Using Data Science to Combat Youth Disparities - Data Science Pop-up Seattle
- 1. #datapopupseattle Using Data Science to Combat Youth Disparities Sean Green Research Data Analyst, City of Seattle CityofSeattle
- 2. #datapopupseattle UNSTRUCTURED Data Science POP-UP in Seattle www.dominodatalab.com D Produced by Domino Data Lab Domino’s enterprise data science platform is used by leading analytical organizations to increase productivity, enable collaboration, and publish models into production faster.
- 3. Understanding disparities A deep dive into the American Community Survey Sean Green, Ph.D. Research Data Analyst City of Seattle
- 4. Ways of capturing socioeconomic data • Product registration surveys • Online behavior and purchase history • Phone surveys • Door-to-door surveys • Workplace/school surveys • The Census and American Community Survey
- 5. The United States Census • The decennial census is mandated by Article I, Section 2 of the US Constitution • Is the most comprehensive source of population demographic information • Is used to apportion representation, and as such, requires a count of individuals and households • From 1940 through 2000 a subset ofAmericans received a long form which contained detailed socioeconomic questions • After 2000 the American Community Survey (ACS) was developed, and eventually replaced the long form as a survey that could be used to provide estimates between decennial censuses
- 6. Three levels of detail Most%comprehensive,% fewer%questions Less%comprehensive,%more% questions,%more%detail Decennial(Census American(Community Survey ACS(PUMS
- 7. What you get with each Decennial%Census American% Community%Survey Public?Use% Microdata Sample • Comprehensive%counts • Total%population • Estimates%for% proportions%of% demographic%groups • Only%available%once%a% decade • Sampling%for%smaller% groups • Questions%regarding% household%income,% educational%attainment,% and%employment%status • Available%yearly%for%areas% of%sufficient%size • Same%questions%as%ACS • Anonymized%individual% responses%for%custom% tables • Available%yearly%for%areas% of%sufficient%size • Higher%uncertainty%bounds% for%small%areas%and%groups
- 8. What the data can tell us about disparities Decennial%Census American% Community%Survey Public?Use% Microdata Sample • Proportionality%of% resources%spent%and% services%offered%by% geography • How%Seattle’s%population% compares%to%the% population%in%other%cities • Socioeconomic%data% aggregated%by% geographic%unit • Which%groups%are%faring% better%or%worse%over% time%in%terms%of% employment,%wages,%and% ease%of%transportation% • Socioeconomic%data%by% household • Individual%and%population? level%factors%that%%are% correlated%with%disparities • How%have%groups%fared%in% our%city%by%geography
- 9. Poverty rates Source:American Community Survey 2007-2010 data 32.9% 21.6% 21.5% 35.0% 17.4% 14.3% 14.6% 14.8% 9.4% 9.0% 8.6% 10.9% 18.6% 22.7% 13.7% 25.8% 15.4% 14.0% 9.8% 13.7% 0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35% 40% 2007 2008 2009 2010 Seattle(Poverty(Rates(by(Race African%American Asian Caucasian Hispanic Other
- 10. Births to teenage mothers Source: Birth Certificate Data, Washington State Department of Health, Center for Health Statistics. 11 3.8 7.4 31.1 20.4 9.3 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Average(King(County(Births(to(Females(Ages(15@17(in(Birth(per(1,000 African%American Asian Caucasian Hispanic Native%American Other
- 11. Math, Reading, and Writing scores Source: Office of the Superintendentof Public Schools;for grades 3,4,5,6,7,8, and 10 47% 65% 70% 84% 86% 91% 72% 83% 86% 50% 62% 70% 47% 60% 66% 50% 52% 74% 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 Math Reading Writing Washington(State(Female(Test(Scores(by(Race African%American Asian Caucasian Hispanic Native%American Other 43% 52% 52% 81% 79% 79% 70% 75% 70% 48% 53% 52% 41% 47% 45% 47% 64% 54% 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 Math Reading Writing Washington(State(Male(Test(Scores(by(Race African%American Asian Caucasian Hispanic Native%American Other
