Chemistry of lipid 3 _lipoprotein chemistry and prostaglandins.pptx
- 5. LIPOPROTEIN
- 10. PROTEIN COMPONENT OF LIPOPROTEIN PROMOTE TRANSPORT AND UPTAKE OF LIPIDS ACTS AS LIGAND ACTIVATION OF ENZYMES APOPROTEINS
- 11. • C-I • C-II • C-III • Except LDL • B-48 • B-100 • A-I • A-II A B C E
- 12. • All liver • Liver • B-48: Intestine • B-100: • Liver • A-I: Liver & Intestine • A-II:Liver A B C E
- 13. CHYLOMICRON Formed in the intestinal mucosal cells Rich in TG Contain apo-B-48 Apo-E Apo-C apo-A
- 14. VLDL Synthesized in the liver Contain apo-B-100, C-II and apo-E
- 19. LDL- Highest CE HDL – Highest protein CM – Highest TG
- 20. ANALYTE NORMAL VALUE Total plasma lipids 400-600mg/dl Total cholesterol 140-200mg/dl HDL cholesterol 40–60 mg/dL LDL cholesterol 80-130mg/dl Triglycerides 50-150mg/dl
- 21. EICOSANOIDS Eicosanoids are formed from 20 carbon PUFA arachidonic acid Eicosanoids Prostanoids Prostaglandins PG Prostacyclins PGI Thromboxanes TX Leukotriens LT What is Eicosanoids? Classification
- 22. PROSTAGLANDINS
- 28. • PGA Keto group at C9; double bond C10 and 11 • PGB Keto group at C9; double bond C8 and 12 • PGD OH group at C9; keto group at C11 • PGE Keto group at C9; OH group at C11 • PGF OH groups at C9 and C11 (Fig.14.2) • PGG Two oxygen atoms, interconnected to each • other, and bonded at C9 and C11; • hydroperoxide group at C15 • PGH Same ring as PGG; but C15 has OH group • PGI Double ring. Oxygen attached to C6 and • C9, to form another 5-membered ring. • Hence called prostacyclin.
- 30. PROSTAGLANDINS - FUNCTIONS Effects on GIT Effects on Inflammation Effects on Respiratory tract Effects on uterus Effects on CVS
- 31. PROSTAGLANDINS - FUNCTIONS PGI2 Vasodilatation Inhibits platelet aggregation PGA and PGE class prostaglandins lower blood pressure. Effects on CVS
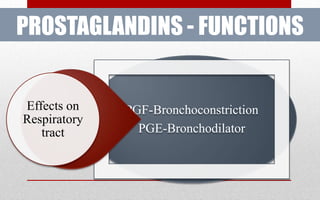
- 33. PROSTAGLANDINS - FUNCTIONS PGF-Bronchoconstriction PGE-Bronchodilator Effects on Respiratory tract
- 34. PROSTAGLANDINS - FUNCTIONS PGE2 Involved in inflammatory response Effects on Inflammation
- 35. PROSTAGLANDINS - FUNCTIONS PGE2 suppress gastric acid secretion Effects on GIT
- 36. Subscript number denotes number of double bonds Capital letters – designate class Most common Thromboxanes [TX]
- 37. Increase platelet aggregation Vasoconstriction Mobilize intracellular calcium Smooth muscle contraction Bronchoconstriction Thromboxanes - FUNCTIONS
- 38. Grouped into 5 classes [A to E] LTC4 Leukotrines [LT]
- 39. Increase chemotaxis Facilitate inflammation & allergic reactions Contraction of smooth muscle Bronchoconstriction Vasoconstriction Leukotrines - Functions
Editor's Notes
- #3: Lipids need to be transported in plasma to tissues and organs to perform their metabolic functions. Given the hydrophobic nature of the neutral fats (TG and cholesterol esters), lipid transport via plasma would not be possible without some form of hydrophillic adaptation. The lipids are transported by a series of micelles called lipoproteins, which consist of an outer monolayer of protein (apolipoprotein) and polar lipids (phospholipid and unesterified cholesterol). The inner core consists of the hydrophobic lipids which is the cholesteryl esters & TAG. Lipoproteins function both to keep their component lipids soluble as they transport them in the plasma, and also to provide an efficient mechanism for transporting their lipid contents and to (and from) the tissues. NB. In humans the transport system is less perfect than in other animals, that is why they experience a gradual deposition of lipid especially cholesterol in tissues (atherosclerosis).
