CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISM - BY MOHAMMAD HAMMAD KHAN
- 1. GALGOTIAS UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOTHERAPY TOPIC- CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISM SUBJECT – PATHOLOGY &MICROBIOLOGY SUBJECT CODE - BPTH2001 • SUBMITTED TO :- DR. VIKAS SHARMA SIR(PT.) PRESENTED BY:- 1. SAURABH RAJ 2. RAKHI 3. MOHAMMAD HAMMAD KHAN 4. MUSKAN KUMARI 5. VANDANA YADAV
- 2. CONTENT THREE KINGDOM CLASSIFICATION FIVE KINGDOM CLASSIFICATION MICRO-ORGANISM DEFINATION TYPESOF MICRO- ORGANISM CLASSIFICATION OF MICRO-ORGANISM. VIRUS, BACTERIA, PROTOZOA, ALGAE, FUNGI SHAPE AND APPEARANCE SIZE OF VIRUS MODE OF REPRODUCTION HABITAT AND NUTRTION MICROORGANISM CAUSING INFECTION
- 3. THREE KINGDOM CLASSIFICATION • THREE KINGDOM CLASSIFICATION was put forward by HAECKEL in order to overcome the limitations of two kingdom classification. • HAECKEL then classified the organisms into 3 kingdom I.e. 1. Kingdom animalia 2. Kingdom plantae 3. Kingdom protista (it includes protozoa,fungi, bacteria and other microorganism)
- 5. FIVE KINGDOM CLASSIFICATION The five kingdom classification was proposed by ROBERT WHITTAKER He broadly divided the organism into kingdoms on the basis of str. Of cell, mode of nutrition, source of nutrition, body organisation and reproduction. The kingdoms include:- •Kingdom Monera(bacteria and archae) •Kingdom Protista( algae and protozoa) •Kingdom Fungi( fungi) •Kingdom Plantae ( plants) •Kingdom Animalia ( animals)
- 7. DEFINATION MICROORGANISMS or microbes are microscopic organisms that exist as unicellular or multicellular. Microorganisms are widespread in nature and are beneficial to life but some can cause serious harm.
- 8. TYPES OF MICROORGANISM • MICRO-ORGANISM ARE GROUPED INTO 5 CATEGORIES VIRUS BACTERIA PROTOZOA ALGAE FUNGI
- 9. CLASSIFICATION Micro-organism are classified on the basis of characteristics:- • SHAPE &APPEARANCE • SIZE • HABITAT • NUTRITION • METHOD OF REPRODUCTION
- 10. VIRUSES
- 11. Shape & Appearance • VIRUSES are the smallest micro- organism. • Viruses consists of strands of nucleic acid(DNA) which protected by a protein coat. • Shapes :- • HELICAL • POLYHEDRAL • SPHERICAL • COMPLEX
- 12. Size of Viruses • Smallest micro-organism. • Size is even smaller than bacteria.
- 13. Mode of Reprduction Viruses reproduce when it is in contact with living cells.
- 14. STEP 1
- 15. STEP 2
- 16. STEP 3
- 17. STEP 4
- 18. STEP 5
- 19. HABITAT AND NUTRITION • The cell where the viruses are attached are called as host cells. • This cell becomes the HABITAT of the viruses. • Viruses do not make their own food. • They obtain food from animals, plants and some bacteria.
- 20. VIRUS CAUSING INFECTION • RHINOVIRUS – causes common cold • RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS – causes infection of both upper respiratory infection(common cold) and lower respiratory infection (pnumonia and bronchiolitis) • HERPES SIMPLE VIRUS- causes cold sores • HEPATITIS A- this virus causes liver and causes hepatitis A • HIV VIRUS- this leads to AIDS. • ENTEROVIRUS – causes viral meningitis
- 21. BACTERIA
- 22. Appearance • Bacteria are surrounded with tough CELL WALL- support and maintain the shape of the cell • Bacteria have hundred of hairlike structures called PILLI- enables bacteria to stick to any surface. • Bacteria have a TAIL - helps in locomotion
- 23. SHAPE OF BACTERIA LONG CHAIN(STREPTOCOCCI) SPIRALROD SHAPEDSPHERICAL BACILI BUNCHES OF GRAPE(STAPHYLOCOCCI)
- 25. Nutrition • Bacteria carried out photosynthesis for food • Some live as parasites • Some live as saprotrophes
- 26. Method of Reproduction BY BINARY FISSION
- 27. Habitat
- 28. BACTERIA CAUSING INFECTION • CLOSTRIDIUM BOTULINUM – life threatening bacterium that produces powerful neurotoxins. • E. COLI - this causes diarrheal illness that may be accompnied by nausea ,vomiting , fever and abdominal cramps. • SALMONELLA – causes fever,diarrhoea and abdominal cramps. • NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE- causes gonorrhea and it also inc. The risk of pelvic inflammatory diseases in women. • MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS - causes TB.
