Dependency Injection and Aspect Oriented Programming presentation
- 1. Dependency Injection and Aspect Oriented Programming
- 2. Steve Erdman Senior Developer, Wharton Computing steve.erdman77@gmail.com
- 4. What is a dependency? Container of functionality defined outside the current code used by that code to achieve its central purpose
- 8. public class WoosterAlone { private RedAstonMartin theCar; public WoosterAlone(){ theCar = new RedAstonMartin(); } public void trip(){ theCar.drive(); } }
- 9. public class WoosterWithGarage { private Garage garage; public WoosterWithGarage(Garage garage){ this.garage = garage; } public void trip(){ garage.claimCar("Best Car").drive(); } }
- 10. public class WoosterAssisted { private Car theCar; public WoosterAssisted(Car theCar){ this.theCar = theCar; } public void trip(){ theCar.drive(); } }
- 11. Why is the better? • Decouples your code • Reduces/Removes glue • Large number of occasions where Wooster needs the car • Red Aston Martin in the shop – Black Jaguar instead • Roads are icy – take all weather car instead
- 12. Decoupling code • Objects should only be responsible for themselves (Single Responsibility Principle) • Design to interfaces • Modularity – Easy to debug – Easy to test – Easy to replace – Easy to iterate
- 13. Glue • The code that joins your objects together • Gluing should not be part of an object’s responsibilities • All other things being equal, the less amount of glue, the better
- 14. Inversion of control • Pull from registry • Dependency Injection
- 15. Dependency Injection process • Register your objects (“beans”) – System determines dependencies • Wire in dependencies • Instantiate your beans
- 16. Dependencies • Property setter to interface – Can use constructor, but won’t get into that • Wiring – Wired explicitly during bean registry – Pulled from other bean/properties – Autowired • By name • By type – Controlled Autowiring
- 17. Registering Beans <bean id=“theCar" name=“RedLightning BestCar” class=“RedAstonMartin“ /> <bean id=“trip” class=“WoosterAssisted”> <property name=“theCar”> <ref bean=“theCar” /> </property> </bean>
- 18. Wiring by pulling @Value(“#{theCar.licensePlateNumber}”) private String garageTicket;
- 19. Autowiring <bean id=“theCar" name=“RedLightning BestCar” class=“RedAstonMartin“ /> <bean id=“trip” class=“WoosterAssisted” autowire=“byType” /> OR <bean id=“trip” class=“WoosterAssisted” autowire=“byName” />
- 20. Annotation Autowiring public class WoosterAssisted { @Autowired private Car theCar; private void setTheCar(Car theCar){ this.theCar = theCar; } public WoosterAssisted(){ } public void trip(){ theCar.drive(); } }
- 21. Annotation Autowiring by Name public class WoosterAssisted { @Resource(name=“RedLightning”) private Car theCar; private void setTheCar(Car theCar){ this.theCar = theCar; } public WoosterAssisted(){ } public void trip(){ theCar.drive(); } }
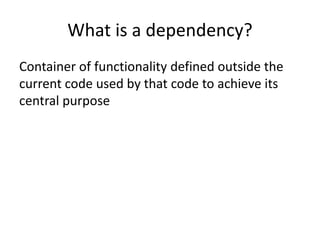
- 22. Autowiring Lists @AutoWired private Car[] cars; private void setCars(Car[] cars){ this.cars = cars; }
- 23. Component Scanning <context:component-scan /> • Registers all the beans it can find • Glue is completely hidden • Can set starting package • Can add include and exclude filters
- 24. Environment sets • Can set beans based on environment • e.g. – Local environment -> embedded database – Testing -> Mocked data connection – Dev environment -> dev SQL Server – Dev + NoSQL -> dev Cassandra Server – Prod -> prod SQL Server
- 25. Bean scopes • Singleton (default) • Prototype (new instance every time) • Request (new instance every request) • Session (new instance every session) • Thread (new instance every thread)
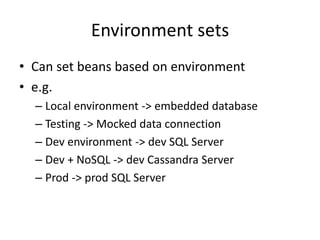
- 26. Basic Messaging public class BasicHelloMain { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello World!"); } }
- 27. Separate Pieces of Functionality • Message content • Message renderer • Connecting content to renderer
