data structure chapter hashing slides for data structures learning
- 1. Data Structure Dictionarys & Hashing
- 2. Dictionary A dictionary is composed of a collection of elements each of which is: Set of (key, value) pairs keys are mapped to values keys must be comparable keys must be unique Examples: Membership in a club Course you have passed Set of loans made in a library Language dictionary A dictionary entry
- 3. Dictionary Example Course Record Dictionary Member Record key student name hw1 ... 123 Stan Smith 49 ... 124 Sue Margolin 56 ... 125 Billie King 34 ... 167 Roy Miller 39 ...
- 4. Dictionary Example To count the occurrences of words in a story: Each dictionary entry is keyed by the word The related value is the count When entering words into dictionary Check if word is already there If no, enter it with a value of 1 If yes, increment its value 4
- 5. Dictionary Operations Test whether dictionary is empty. Test whether dictionary is full. Insert new item into dictionary. Remove item with given search key from dictionary. Remove all items from dictionary. Get item with a given search key from dictionary. Test whether dictionary contains an item with given search key.
- 6. Possible Implementations of Dictionary? Trees (BST, AVL, Splay,….) Lists Hash tables
- 7. Hash Tables
- 8. Hash table A Hash table is defined as a data structure used to insert, look up, and remove key-value pairs quickly. It operates on the hashing concept, where each key is translated by a hash function into a distinct index in an array. The index functions as a storage location for the matching value. In simple words, it maps the keys with the value.
- 9. What is a Hash Table ? • Effective way of implementing dictionaries. The simplest kind of hash table is an array of records. Element whose key is k is obtained by indexing into the kth position of the array. Applicable when we can afford to allocate an array with one position for every possible key. [ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] . . . [ 700]
- 10. Hashing Use hash function to map keys into positions in a hash table Ideally: If element e has key k and h is hash function, then e is stored in position h(k) of table To search for e, compute h(k) to locate position. If no element, dictionary does not contain e.
- 12. Hash Table • The ADT Hash Table is an array of elements (associated with a search key unique for each element), together with an hash function and access procedures (insert, delete, search...). • The hash function determines the location in the table of a new element, using its search key. In a similar way, permits to locate the position of an existing element. • The hash function takes a search key and maps it into an integer array index.
- 13. 13 Properties of Good Hash Functions Must return number 0, …, tablesize Should be efficiently computable. Shouldminimize collisions = different keys hashing to same index
- 14. Truncation in Hashing Truncation in Hashing: Definition: Truncation is a simple method for creating a hash function by ignoring part of the key and using certain selected digits (or parts) from the key to generate an index.
- 16. Problem with Truncation: While truncation is very fast, it's not always effective because: • It may not spread keys evenly across the table. • This could cause collision (many keys going to the same index), which reduces performance. 16
- 17. Folding is a hashing technique where the key is split into parts, and those parts are combined (usually by adding or multiplying) to produce a hash value (index). Folding in Hashing
- 18. Folding in Hashing Example
- 19. This hashing method uses modulus division to calculate the index. The hash function is: h(key)=key mod TableSize That means: • Divide the key by the size of the table. • Take the remainder as the index. Modular Arithmetic in Hashing
- 20. 20 Modular Arithmetic in Hashing Example
- 21. Let’s Try…
- 22. Inserting a New Record In order to insert a new record, the key must somehow be converted to an array index. The index is called the hash value of the key. [ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 700] Number 506643548 Number 233667136 Number 281942902 Number 155778322 . . . Number 580625685
- 23. Inserting a New Record Typical way create a hash value: (Key mod TableSize) [ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 700] Number 506643548 Number 233667136 Number 281942902 Number 155778322 . . . Number 580625685 What is (580625685 mod 701) ?
- 24. Inserting a New Record Typical way to create a hash value: [ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 700] Number 506643548 Number 233667136 Number 281942902 Number 155778322 . . . Number 580625685 (Number mod 701) What is (580625685 mod 701) ? 3
- 25. Inserting a New Record The hash value is used for the location of the new record. Number 580625685 [ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 700] Number 506643548 Number 233667136 Number 281942902 Number 155778322 . . . [3]
- 26. Inserting a New Record The hash value is used for the location of the new record. [ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 700] Number 506643548 Number 233667136 Number 281942902 Number 155778322 . . . Number 580625685
- 27. Collisions Here is another new record to insert, with a hash value of 2. [ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 700] Number 506643548 Number 233667136 Number 281942902 Number 155778322 . . . Number 580625685 Number 701466868 My hash value is [2].