- #22: Almost all mammalian cells except red blood cells produce prostaglandins and their related compounds, the prostacyclins, thromboxanes, leukotrienes and lipoxins, known collectively as eicosanoids since they are all C20 compounds; Greek: eikosi, twenty). The eicosanoids, like endocrine hormones, have profound physiological effects at extremely low concentrations. For example, they mediate the following: (1) the inflammatory response, notably as it involves the joints (rheumatoid arthritis), skin (psoriasis), and eyes; (2) the production of pain and fever; (3) the regulation of blood pressure; (4) the induction of blood clotting; (5) the control of several reproductive functions such as the induction of labor; and (6) the regulation of the sleep/wake cycle. The enzymes that synthesize these compounds and the receptors to which they bind are therefore the targets of intensive pharmacological research. The eicosanoids are also hormonelike in that they bind to G-protein-coupled receptors (Section 19-2B), and many of their effects are intracellularly mediated by cAMP. Unlike endocrine hormones, however, they are not transported in the bloodstream to their sites of action. Rather, these chemically and biologically unstable substances (some decompose within minutes or less in vitro) are local mediators (paracrine hormones; Section 19-1); that is, they act in the same environment in which they are synthesized.
- #24: Prostaglandins are all derivatives of the hypothetical C20 fatty acid prostanoic acid in which carbon atoms 8 to 12 form a cyclopentane ring (Fig. 25-66a). Prostaglandins A through I differ in the substituents on the cyclopentane ring (Fig. 25-66b):PGAs are ,-unsaturated ketones,PGEs are-hydroxy ketones, PGFs are 1,3-diols, etc. In PGF, the C9 OH group is on the same side of the ring as R1; it is on the opposite side in PGF.The numerical subscript in the namerefers to the number of double bonds contained on the side chains of the cyclopentane ring (Fig. 25-66c). In humans, the most prevalent prostaglandin precursor is arachidonic acid (5,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid), a C20 polyunsaturated fatty acid that has four nonconjugated double bonds.The double bond at C14 is six carbon atoms from the terminal carbon atom (the carbon atom), making arachidonic acid an –6 fatty acid. As Sune Bergström and Bengt Samuelsson demonstrated, arachidonic acid is synthesizedsynthesized from the essential fatty acid linoleic acid (also an –6 fatty acid). This occurs via its desaturation with a 6- desaturase to yield -linolenic acid (GLA), followed by elongation and a second desaturation, this time with a 5- desaturase (Fig. 25-67; Section 25-4E). Prostaglandins with the subscript 1 (the “series-1” prostaglandins) are synthesized from dihomo--linolenic acid (DGLA; 8,11,14- eicosatrienoic acid), whereas “series-2” prostaglandins are synthesized from arachidonic acid. -Linolenic acid (ALA), another essential fatty acid since the 15-desaturase required for its synthesis occurs only in plants, is a precursor of 5,8,11,14,17-eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and the “series-3” prostaglandins. Since arachidonate is the primary prostaglandin precursor in humans, we shall mostly refer to the series-2 prostaglandins in our examples. Note, however, that when dietary linoleic acid and -linolenic acid are equally available, the relative activities of the 5- and 6- desaturases are important in determining the relative amounts of these prostaglandin precursors. Hvon Euler thought that these compounds originated in the prostate gland (hence their name) but they were later shown to be synthesized in the seminal vesicles.
















![HDL
Contain
Apo-A-I[Major]
Apo-C
Apo-E](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemistryoflipid3lipoproteinchemistryandprostaglandins-230830173608-70057050/85/Chemistry-of-lipid-3-_lipoprotein-chemistry-and-prostaglandins-pptx-17-320.jpg)






![PROSTAGLANDINS[PG]
Nomenclature
Classification
Subscript](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemistryoflipid3lipoproteinchemistryandprostaglandins-230830173608-70057050/85/Chemistry-of-lipid-3-_lipoprotein-chemistry-and-prostaglandins-pptx-24-320.jpg)










![Subscript number denotes number of double bonds
Capital letters – designate class
Most
common
Thromboxanes [TX]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemistryoflipid3lipoproteinchemistryandprostaglandins-230830173608-70057050/85/Chemistry-of-lipid-3-_lipoprotein-chemistry-and-prostaglandins-pptx-36-320.jpg)

![Grouped into 5 classes [A to E]
LTC4
Leukotrines [LT]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemistryoflipid3lipoproteinchemistryandprostaglandins-230830173608-70057050/85/Chemistry-of-lipid-3-_lipoprotein-chemistry-and-prostaglandins-pptx-38-320.jpg)