- 29. PROTOZOA
- 30. Size & Appearance • They are unicellular microscopic organism • They have complex internal str. I.e. such as nuclei containing genetic material • Size ranges from 5- 250 micrometer. • It does't have fixed shape • AMOEBA have pseudopodia – help in locomotion and engulfing food • PARAMESIUM have cilia- help in locomotion and engulfing food
- 32. Habitat AMOEBA • SOIL • FRESH WATER • OCEAN • OTHER ORGANISM AS PARASITES PARAMESIUM • FRESH WATER
- 34. Mode of Reproduction AMOEBA • BINARY FISSION PARAMESIUM • BINARY FISSION • CONJUGATION
- 35. BINARY FISSION
- 36. CONJUGATION
- 37. PROTOZOA CAUSING INFECTION • CRYPTOSPORIDIUM PARVUM- causes cryptosporidiosis(an intestinal illness). • ENTAMOEBA HISTOLYTICA- causes amoebiasis which is known as amoebic dysentery. • CYCLOSPORA CAYETANENSIS- causes cyclosporiasis • Protozoas mainly cause GI TRACT infections.
- 38. ALGAE
- 39. Appearance • Algae are eukaryotic organism • They have no roots, stems or leaves but have chlorophyll • Algae are multicellular or unicellular
- 40. Habitat • Unicellular algae found in water. • Algae may occur in moist soil or on the surface of moist rock and wood. • Alage live with fungi in lichens.
- 41. Nutrition • Most of the algae are PHOTOAUTOTROPHIC(prepare their food by their own with the help of chlorophyll and sunlight) • Some of the algae are CHEMOHETEROTROPHIC( obtain energy from chemical reactions and nutrients from preformed organic matter. • Most species are saprophytes. • Some are parasites.
- 42. Mode of Reproduction • Reproduction occurs in both ASEXUAL and SEXUAL forms.
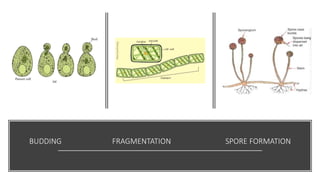
- 43. Asexual reproduction • It occurs through the FRAGMENTATION of colonial and filamentous algae • It also occur through SPORE FORMATION (it takes place through mitosis) • It also takes place through BUDDING
- 44. BUDDING FRAGMENTATION SPORE FORMATION
- 45. Sexual Reproduction • Algae forms differentiated sex cells that fuse to produce a DIPLOID ZYGOTE. • The ZYGOTE develops into a sexual spore which germinates when conditions are favourable to reproduce and reform the haploid organism having a single set of chromosomes. • This pattern of reproduction is called ALTERATION OF GENERATION
- 47. FUNGI
- 48. Appearance & Size • The plant body may be unicellular or filamentous. • The filament is known as HYPHAE and its enlarged mass is known as MYCELIUM. • There cell wall consists of CHITIN. • Their diameter is 2- 10micrometer and upto several centimeters in length.
- 50. Habitat • The fungi is cosmopolitan in distribution and occur in almost all possible habitats. • Most of the fungi are terrestial which grow in soil, on dead and decaying organic material. • Some grow on both plants and animals. • They can also grow on foods like jam, bread, fruits etc. • Some are also found in water. • They are also present in air .
- 52. Nutrition • They are heterotrophics in nature due to the absense of chlorophyll. • Some of them are parasites, saprophytes, symbio nts
- 53. Mode of Reproduction • The fungi reproduces by all the three means:- 1. VEGETATIVE- fragmentation, budding, fission 2. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION- zoospores, conidia, oidia, chlamydospore. 3. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION- plasmogamy, karyogamy, meiosis
- 54. VEGETATIVE REPRODUCTION IN FUNGI
- 57. FUNFI CAUSING INFECTION • TRICHOPHYTON RUBRUM- it causes an ATHLETE'S FOOT , is a fungal infection of foot. • CANDIDA ALBICANS- this causes the VAGINAL YEAST INFECTION in women. • TRICHOPHYTON- this causes a contagious fungal infection, RINGWORM