Data Structures and Algorithms - Lec 05.pptx
- 1. LINKED LIST Lecture 05 IT 2301 / CS 2301 Dhanushka Jayasinghe
- 2. What is Linked List ? • A linked list is the most sought-after data structure when it comes to handling dynamic data elements. • A linked list is a linear data structure that includes a series of connected nodes. Here, each containing data fields and one or two references (links) pointing to the next and/or previous nodes. • The last node contains null in its second field because it will point to no node. • A linked list can grow and shrink its size, as per the requirement. • It does not waste memory space.
- 4. Why use linked list over Array? Array contains following limitations: • The size of array must be known in advance before using it in the program. • Increasing size of the array is a time taking process. It is almost impossible to expand the size of the array at run time. • All the elements in the array need to be contiguously stored in the memory. Inserting any element in the array needs shifting of all its predecessors. Linked list is the data structure which can overcome all the limitations of an array. Using linked list is useful because, • It allocates the memory dynamically. All the nodes of linked list are non-contiguously stored in the memory and linked together with the help of pointers. • Sizing is no longer a problem since we do not need to define its size at the time of declaration. List grows as per the program's demand and limited to the available memory space.
- 5. Types of Linked List Following are the various types of linked list. 1) Singly Linked List − The nodes only point to the address of the next node in the list. 1) Doubly Linked List − The nodes point to the addresses of both previous and next nodes. 1) Circular Linked List − The last node in the list will point to the first node in the list. It can either be singly linked or doubly linked
- 6. Singly Linked Lists Singly linked lists contain two “buckets” in one node; one bucket holds the data and the other bucket holds the address of the next node of the list. Traversals can be done in one direction only as there is only a single link between two nodes of the same list.
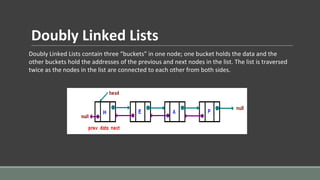
- 7. Doubly Linked Lists Doubly Linked Lists contain three “buckets” in one node; one bucket holds the data and the other buckets hold the addresses of the previous and next nodes in the list. The list is traversed twice as the nodes in the list are connected to each other from both sides.
- 8. Circular Linked Lists ⮚ In a circularly linked list, the first and final nodes are linked together. This can be done for both singly and doubly linked lists. ⮚ Begin at any node and follow the list in either direction until return to the original node. ⮚ No beginning or end. ⮚ Since the last node and the first node of the circular linked list are connected, the traversal in this linked list will go on forever until it is broken. • Singly-circularly-linked List • Doubly-circularly-inked List
- 9. Singly Circularly Linked List
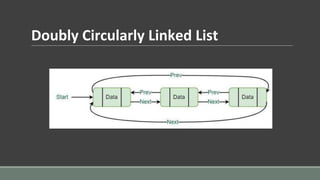
- 10. Doubly Circularly Linked List
- 11. Linked List Node A node consists with the data stored in the node and a pointer to the next node in the list
- 12. How to declare a linked list? Linked list contains two parts, and both are of different types, i.e., one is the simple variable, while another is the pointer variable. We can declare the linked list by using the user-defined data type structure. struct node { int data; struct node *next; } ;
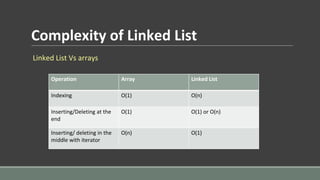
- 13. Complexity of Linked List Linked List Vs arrays Operation Array Linked List Indexing O(1) O(n) Inserting/Deleting at the end O(1) O(1) or O(n) Inserting/ deleting in the middle with iterator O(n) O(1)
- 14. Linked List vs Arrays ◦ Elements can be inserted into linked lists indefinitely ◦ An array will eventually either fill up or need to be resized ◦ Arrays allow random access while linked list allow only sequential access to elements ◦ Singly linked lists can traverse only in one direction ◦ Linked lists require extra storage for reference
- 15. Doubly Linked vs Singly Linked oDoubly Linked Lists required more space per node oDLL is easier to manipulate because they allow sequential access to the list in both directions. oCan be insert or delete node in a constant number of operations given only that nodes address oSLL requires the previous nodes address in order to correctly insert or delete
- 16. Circularly Linked vs Linearly Linked o Circular Linked Lists are most useful for describing naturally circular structures o Able to traverse the list starting at any point o Quick access to the first and the last record through a single pointer o Complexity of iteration
- 17. Advantages of Linked list • Dynamic data structure - The size of the linked list may vary according to the requirements. Linked list does not have a fixed size. • Insertion and deletion - Unlike arrays, insertion, and deletion in linked list is easier. Array elements are stored in the consecutive location, whereas the elements in the linked list are stored at a random location. To insert or delete an element in an array, we have to shift the elements for creating the space. Whereas, in linked list, instead of shifting, we just have to update the address of the pointer of the node. • Memory efficient - The size of a linked list can grow or shrink according to the requirements, so memory consumption in linked list is efficient. • Implementation - Various advanced data structures can be implemented using a linked list like a stack, queue, graph, hash maps, etc.
- 18. Disadvantages of Linked list • Memory usage - In linked list, node occupies more memory than array. Each node of the linked list occupies two types of variables, i.e., one is a simple variable, and another one is the pointer variable. • Traversal - Traversal is not easy in the linked list. If we have to access an element in the linked list, we cannot access it randomly, while in case of array we can randomly access it by index. For example, if we want to access the 3rd node, then we need to traverse all the nodes before it. So, the time required to access a particular node is large. • Reverse traversing - Backtracking or reverse traversing is difficult in a linked list. In a doubly-linked list, it is easier but requires more memory to store the back pointer.
- 19. Linked List operations 1.Traversing: To traverse all nodes one by one. 2.Insertion: To insert new nodes at specific positions. 3.Deletion: To delete nodes from specific positions. 4.Searching: To search for an element from the linked list.
- 20. Linked List operations SINGLY LINKED LIST
- 21. Insertion - At the front of the linked list 1. START 2. Create a node to store the data 3. Check if the list is empty 4. If the list is empty, add the data to the node and assign the head pointer to it. 5. If the list is not empty, add the data to a node and link to the current head. Assign the head to the newly added node. 6. END
- 22. Insertion - After a given node 1. START 2. Create a new node and assign data to it 3. Iterate until the node at position is found 4. Point first to new first node 5. END
- 23. Insertion - At the end of the linked list 1. START 2. Create a new node and assign the data 3. Find the last node 4. Point the last node to new node 5. END