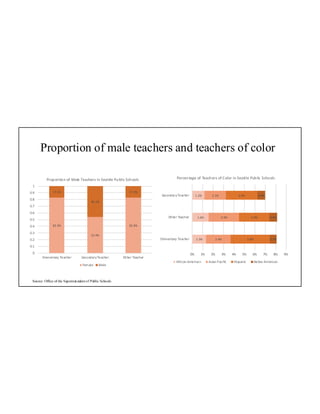
- 12. Proportion of male teachers and teachers of color Source: Office of the Superintendentof Public Schools 82.9% 53.9% 82.8% 17.1% 46.1% 17.2% 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 Elementary%Teacher Secondary%Teacher Other%Teacher Proportion%of%Male%Teachers%in%Seattle%Public%Schools Female Male 1.3% 1.6% 1.2% 2.4% 2.9% 2.1% 3.8% 2.9% 3.0% 0.7% 0.8% 0.8% 0% 1% 2% 3% 4% 5% 6% 7% 8% 9% Elementary%Teacher Other%Teacher Secondary%Teacher Percentage%of%Teachers%of%Color%in%Seattle%Public%Schools African%American Asian%Pacific Hispanic Native%American
- 13. Educational Attainment 12.3% 18.7% 4.9% 3.3% 13.2% 18.8% 23.6% 12.6% 7.2% 31.7% 47.4% 33.0% 41.4% 50.0% 37.9% 1.6% 2.6% 5.5% 12.0% 1.3% 17.0% 22.1% 34.5% 23.2% 11.1% 2.8% 1.1% 4.8% 4.8% 0.0% 10.0% 20.0% 30.0% 40.0% 50.0% 60.0% 70.0% 80.0% 90.0% 100.0% Other Hispanic Caucasian Asian/Pacific African%American Educational(Attainment(by(race(for(Seattle(Youths(Aged(18@24( Less%than%HS HS%Diploma%or%Equivalent Some%College Associate's%Degree Bachelor's%Degree MA%or%Higher Source:%American%Community%Survey%PUMS%2009?2013
- 14. Youth Labor Force Status Source:American Community Survey PUMS 2009-2013 49.6% 67.3% 74.7% 66.0% 35.2% 54.8% 24.2% 10.2% 11.0% 13.2% 16.6% 20.5% 26.2% 22.5% 14.3% 20.8% 48.2% 24.7% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% Afr ican%American Asian Caucasian Hispanic Native%American Othe r Seattle(Labor(Force(Status(by(Race(for(Youth(16@24 Employed Unemployed Not%in%labor%force
- 15. Trusted Adult Source: Healthy Youth Survey 63.7% 57.7% 83.4% 56.1% 71.7% 63.9% 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 Percent%Seattle%10th%and%12th%Graders%of%Children%by%Race%Who% Report%Having%a%Trusted%Adult%with%whom%to%Talk African%American Asian Caucasian Hispanic Native%American Other
- 16. Exposure to Injury and Violence Risk Source: CDC Youth Risk Behavior SurveillanceSystem Accessed 9/24/15 Much%less%than%population%percentage 1 Less%than%population%percentage 2 Equal%to%population%percentage 3 More%than%population%percentage 4 Much%more%than%total%percentage 5 African( American Asian Caucasian Hispanic Other Rode(with(a(driver(who(had(been(drinking(alcohol (in(a(car(or(other(vehicle(one(or( more(times(during(the(30(days(before(the(survey) -1.6 -5.6 1.2 9.2 -0.2 Carried(a(gun (on(at(least(1(day(during(the(30(days(before(the(survey) 2.4 -0.7 -2.5 3.5 -2.6 Carried(a(weapon(on(school(property (such(as,(a(gun,(knife,(or(club(on(at(least(1(day( during(t he(30(days(before(the(survey) 1.6 -2.1 -1.7 3.6 Were(threatened(or(injured(with(a(weapon(on(school(property (such(as,(a(gun,(knife,( or(club(one(or(more(times(during(the(12(months(before(the(survey) 1.8 -1.1 -1.7 0 3.1 Were(in(a(physical(fight(on(school(property (one(or(more(times(during(the(12(months( before(the(survey) 5.4 -3.6 -4.7 6.9 1.9 Did(not(go(to(school(because(they(felt (unsafe(at(school(or(on(their(way(to(or(from( school(on(at(least(1(day(during(the(30(days(before(the(survey) 1.9 -0.7 -2.3 1 -0.1 Were(electronically(bullied (including(being(bullied(through(e@mail,(chat(rooms,( instant(messaging,(websites,(or(texting(during(the(12(months(before(the(survey) -3.5 0.4 0.1 1.8 1.8 Were(bullied(on(school(property (during(the(12(months(before(t he(survey) -3.7 -1.1 2.1 -1.3 1.3 Were(ever(physically(forced(to(have(sexual(intercourse (when(they(did(not(want(to) 0.5 -1.5 -2.2 4.8 1.9 Felt(sad(or(hopeless (almost(every(day(for(2(or(more(weeks(in(a(row(so(that(they( stopped(doing(some(usual(activities(during(the(12(months(before(the(survey) -1 0.1 -1.9 2.3 8.8 Seriously(considered(attempting(suicide (during(the(12(months(before(t he(survey) 1.6 -0.9 -2 -1.5 5.9 Made(a(plan(about(how(they(would(attempt(suicide (during(the(12(months(before(t he( survey) -1.4 0.9 -1.4 -1.5 7.1 Attempted(suicide (one(or(more(times(during(the(12(months(before(the(survey) 5.1 -1.8 -3.8 1.3 -1.7 Attempted(suicide(that(resulted(in(an(injury,(poisoning,(or(overdose(that(had(to(be( treated(by(a(doctor(or(nurse (during(the(12(months(before(t he(survey) 0.3 0.3 -1.9 1.9 0.2
