Dental Management of Patient with Leukemia
- 2. Outline Case scenario Case analysis Background Types of leukemia Etiology of leukemia Signs and symptoms of leukemia Medical diagnostic tests Management of leukemia Oral manifestation Dental Management Treatment plan modification 2
- 3. Case 2 A 52 year old came to your clinic for severe bleeding gums. Extraoral examination revealed multiple bruises on the arms and legs (when further asked she reports bruising much more easily lately). Intraoral examination showed enlarged gingiva that bleeds easily. History revealed that she has had flulike symptoms for the past 4 weeks, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, shortness of breath and bone/joint pain. 3
- 4. Case Analysis 52 years oldAge femaleGender severe bleeding gums Chief complaint Flulike symptoms for the past 4 weeks, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, shortness of breath, bone/joint pain. Medical history Not providedDental history Extraoral examination multiple bruises on the arms and legs Intraoral examination enlarged gingiva that bleeds easily 4
- 5. 5
- 6. leukemia is cancer of the WBCs that affects the bone marrow and circulating blood. It involves exponential proliferation of a clonal myeloid or lymphoid cell. 6
- 7. Etiology of leukemia The cause of leukemia is unknown Increased risk is associated with large doses of ionizing radiation, certain chemicals( benzene), and infection with specific viruses [EPV] and human lymphotropic virus [HTLV]-1 Cigarette smoking and exposure to electromagnetic fields also have been proposed to be causative. Genetic factors may cause cytogenetic abnormalities that affect transcriptional cascades of myeloid precursor cells. 7
- 8. Types of Leukemia & Pathophysiology Acute leukemia Result from accumulation of immature , functionless WBCs in the marrow and blood Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) Chronic leukemia Have slower onset which allows production of larger numbers of more mature, functional cells Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) 8
- 9. Signs and symptoms •Night sweats •Fatigue and weakness •Weight loss •Bone pain and tenderness •painless, swollen lymph nodes (especially in the neck and armpits) •Enlargement of the liver or spleen •Petechiae •Bleeding and bruising easily •Fever or chills •Frequent infections 9
- 10. Potential Medical Problems • Anemia which is a condition in which a person has low number of red cells which can cause fatigue and shortness of breath • Neutropenia is condition when there is low number of white cells • Thrombocytopenia 10
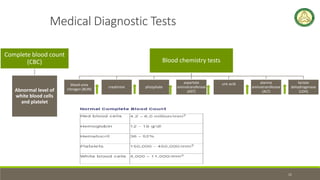
- 11. Medical Diagnostic Tests Complete blood count (CBC) Abnormal level of white blood cells and platelet Blood chemistry tests blood urea nitrogen (BUN) creatinine phosphate aspartate aminotransferase (AST) uric acid alanine aminotransferase (ALT) lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) 11
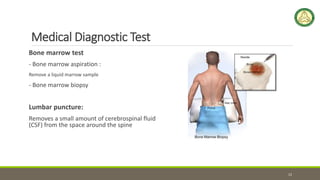
- 12. Medical Diagnostic Test Bone marrow test - Bone marrow aspiration : Remove a liquid marrow sample - Bone marrow biopsy Lumbar puncture: Removes a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the space around the spine 12
- 13. Oral manifestations Gingival Enlargement Direct infiltration with leukemic cells of local tissues, through immunodeficiency, thrombocytopenia Gingival ulceration Result from impaired immune defense in combating normal microbial flora Oral infection Manifestations of thrombocytopenia are more common when the platelet count is below 50,000 cells/mm3and may manifest as bruising, petechiae in the hard and soft palate, and also spontaneous gingival bleeding, especially if the platelet count is below 20,000 cells/mm3 13
- 14. Oral Complications Primary complications (Mainly occurring due to the disease itself ) leukemic gingival enlargement. Secondary complications (Associated with direct effect of the radiation or chemotherapy) These include tendency to bleeding, susceptibility to infections, and ulcers Tertiary complications (Due to complex interplay of therapy itself, its side effect, and a systemic condition arising out of the therapy) Ulcerations, mucositis, taste alteration, candidiasis, gingival bleeding, xerostomia, dysphasia, opportunistic infections and trismus. 14
