Concept on PCR,RAPD,AFLP
- 1. A Presentation on PCR, RAPD & AFLP Md. Nahidul Islam Dept. of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology. Jessore University of Science and Technology. Jessore 7408,Bangladesh
- 2. Outline PCR • History • Definition • Requirement or Reaction components • Procedure of PCR • Example of PCR programme • Benefits of PCR • Limitations of PCR • Application of PCR
- 3. RAPD Principle Definition Modification of RAPD Procedure of RAPD Advantages Drawbacks Application
- 4. AFLP Introduction Definition Procedure of AFLP Benefits Drawbacks Application
- 5. PCR Polymerase Chain Reaction History • Invented by Kary Mullis 1983 • 1985: First publication of PCR by Cetus Corporation appears in Science. • 1986: Purified Taq polymerase is first used in PCR • 1993:Dr. Kary Mullis Received Nobel Prize in Chemistry for conceiving PCR technology.
- 6. Definition An in-vitro amplification technique allows synthesizing millions of copies of the gene or DNA of interest from a single copy. Also called “polymerase” because the only enzyme used in this reaction is DNA polymerase
- 7. Requirement or Reaction components • Template (DNA/RNA/Plasmid) • Oligonucleotide Primer • Deoxynucleotide triphosphates or dNTPs (Mixture of dATP, dTTP, dCTP, dGTP) • Taq DNA Polymerase • Buffer system • MgCl2 • Water
- 8. Procedure of PCR • A PCR cycle consist of 3 steps : 1.Denaturation: • Reaction mixture heated to 94°C for 1 minute. • The temperature denatures dsDNA into two single strands due to breakage in weak hydrogen bonds.
- 9. 2.Primer annealing: • The reaction temperature is rapidly lowered to 54-60°C for 1.5 minute. • The primers to bind (anneal) to their complementary sequence in the template DNA. 3.Elongation: • Also known at extension, this step usually occurs at 72°C
- 10. • Addition of nucleotides by Taq polymerase. • Duration to complete cycle 4-5 min. • In each cycle the number of DNA gets doubled-2- 4-8-16…… • A reaction usually consists of 30-35 cycle forming about million copies
- 12. Example of PCR programme • Initial denaturation 94°C for 5 mins • Thermo-cycle file - 30 cycles of • Denaturation : 94°C for 1 mins • Annealing : 55°C -30 secs to 1mins • Extension : 72°C for 45 secs • Final extension 72°C for 5 mins • Holding ( soak ) fileusually 4°c
- 13. Benefits of PCR • Specific amplification. • Rapid. • Most accurate and feasible technique. • Extremely sensitive. • Easy of use.
- 14. Limitations of PCR • Setting up and running requires high technical skill. • High equipment cost. • High test cost. • High sterile environment should be provide
- 15. Application of PCR • To amplify DNA fragments isolated from organisms. • Used to detect genetic disease. • In forensic science , in DNA fingerprinting • PCR products can be used as probes • Pre-natal diagnosis • Gene therapy
- 16. RAPD Principle Abbreviation for Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA. A PCR based molecular marker technique. Invented by Williams et al. (1990). Needs one primer for amplification.
- 17. Definition A molecular technique in which random DNA are amplified by the polymerase chain reaction using single primers of arbitrary nucleotide sequence. It is a type of PCR reaction, but the segments of DNA that are amplified are random.
- 18. Modification Of RAPD AP-PCR (Arbitrarily Primed PCR) DAMD (Directed Amplification of Mini-satellite Region DNA). ISSR(Inter-Simple Sequence Repeat).
- 19. AP-PCR • Arbitrary Primed PCR • Amplification occurs in three parts • Higher concentration primer is used at first cycle • Analyzed on acryl amide gels • Detected by autoradiograph
- 20. DAMD • Directed Amplification of Minisatellite Region DNA • Use VNTR as primer • Detect polymorphism
- 21. ISSR • Inter-Simple Sequence Repeat • Used as Molecular Marker • Lying between adjacent Microsatellites • Used to detect polymorphism
- 22. Protocol of RAPD analysis Taq DNA polymerase, Primer, dNTPs and Buffer DNA isolation Keep the tubes in PCR thermo cycler DNA strand separated Annealing of primer (36ºC, 2min) Denature DNA (94°C, 1min)
- 23. Primer annealed of template DNA strands DNA synthesis (72ºC, 1.5min) Complementary strand synthesis Amplified products separated by gel electrophoresis 35 to 45 cycle
- 25. Advantages of RAPD • Quick and efficient screening for DNA • Involves no radioactive assays. • Requires a small amount of DNA. • Requires no probes. • Involves no blotting or hybridization steps.
- 26. Drawbacks of RAPD • Efficiency and low expensive. • Low reproducibility. • Highly sensitive and complicated procedure. • Markers are dominant. • PCR cycling conditions greatly influence the out come.
- 27. Application of RAPD • Gene mapping. • DNA fingerprinting. • Phylogenetic analysis. • Mapping of traits. • Identification of the somatic hybrids. • Analysis of genetic structure
- 28. AFLP Introduction • Full form is ‘Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism. • A PCR based method; developed by Vos et al. in 1995. • A combination of RFLP and RAPD methods. • Detect polymorphism.
- 29. Definition A technique used to amplify genomic restriction fragments from a complex mixture of DNA fragments which is generated by specific restriction endonucleases. Technique in which differences in restriction fragments are revealed by PCR.
- 30. Procedure of AFLP Following steps are involved in AFLP process Restriction Digestion Adaptor ligation Amplification Electrophoresis
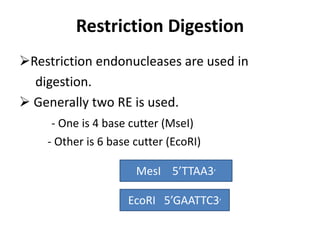
- 31. Restriction Digestion Restriction endonucleases are used in digestion. Generally two RE is used. - One is 4 base cutter (MseI) - Other is 6 base cutter (EcoRI) MesI 5’TTAA3’ EcoRI 5’GAATTC3’
- 32. Adaptor Ligation Two end specific adaptors (a different one for each enzyme) are ligated to the digested fragments. In case of MesI and EcoRI -one adaptor will complement to the Msel cut end -the other will complement to the EcoRI cut end DNA with sticky end Adaptor 1 Adaptor 2 Adaptor 2Adaptor 1
- 33. Amplification • PCR is used • Amplification occurs for selected fragments only • Two PCR primers complementary to the two adaptors • Primers are labeled with radioactive or fluorescence dye
- 34. Electrophoresis Polyacrylamide gel is used for separating DNA bands. 30-100 DNA bands can be detected Selected fragments will show in band
- 35. Fig: Procedure of AFLP
- 36. Benefits of AFLP Used for genome mapping. Highly polymorphic. High reproducibility. Different parts of the genome can be analyzed. Discriminates heterozygote's from homozygote's by using gel scanner.
- 37. Drawbacks of AFLP Complex procedure. Technically more demanding than RAPD. Requires experience of sequencing gels. Highly expensive and requires more DNA than RAPD
- 38. Application Of AFLP Creation of genetic maps for new species Determination of relatedness among cultivars Establishment of linkage groups in crosses Useful in genetic studies such as biodiversity evaluation, genotyping etc. In criminal identification and paternity tests.