Chapter19 140331234115-phpapp02
- 1. Chapter 19: CarboxylicChapter 19: Carboxylic AcidsAcids CarboxyCarboxy group: -COOH, -COgroup: -COOH, -CO22H,H,
- 2. Naming: Alkanoic AcidsNaming: Alkanoic Acids IUPAC: Replace –IUPAC: Replace –ee of alkane name withof alkane name with –oic acid–oic acid O OH 4-Methylhexanoic acid4-Methylhexanoic acid C1C1 Cyclic:Cyclic: Cycloalkanecarboxylic acidsCycloalkanecarboxylic acids O OH Cyclohexanecarboxylic acidCyclohexanecarboxylic acid OHO 1-Naphthalenecarboxylic acid1-Naphthalenecarboxylic acid C1, as in cyclicC1, as in cyclic aldehydesaldehydes
- 4. Carboxylic acids takeCarboxylic acids take precedenceprecedence over other groups:over other groups: Include as many functions as possible in stemInclude as many functions as possible in stem (Better than 4-acetylheptanoic acid)(Better than 4-acetylheptanoic acid)
- 6. The carboxy group is polar,The carboxy group is polar, undergoes hydrogen bonding, andundergoes hydrogen bonding, and forms dimers:forms dimers: Dimerization causes relativelyDimerization causes relatively high melting and boiling pointshigh melting and boiling points
- 8. 11 H NMR Chemical ShiftsH NMR Chemical Shifts HO C O H 10-13 ppm10-13 ppm 2-2.5 ppm2-2.5 ppm cf. aldehydescf. aldehydes and ketonesand ketones Aldehyde likeAldehyde like H C O OH
- 10. 1313 C NMR ChemicalC NMR Chemical ShiftsShifts Not quiteNot quite as low fieldas low field as aldehydeas aldehyde or ketoneor ketone
- 11. IR SpectroscopyIR Spectroscopy Two important bands:Two important bands: ννO-HO-H = 2500-3300 cm= 2500-3300 cm-1-1 ,, ννC=OC=O = 1710= 1710 -1-1
- 12. ResonanceResonance ~200 ppm~200 ppm ~180 ppm~180 ppm
- 13. AcidityAcidity The carboxy group is relatively acidic:The carboxy group is relatively acidic: AcetateAcetate Reasons: 1. CarbonylReasons: 1. Carbonyl carboncarbon is inductively stronglyis inductively strongly electronelectron withdrawingwithdrawing, 2., 2. CarboxylateCarboxylate ion is stabilized byion is stabilized by resonanceresonance
- 14. Compare …Compare … H 2-Propenyl (allyl)2-Propenyl (allyl) CH2 H2CBBHH ++ ppKKaa ~ 40~ 40 B++
- 15. Electron withdrawingElectron withdrawing groupsgroups increaseincrease the acidity (decreasethe acidity (decrease ppKKaa):): CFCF33COOHCOOH ppKKaa ~ 0.23~ 0.23 DistanceDistance affects acidity:affects acidity: COOH COOH Cl ppKKaa 4.194.19 ppKKaa 3.983.98
- 16. BasicityBasicity Protonated on theProtonated on the carbonyl oxygencarbonyl oxygen:: Allows forAllows for allylic resonanceallylic resonance
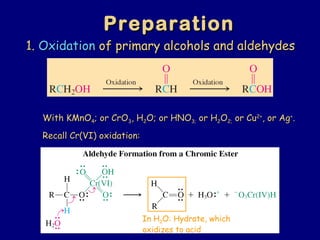
- 17. 1.1. OxidationOxidation of primary alcohols and aldehydesof primary alcohols and aldehydes With KMnOWith KMnO44; or CrO; or CrO33, H, H22O; or HNOO; or HNO3;3; or Hor H22OO2;2; or Cuor Cu2+2+ , or Ag, or Ag++ .. Recall Cr(VI) oxidation:Recall Cr(VI) oxidation: PreparationPreparation In H2O: Hydrate, which oxidizes to acid
- 18. 2.2. CarbonationCarbonation: Organometallic: Organometallic reagents and carbon dioxidereagents and carbon dioxide Example:Example: Synthetic strategy:Synthetic strategy: RHRH →→ RXRX →→ RMgBrRMgBr →→ RCORCO22HH
- 19. 3.3. Nitrile hydrolysisNitrile hydrolysis Mechanism:Mechanism: Tautomerization
- 20. COOH Cl C≡N Cl 1.NaOH, H2O 2. H+, H2O 90% Cyanohydrin-hydrolysis:Cyanohydrin-hydrolysis: αα-Hydroxy acids-Hydroxy acids
- 21. ReactionsReactions Nucleophilic substitution occursNucleophilic substitution occurs byby addition-eliminationaddition-elimination Lead to carboxylic acid derivatives:Lead to carboxylic acid derivatives: General:General: :Nu:Nu EE++ LeavingLeaving groupgroup
- 22. Elimination Nucleophilic SubstitutionNucleophilic Substitution by Addition- Eliminationby Addition- Elimination TetrahedralTetrahedral intermediateintermediate Addition : :Potential problem: AcidityPotential problem: Acidity Acid or base catalyzedAcid or base catalyzed
- 23. Base Catalyzed MechanismBase Catalyzed Mechanism Must not compete with :NuMust not compete with :Nu--
- 24. Acid Catalyzed MechanismAcid Catalyzed Mechanism
- 25. Synthesis of CarboxylicSynthesis of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesAcid Derivatives A.A. AlkanoylAlkanoyl HalidesHalides:: R C O OH X=X= Cl, BrCl, Br + - Cl + - OHR C O Cl MoreMore stablestable LessLess stablestable PoorPoor NuNu Bad leavingBad leaving group, stronggroup, strong base, goodbase, good NuNu uphilluphill
- 26. Therefore use other reagents:Therefore use other reagents: SOClSOCl22, PCl, PCl55, PBr, PBr33 SOClSOCl22:: Mechanism:Mechanism: First step is to convert theFirst step is to convert the bad leaving group OH into a good onebad leaving group OH into a good one GoodGood leavingleaving groupgroup