- 15. Management of Leukemia Chemotherapy The main treatment for many kinds of leukemia It has 3 phases: 1- Induction 2- Consolidation 3- Maintenance Radiation therapy To prevent leukemia from spreading to, or treat leukemia that has spread to, the central nervous system (CNS) Bone marrow transplant 15
- 16. Dental management of patient with Leukemia Before starting the dental treatment: Refer the patient for medical evaluation and treatment Hematological information is needed before any invasive procedures (such as extractions)as leukemia patients have higher bleeding tendencies and they are liable to infections. Preventive oral care is important in leukemia patients such as: • Frequent topical fluoride applications • Fissure sealants • Dietary advice to the patient • Give proper tooth brushing instructions to both patient and parents • Antibiotic cover is needed before any surgery to prevent any postoperative infection 16
- 17. Dental management of patient with Leukemia Deliverska, Elitsa G., and Assya Krasteva. "Oral signs of leukemia and dental management–literature data and case report." J of IMAB 19.4 (2013): 388-391. 17
- 18. Treatment Plan Modification Patient Prior to Chemotherapy Dental treatment should be scheduled in consultation with the oncologist The dental examination should perform before initiation of chemotherapy Dental treatment at this stage is based on priorities and should be directed to the acute needs Eliminate existing of infection and manage potential sources of infection and sites of trauma Elective treatment should be postponed to a time when the patient is appropriate for clinical and laboratory conditions Educate the patient about the importance of maintaining oral health in reducing problems before, during, and after cancer treatment Warn about the possible effects of chemotherapy in the oral cavity, such as mucositis 18
- 19. Treatment Plan Modification Patient During Chemotherapy The most appropriate time to schedule dental treatment during chemotherapy is after patients' blood counts have recovered, usually just prior to their next course of chemotherapy General consideration : Alcohol-based mouthwashes and full-strength peroxide solutions or gels should not be used due to their drying and irritating effects. The prophylactic use of chlorhexidine rinse is helpful in suppressing bacterial colonization 19
- 20. How to manage the bleeding Use of hemostatic agent Epinephrine helps to reduce the flow of blood 20
- 21. Treatment Plan Modification Patients after Chemotherapy Patients are considered cured of leukemia and not having oral manifestations due to illness or chemotherapy The patient is considered low risk and can be met with normal dental treatment regimens 21
- 22. References •Little, James W et al. Little And Falace's Dental Management Of The Medically Compomised Patient. 8th ed. •Sol Silverman. Essentials Of Oral Medicine. 1st ed. 2001. •Zimmermann, Caroline et al. "Dental Treatment In Patients With Leukemia". Journal of Oncology 2015 (2015): 1-14. Web. •"Oral & Dental Care". Bccancer.bc.ca. N.p., 2017. Web. 11 May 2017. •Deliverska, Elitsa G., and Assya Krasteva. "Oral signs of leukemia and dental management– literature data and case report." J of IMAB 19.4 (2013): 388-391. •"Diagnosis Of Leukemia - Canadian Cancer Society". www.cancer.ca. N.p., 2017. Web. 11 May 2017. 22
- 23. Quick Test 1- Which of following is considered primary complication of leukemia: A. Gingival enlargement B. Ulceration C. Mucositis 2- Which is not correct regarding dental management of patient with Leukemia: A. Refer the patient before starting the treatment for medical evaluation B. Preventive oral care is important in leukemia patients C. Treat the acute needs then refer the patient 23
- 24. 3- All of following are symptoms of leukemia except A. Bruising B. Weight loss C. Bone pain D. Excessive salivation 24







![Etiology of leukemia
The cause of leukemia is unknown
Increased risk is associated with large doses of ionizing radiation, certain chemicals(
benzene), and infection with specific viruses [EPV] and human lymphotropic virus [HTLV]-1
Cigarette smoking and exposure to electromagnetic fields also have been proposed to be
causative.
Genetic factors may cause cytogenetic abnormalities that affect transcriptional cascades
of myeloid precursor cells.
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leukemia-170531185743/85/Dental-Management-of-Patient-with-Leukemia-7-320.jpg)