- 17. Alcohol and drug use Source: CDC Youth Risk Behavior SurveillanceSystem Accessed 9/24/15 Much%less%than%population%percentage 1 Less%than%population%percentage 2 Equal%to%population%percentage 3 More%than%population%percentage 4 Much%more%than%total%percentage 5 African( American Asian Caucasian Hispanic Other Ever(had(at(least(one(drink(of(a lcohol (on(at(least(1(day(during(their(life) -15 -9 11 10.2 10 Drank(alcohol(before(age(1 3(years (for(the (first(time(other(than(a(few(sips) 0.9 -1.9 -3.4 11.4 -1.4 Currently(drank(alcohol (at(least(one(drink(of(alcohol(on(at(least(1 (day(during(the( 30(days(be fore(the(survey) -7.3 -13.1 9.2 6.1 7.2 Had(five(or(more(drinks(of(alcohol(in(a(row (within(a(couple(of(hours(on(at (least (1( day(during(the(30 (days(before(the (survey) -6.6 -8 6 6 5.7 Ever(used(marijuana (one(or(more(t imes(during(their(life) -2 -14.2 4.9 14.3 5.1 Tried(marijuana(before(age(13(years (for(the (first(time) 3.2 -4.1 -3.6 10.7 -0.3 Currently(used(marijuana (one(or(more(t imes(during(the(30(days(before(t he(survey) -0.5 -11.6 4.2 9.2 3.5 Ever(injected(any(illegal(drug (used(a(ne edle(to(inject (any(illegal(drug(into(their( body(one(or(more(times(during(their(life) 1.7 -1.4 -1 -0.1 2.6 Were(offered,(sold,(or(given(an(illegal(drug(on(school(property (during(the(12 ( months(before(the (survey) -0.5 -7 0.4 6 10.2
- 18. Tobacco use Source: CDC Youth Risk Behavior SurveillanceSystem Accessed 9/24/15 Much%less%than%population%percentage 1 Less%than%population%percentage 2 Equal%to%population%percentage 3 More%than%population%percentage 4 Much%more%than%total%percentage 5 African( American Asian Caucasian Hispanic Other Ever(tried(cigarett e(smoking (even(one(or(two(puffs) -2.3 -7.1 0.6 12.5 7.9 Smoke d(a(whole(cigarette(before(a ge(13(years (for(the (first(time) 2.8 -2.8 -3.1 6 2.5 Currently(smoked(cigarett es (on(at(least(1(day(during(the(3 0(days(before(the( survey) -3 -4 0.9 4.6 0.7 Currently(smoked(cigarett es(frequently (on(20(or(more(days(during(the(30(days( before(the(survey) -1.7 -1.8 0.9 2.5 1.2 Smoke d(cigarettes(on(school(property (on(at(least(1(day(during(the(3 0(days( before(the(survey) -2 -1.7 0.5 3.3 0.1 Ever(smoked(at(least(one(cigarette (every(day(for(30(days -3.4 -2.8 1.8 2.7 1.6 Smoke d(cigarettes(on(all(30 (days (during(the(30 (days(before (the(survey) -1.3 -1.6 0.5 2.1 0.6 Currently(used(smoke less(tobacco (chewing(tobacco,(snuff,(or(dip(on(at(least(1( day(during(the(30 (days(before(the (survey) -0.9 -1.8 -0.9 3.6 1.2 Currently(used(cigars (cigars,(cigarillos,(or(litt le(cigars(on(at(lea st(1(day(during(t he( 30(days(be fore(the(survey) -1.1 -2.6 -0.5 4.2 -1.5 Currently(used(tobacco (current(cigarette (use,(curre nt(smoke less(tobacco(use,(or(( curre nt(cigar(use) -2.9 -3.3 1.2 5.8 1.3
- 19. Making the data more accessible
- 20. Clustering: Beyond predetermined groupings
- 21. Shortcomings in the data • The Census does a poor job of capturing data on the homeless, incarcerated populations, and undocumented aliens • These groups often bear the brunt of disparities • The ACS does not permit estimates of small population groups, such as many of our immigrant and refugee communities, which makes it difficult to know where the provide services • The data capture population-level counts, but do not provide an easy solution for measuring changes due to migration • Aggregate statistics may improve without having treated the root problem
- 23. #datapopupseattle Thank You To Our Sponsors