesterone/sperm Sperm responses to oocyte-derived factors Top Abstract Sperm responses to oocyte... Effect of progesterone on... Response of human spermatozoa... Generation of [Ca2+]i... Role of progesterone-induced... Compartmentalized [Ca2+]I... References After deposition in the female tract, a mammalian sperm must swim to the oocyte, requiring both motility through a viscous environment and (probably) chemotactic control of that motility. On reaching the oocyte–cumulus complex, the cell has to penetrate the layers of cumulus and zona pellucida, a process dependent upon both the acrosome reaction (AR) and regulation of motility. The sperm must, therefore, detect and respond appropriately both ‘remotely’ (to factors derived from the oocyte) and also to stimuli presented upon direct contact with the egg. These stimuli must elicit intracellular signals that achieve complex regulation of the flagellum (both beat mode and directional) and appropriately timed activation of the AR. Sperm responses to factors derived from the egg and its vestments are primarily mediated through [Ca2+]i, which is known to control flagellar activity both during regulation of flagellar beat mode (Ho et al., 2002; Harper et al., 2004 ) and during chemotactic responses (Spehr et al., 2003 , 2004 ). Ca2+ is also pivotal to induction of the AR (Publicover and Barratt, 1999). At least two components of the egg vestments, zona pellucida and progesterone (secreted at high concentrations by the cumulus cells), activate Ca2+ signalling in mammalian spermatozoa (Florman et al., 1989 ; Blackmore et al., 1990) . The induction of the AR by solubilized zona pellucida has been studied in detail in the mouse model and involves activation of a T-type voltage-operated calcium chanel (VOCC) followed by store mobilization and prolonged (probably) capacitative Ca2+ influx (Florman et al., 1992; Evans and Florman, 2002 ). In contrast, the significance of progesterone is much less clear. The responsiveness of human spermatozoa to progesterone correlates with the fertilization rate at IVF (Krausz et al., 1996 ; Forti et al., 1999 ; Giojalas et al., 2004 ), and removal of cumulus cells from oocytes significantly reduces the success rate of IVF in most mammals (Tanghe et al., 2002 ; van Soom et al., 2002). However, the most commonly observed effect of progesterone-induced Ca2+ influx, stimulation of the AR, is arguably not an adaptive response. Human spermatozoa respond with elevation of [Ca2+]i and the AR to doses well below the 1–10 µmol/l that is believed to occur adjacent to the oocyte (Osman et al., 1989 ; Baldi et al., 1991 ; Harper et al., 2003) . The AR should therefore occur in many cells before they enter the cumulus, potentially compromising their ability subsequently to penetrate the zona. Identification of a Testicular Odorant Receptor Mediating Human Sperm Chemotaxis Marc Spehr,1 Günter Gisselmann,1 Alexandra Poplawski,1 Jeffrey A. Riffell,2 Christian H. Wetzel,1 Richard K. Zimmer,23 Hanns Hatt1* Although it has been known for some time that olfactory receptors (ORs) reside in spermatozoa, the function of these ORs is unknown. Here, we identified, cloned, and functionally expressed a previously undescribed human testicular OR, hOR17-4. With the use of ratiofluorometric imaging, Ca2+ signals were induced by a small subset of applied chemical stimuli, establishing the molecular receptive fields for the recombinantly expressed receptor in human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells and the native receptor in human spermatozoa. Bourgeonal was a powerful agonist for both recombinant and native receptor types, as well as a strong chemoattractant in subsequent behavioral bioassays. In contrast, undecanal was a potent OR antagonist to bourgeonal and related compounds. Taken together, these results indicate that hOR17-4 functions in human sperm chemotaxis and may be a critical component of the fertilization process.