Computer Programming (C++)Pointers and Arrays
- 3. Modifying Variables Using Pointers
- 4. 4 Pointers #include “timetype.h” : enum ColorType {RED, GREEN, BLUE}; struct PatientRec { int idNum; int height; int weight; }; int alpha; ColorType color; PatientRec Patient; TimeType startTime (8,30,0); int* intPtr=α ColorType* ColorPtr=&color; PatientRec* PatientPtr=&patient; TimeType* timePtr=&startTime; (*patientPtr).idNum; (*patientPtr).height; (*patientPtr).weight; PointerExpression->MemberName (*PointerExpression).MemberName The general rule for selection Dot operator if the first operand denotes: struct, class or union variable Arrow Operator if the first operand denotes: a pointer to a struct, class, or union variable.
- 5. 5
- 6. 6 Constant pointer vs. Pointer to constant A constant pointer is declared using *const: base type *const pointer name; It is an error to change the constant pointer’s value; but the value of object this constant pointer points to can be changed. A pointer to constant is declared as: const base type *pointer name; It is ok to change the value of the pointer, but value of the constant which is referred to by the pointer can not be changed.
- 7. 7 Constant pointer vs. Pointer to constant Example 1: int x = 0, y = 0; const int * ptr1 = &x; // pointer to a constant int * ptr2 = &x; ptr1 = &y; // ok: can change ptr1 *ptr1 = 5; // error: can't change referent object ptr2 = &y; // ok *ptr2 = 5; // ok
- 8. 8 Constant pointer vs. Pointer to constant Example 2: int * const ptr = &x; // constant pointer *ptr = 5; // ok : can change what ptr points to ptr = &y; // error: can't change ptr
- 9. 9 Pointers and Dynamic Memory Allocation Static memory allocation: Example: int x; double y = 12.3456; int a[10]; The memory for the object is allocated by the compiler at the compile time. These objects are named variables on the stack at runtime.
- 10. 10 Pointers and Dynamic Memory Allocation Dynamic memory allocation: The memory allocation is done at run-time. The objects are unnamed variables on the heap manipulated indirectly through pointers.
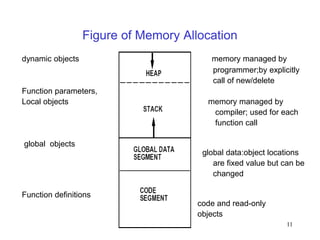
- 11. 11 Figure of Memory Allocation dynamic objects memory managed by programmer;by explicitly call of new/delete Function parameters, Local objects memory managed by compiler; used for each function call global objects global data:object locations are fixed value but can be changed Function definitions code and read-only objects
- 12. 12
- 13. 13








![9
Pointers and Dynamic Memory Allocation
Static memory allocation:
Example:
int x;
double y = 12.3456;
int a[10];
The memory for the object is allocated by the compiler
at the compile time. These objects are named
variables on the stack at runtime.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-10pointers-dynamicdata-ii-200412063712/85/Computer-Programming-C-Pointers-and-Arrays-9-320.jpg)