- 28. Separate Messaging public class SimpleMessageProvider { public String getMessage() { return "Hello World!"; } }
- 29. Separate Messaging public class StandardOutMessageRenderer { private SimpleMessageProvider provider; public StandardOutMessageRenderer(){ setMessageProvider(new SimpleMessageProvider()); } public void setMessageProvider(SimpleMessageProvider provider) { this.provider = provider; } public SimpleMessageProvider getMessageProvider() { return provider; } public void render() { System.out.println(getMessageProvider().getMessage()); } }
- 30. Separate Messaging public class HelloWorldMain { public static void main(String[] args) { StandardOutMessageRenderer renderer = new StandardOutMessageRenderer(); renderer.render(); } }
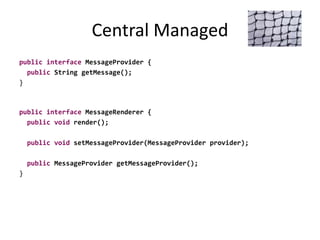
- 31. Central Managed public interface MessageProvider { public String getMessage(); } public interface MessageRenderer { public void render(); public void setMessageProvider(MessageProvider provider); public MessageProvider getMessageProvider(); }
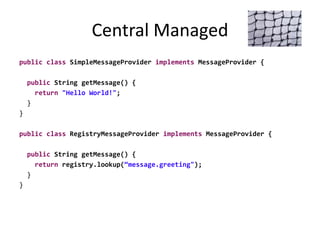
- 32. Central Managed public class SimpleMessageProvider implements MessageProvider { public String getMessage() { return "Hello World!"; } } public class RegistryMessageProvider implements MessageProvider { public String getMessage() { return registry.lookup(“message.greeting"); } }
- 33. Central Managed public class StandardOutMessageRenderer implements MessageRenderer { private MessageProvider provider; public void setMessageProvider(MessageProvider provider) { this.provider = provider; } public MessageProvider getMessageProvider() { return provider; } public void render() { if (getMessageProvider()==null){ throw new RuntimeException("Missing MessageProvider"); } System.out.println(getMessageProvider().getMessage()); } }
- 34. Central Managed public class HelloWorldMain { public static void main(String[] args) { MessageProvider provider = new SimpleMessageProvider(); MessageProvider provider = new RegistryMessageProvider(); MessageRenderer renderer = new StandardOutMessageRenderer(); renderer.setMessageProvider(provider); renderer.render(); } }
- 35. Dependency Injected @Service("simpleMessageProvider") public class SimpleMessageProvider implements MessageProvider { public String getMessage() { return "Hello World!"; } }
- 36. Dependency Injected @Service public class StandardOutMessageRenderer implements MessageRenderer { private MessageProvider provider; public void setMessageProvider(MessageProvider provider) { this.provider = provider; } public MessageProvider getMessageProvider() { return provider; } public void render() { if (getMessageProvider()==null){ throw new RuntimeException("Missing MessageProvider"); } System.out.println(getMessageProvider().getMessage()); } }
- 37. Dependency Injected <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd"> <context:annotation-config /> <context:component-scan base-package="edu.upenn.wharton.messaging.ioc.di.annotation" /> </beans>
- 38. Dependency Injected public class HelloWorldMain { public static void main(String[] args) { GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(); ctx.load("classpath:di-central-app-context.xml"); ctx.refresh(); MessageRenderer renderer = ctx.getBean("messageRenderer"); renderer.render(); } }
- 39. Dependency Injected @Service("injectedMessageProvider") public class InjectedMessageProvider implements MessageProvider { private String message; public void setMessage(String message){ this.message = message; } public String getMessage() { return message; } }
- 40. Dependency Injected <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd"> <context:annotation-config /> <bean id="messageProvider" class="edu.upenn.wharton.messaging.ioc.di.annotation.InjectedMessageProvider"> <property name="message"> <value>Hello World!</value> </property> </bean> <context:component-scan base-package="edu.upenn.wharton.messaging.ioc.di.annotation" include-classes="*Renderer" /> </beans>