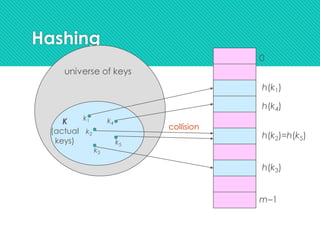
- 28. Methods of Collision Resolution Chaining: Store all elements that hash to the same slot in a linked list. Store a pointer to the head of the linked list in the hash table slot. Open Addressing: All elements stored in hash table itself. When collisions occur, use a systematic (consistent) procedure to store elements in free slots of the table. k2 0 m–1 k1 k4 k5 k6 k7 k3 k8
- 29. Collision Resolution by Chaining 0 m–1 h(k1)=h(k4) h(k2)=h(k5)=h(k6) h(k3)=h(k7) U (universe of keys) K (actual keys) k1 k2 k3 k5 k4 k6 k7 k8 h(k8) X X X
- 30. k2 Collision Resolution by Chaining 0 m–1 U (universe of keys) K (actual keys) k1 k2 k3 k5 k4 k6 k7 k8 k1 k4 k5 k6 k7 k3 k8
- 31. Linear Probing Linear probing is a collision resolution method in open addressing hash tables. When a collision occurs (i.e., two keys map to the same index), the algorithm checks the next available slot in a linear (sequential) manner. 31








![What is a Hash Table ?
• Effective way of implementing dictionaries.
The simplest kind of hash table is an array of records.
Element whose key is k is obtained by indexing into the kth position of the array.
Applicable when we can afford to allocate an array with one position for every
possible key.
[ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ]
. . .
[ 700]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7hashing-250524130543-7ca7b7e9/85/data-structure-chapter-hashing-slides-for-data-structures-learning-9-320.jpg)











![Inserting a New Record
In order to insert a new record, the
key must somehow be converted to
an array index.
The index is called the hash value of
the key.
[ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 700]
Number 506643548
Number 233667136
Number 281942902
Number 155778322
. . .
Number 580625685](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7hashing-250524130543-7ca7b7e9/85/data-structure-chapter-hashing-slides-for-data-structures-learning-22-320.jpg)
![Inserting a New Record
Typical way create a hash value:
(Key mod TableSize)
[ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 700]
Number 506643548
Number 233667136
Number 281942902
Number 155778322
. . .
Number 580625685
What is (580625685 mod 701) ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7hashing-250524130543-7ca7b7e9/85/data-structure-chapter-hashing-slides-for-data-structures-learning-23-320.jpg)
![Inserting a New Record
Typical way to create a hash value:
[ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 700]
Number 506643548
Number 233667136
Number 281942902
Number 155778322
. . .
Number 580625685
(Number mod 701)
What is (580625685 mod 701) ? 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7hashing-250524130543-7ca7b7e9/85/data-structure-chapter-hashing-slides-for-data-structures-learning-24-320.jpg)
![Inserting a New Record
The hash value is used for the
location of the new record.
Number 580625685
[ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 700]
Number 506643548
Number 233667136
Number 281942902
Number 155778322
. . .
[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7hashing-250524130543-7ca7b7e9/85/data-structure-chapter-hashing-slides-for-data-structures-learning-25-320.jpg)
![Inserting a New Record
The hash value is used for the
location of the new record.
[ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 700]
Number 506643548
Number 233667136
Number 281942902
Number 155778322
. . .
Number 580625685](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7hashing-250524130543-7ca7b7e9/85/data-structure-chapter-hashing-slides-for-data-structures-learning-26-320.jpg)
![Collisions
Here is another new record to insert,
with a hash value of 2.
[ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 700]
Number 506643548
Number 233667136
Number 281942902
Number 155778322
. . .
Number 580625685
Number 701466868
My hash
value is
[2].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7hashing-250524130543-7ca7b7e9/85/data-structure-chapter-hashing-slides-for-data-structures-learning-27-320.jpg)





