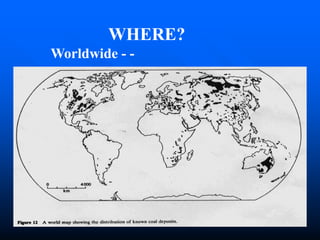
coal.ppt
- 2. “Coal in truth stands not beside but entirely above all other commodities. It is the material energy of the country- the universal aid, the factor in everything we do with coal, almost any feat is possible; without it we are thrown back into the laborious poverty of early times” (DiCiccio, 1996).
- 3. COAL Coal is one of the principal mineral fuel Defined by Stutzer and Noe as a combustible rock which had its orgin in the accumulation and partial decomposition of vegetation. Is a sedimentary rock usually found in layers with other sedimentary rocks such as shale, limestone and sandstone Is not a metamorphic rock or igneous
- 4. COAL Is a sedimentary rock usually found in layers with other sedimentary rocks such as shale, limestone and sandstone
- 5. Chemically coals are composed of • Organic • Mineral matter. Organic mass consists of • Carbon 60 to 90% • Hydrogen 1 to 2% • Oxygen 2 to 20% • Nitrogen 1 to 3% • And slight amount of sulphur and phosphrous. • From lignite to anthracite there is a progressive elimination of water, oxygen and hydrogen and an increase in carbon.
- 6. Classification of Coal • Vitrain • Durain • Clarain
- 7. Vitrain or (anthraxylon) • constitutes thin bands of bright, glassy- looking, jet like coal with conchoidal fracture. • The woody structure is not visible megascopically. Its brilliance, approaching jet, varies with the rank of coal. • Vitrain supplies cooking qualities
- 8. Durain • Dull coal, lacking lustre and having an earthy appearance. • Hard, black to lead-grey in colour, and consists of cuticles, spores. • Formed in water less toxic than for vitrain.
- 9. Clarian • Forms as thin bands in coal • Characterized by bright colour and silky lusture. • Composed largely of translucent attritus. Attritus is finely divided plant residue composed of the more resistant plant products.
- 10. Ranks and Kinds of Coal and Classification Coals are divided into four main groups Anthracite or hard coal Bituminous or Soft coal Lignite Cannel Coal Peat
- 11. Each groups is divided into ranks The lowest rank upwards are Lignite Brown coal Subbituminous Bitiminous Superbituminous (three ranks) Semianthracite Anthracite
- 12. Carbon Peat Lignite Sub Bituminous Bituminous Anthracite Coal Quality Pyramid – lowest rank upwards are
- 13. PEAT Peat is not coal eventhough it is a fuel. It is an accumulation of partly decomposed vegetable matter that represent the first stage in the formation of all coals.
- 14. LIGNITE • Lignite (brown coal) is the second stage. • Brownish black and is composed of woody matter embedded in macerated and decomposed vegetable matter. • Banded and jointed and because of its high moisture content, slacks or disintegrates after drying in the air.
- 15. • It is subjected to spontaneous combustion and has low heating value. • It is used for local fuels and to make producer gas, and in powdered form for heating and steam rising.
- 16. BITUMINOUS • Dense, dark, brittle banded coal that is well jointed and breaks into cubical or prismatic blocks and does not disintegrate upon exposure to air. • Vegetative matter is not ordinary visible to the eye. • Dull and bright bands and smooth hackly layers are evident.
- 17. • Ignites readily and burns with a smoky yellow flame • Low moisture, medium volatile matter and high fixed carbon and high heating value. • It is the most used and desired coal in the world and serves for steam, heating gas and cooking.
- 18. SUBBITUMINOUS • Intermediate coal is often difficult to distinguish from bituminous coal. • Dull, black and waxy. • Shows little woody matter, is banded, and splits parallel to the bedding but lacks the columinar cleavage of bituminous coal. • Some varities disintegrate upon exposure. • Good clean fuel but of relatively low heating
- 19. ANTHRACITE Jet-black, hard coal that has high lustre, is brittle, and breaks with a conchoidal fracture. Ignites slowly, is smolkeless, burns with a short blue flame, has low sulfur comtent, and has high heating value. It is restricted in distribution and was used exclusively for domestic heating and used for producing carbon.
- 21. PEAT Highly organic material forming a dark brown mass—low energy value and high moisture content
- 22. LIGNITE Peat that has undergone anaerobic (i.e. without oxygen) decay
- 23. SUB BITUMINOUS Black coal formed under greater pressure and overburden than lignite with higher carbon content
- 24. BITUMINOUS Highest quality soft(i.e bituminous) coal containing high carbon and heat value
- 25. ANTHRACITE Hard coal with highest carbon and energy content. NE counties of PA.
- 26. Formation of coal Organic matter derived mostly from land plants accumulates in low-energy environment (like a swamp). Oxidative decay uses up lots of oxygen, rendering the sediment pore waters devoid of oxygen (anoxic). Gentle cooking and pressing (lithification) as a result of increasing burial depth remove the pore water and increase carbon content (due to release of volatile components of the organic molecules). Low grade coal (lignite) cooked very little. High grade coal (anthracite) cooked a lot (close to being a metamorphic rock). Lower grade coal tends to contain minerals such as pyrite, which formed under the reducing (low-oxygen) conditions.
- 27. Coal Characteristics Lignite—25-35% carbon; Sub bituminous—35-45% carbon; Bituminous—45-86% carbon; Anthracite—86-98% carbon;