- 27. Same as ROHSame as ROH RCl, except addition-eliminationRCl, except addition-elimination and not Sand not SNN22 Then it is addition-elimination:Then it is addition-elimination:
- 29. PBrPBr33 Mechanism:Mechanism: 1.1. 2.2. R O OH PBr2Br R O OPBr2 HBr++:: R O OPBr2 ++ H+ Br - R OH OPBr2 R O Br +HOPBr2 Br : : :: : : : : 1 2
- 30. B.B. AnhydridesAnhydrides Cyclic anhydrides: Just heat, or SOClCyclic anhydrides: Just heat, or SOCl22
- 31. C.C. Esters:Esters: Alcohols + carboxylic acids, cat. mineral acid, reversibleAlcohols + carboxylic acids, cat. mineral acid, reversible Example:Example: ΔΔHH º ~ 0,º ~ 0, ΔΔSS º ~ 0,º ~ 0, ΔΔGG º ~ 0º ~ 0 Reverse:Reverse: Ester hydrolysisEster hydrolysis, driven by excess H, driven by excess H22O. Can also beO. Can also be effected by aqueous NaOH (Chapter 6: RX + Naeffected by aqueous NaOH (Chapter 6: RX + Na+-+- OO22CR).CR). EsterHydrEsterHydr GallagGallag
- 32. MechanismMechanism:: HH++ mineral acid, e.g., Hmineral acid, e.g., H22SOSO44, HCl, proceeds initially, HCl, proceeds initially likelike acetalizationacetalization of aldehydes and ketonesof aldehydes and ketones Note: Carbonyl oxygen is alwaysNote: Carbonyl oxygen is always more basicmore basic thanthan hydroxy oxygen, because ofhydroxy oxygen, because of resonanceresonance in thein the protonated product.protonated product.
- 33. EsterEster
- 34. Intramolecular esterification:Intramolecular esterification: LactonesLactones Even without removing the water the equilibrium isEven without removing the water the equilibrium is favorable because of entropy (favorable because of entropy (positivepositive). As always in). As always in reversible reactions (thermodynamic control),reversible reactions (thermodynamic control), cyclization is best for five and six membered rings.cyclization is best for five and six membered rings.
- 35. D.D. AmidesAmides This method is rarely used. Problem: FastThis method is rarely used. Problem: Fast (although reversible) salt formation (reverse is(although reversible) salt formation (reverse is slow, henceslow, hence ΔΔ needed)needed) Heat carboxylic acid with an amine:Heat carboxylic acid with an amine: Note: MNote: M++ -- NHNH22 are alsoare also called amides.called amides.
- 36. Mechanism:Mechanism: Highly pHighly pHH dependent profile. We shall see independent profile. We shall see in Chapter 20 that amide formation is betterChapter 20 that amide formation is better accomplished by “activation” of the carboxyaccomplished by “activation” of the carboxy group, as in alkanoyl halides or anhydrides orgroup, as in alkanoyl halides or anhydrides or even esters.even esters.
- 37. Cyclic amides:Cyclic amides: ImidesImides from dioicfrom dioic acids, oracids, or lactamslactams fom amino acidsfom amino acids Imide formation:Imide formation:
- 38. Lactam formation:Lactam formation: Penicillins are lactams:Penicillins are lactams: N S O COOH HHRHN OH R' R’OH stands for transpeptidase, theR’OH stands for transpeptidase, the enzyme necessary for all cell wallenzyme necessary for all cell wall construction. Osmotic pressure in aconstruction. Osmotic pressure in a cell is enormous, 10-20 atm. Penicillincell is enormous, 10-20 atm. Penicillin causes literally an explosion.causes literally an explosion.
- 39. Other Reactions ofOther Reactions of Carboxylic AcidsCarboxylic Acids 1.1. ReductionReduction by LiAlHby LiAlH44 Mechanism complex,Mechanism complex, not clear, possibly via:not clear, possibly via: C O O H R Al Li H:
- 40. 2.2. Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky Reaction:Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky Reaction: MakesMakes αα-bromocarboxylic acids-bromocarboxylic acids P + BrP + Br22 PBrPBr33 Important functionalization; can be exploited to accessImportant functionalization; can be exploited to access αα-amino acids. Mechanism is reminiscent of acid-amino acids. Mechanism is reminiscent of acid catalyzed halogenation of aldehydes and ketones.catalyzed halogenation of aldehydes and ketones. Jakob VolhardJakob Volhard (1834-1910)(1834-1910) Nikolaj Zelinski (1861-1953) Carl Magnus von Hell (1849-1926)
- 41. Mechanism:Mechanism: As in the acid catalyzed halogenation of aldehydes and ketones,As in the acid catalyzed halogenation of aldehydes and ketones, this needsthis needs enolizationenolization of RCHof RCH22COOH. However, the COOH groupCOOH. However, the COOH group is too stable to enolize sufficiently, hence it requiresis too stable to enolize sufficiently, hence it requires activationactivation to RCHto RCH22C(O)Br.C(O)Br. pKa ~ 16!
- 43. Detailed mechanisms of steps 2 and 3:Detailed mechanisms of steps 2 and 3: