Clamp connectins
- 2. Clamp Connection ● It operates to ensure the maintenance of the dikaryotic condition in each new cell or compartment of the secondary mycelium. ● Structure formed by two hyphal cells of certain fungi. ● Used to create genetic variation like croizer mechanism of sexual reproduction.
- 3. ● When a binucleate hyphal tip is ready to divide, it arises between the two nuclei and form a hook.
- 4. Mechanism of Clamp connection
- 5. Role of clamp connection in maintaining a dikaryon
- 6. ● It is interesting to note that some mycologists have likened these structures to the hooks of the ascogenous hyphae in Ascomycota.
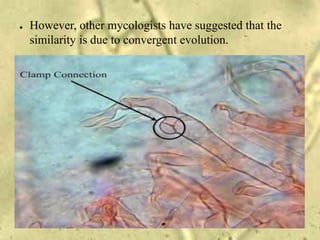
- 7. ● However, other mycologists have suggested that the similarity is due to convergent evolution.
- 8. Dolipore Septum ● In some species, the septum wall simply tapers toward the central pore while in others the septal wall near the pore is thickened to form a characteristic dough nut like or barrel- shaped swelling. This latter type of septum is called a dolipore septum.
- 9. ● It is a dome- shaped, membranous structure referred to here as the septal pore cap. ● The structure appears to consist of modified endoplasmic reticulum and is an integral and functional part of the septal apparatus.
- 11. ● Although the caps of some species appear as continuous, non- porous structures, those of most species are perforate. ● In some cases, the perforations are large and of irregular size and spacing while in other cases they are smaller and of regular size and spacing.
- 12. Functions of Doliopore Septum ● It is probably safe to say that its exact function remains unclear. ● It would seem, however, that the pore cap acts as a screen or sieve, possibly permitting the passage of some cellular components from one cell to the next while retarding others. ● Various ultrastructural and cytochemical changes also have been reported in doliopore septa during basidiocarp development.