- 42. Dependency Injection - injects registered dependency objects into established Interface properties Aspect Oriented Programming - injects entirely new functionality
- 43. What is not a dependency? Functionality included in the flow of a request that is not part of the central purpose of the current object. Good example of this is cross cutting concerns, such as logging or security
- 44. Back to Jeeves and Wooster
- 45. Wooster wants to • Keep track of all the things he does, for his autobiography • Keep track of the lies he tells his Aunt Agatha • Keep his financial accounts in order • Not intrude where he is not wanted • Speak to foreign chaps without having to learn their lingo
- 46. This involves • Keep track of all the things he does, for his autobiography - Logging • Keep track of the lies he tells his Aunt Agatha - Caching • Keep his financial accounts in order - Transactions • Not intrude where he is not wanted - Security • Speak to foreign chaps without having to learn their lingo -Translation
- 47. @Logged public class WoosterActions { @Cached public String generateLieForAuntAgatha(String situation, Date occurrence){ ... } @Transactional public void transferMoney(int amount, Account accountFrom, Account accountTo){ ... } public enterClub(@Secured(“Wooster Approved”) Club club){ ... } @Translate public void talkTo(String message, Person listener){ ... } @Translate public String listenTo(Person talker){ ... } }
- 48. Aspect components • Join Point – a place in code that can be the target for an aspect • Point Cut – The query that selects the join points that will the be targets for the aspect • Advice – The code that will be run at the selected Join Points
- 49. Join Point, Point Cuts, WTH??? • Very much like CSS/jQuery selectors • A Join Point is anywhere that can be joined – In selectors, this is any DOM element • Selectors match on things like DOM hierarchy, element type, id, attributes, etc. • Point cuts match on things like Class, Package, or Method names, Method signature, Annotations, etc.
- 50. Why is there a formal name for Join Points? • Join points give us access to the runtime values when advice is being run – Current class – Method name – Argument names and values – Annotations – etc.
- 51. AspectJ Point Cut syntax <match type>(<access> <return type> <class>.<method>(<method parameters>)) e.g. – execution(public String Wooster.*(..)) – execution(* @Logging*.*(..)) Don’t focus on this. I’m using fake syntax in my examples.
- 52. Composite Point Cuts • && = AND • || = OR • ! = NOT
- 53. Advice types • Before • After • After Returning • After Throwing • Around
- 54. Before Advice @Before(“joinMethod”) public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint){ beforeAction(); } public void joinMethod(){ insideAction(); } public void joinMethod(){ beforeAction(); insideAction(); }
- 55. After Advice @After(“joinMethod”) public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint){ afterAction(); } public void joinMethod(){ insideAction(); } public void joinMethod(){ insideAction(); afterAction(); }
- 56. Around Advice @Around(“joinMethod”) public void doBefore(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){ beforeAction(); joinPoint.proceed(); afterAction(); } public void joinMethod(){ insideAction(); }
- 57. Around Advice (continued) public void joinMethod(){ beforeAction(); insideAction(); afterAction(); }
- 58. Inter Type Definitions (ITD) • Adds code at compile time to matching Join Points • Enables the Mixin behavior of many advices • Can set up a dependency injection
- 59. @Logged public class WoosterActions { @Cached public String generateLieForAuntAgatha(String situation, Date occurrence){ lieGeneratingCode(situation, occurrence); } @Transactional public void transferMoney(int amount, Account accountFrom, Account accountTo){ transferFromAccount(accountFrom, amount); transferToAccount(accountTo, amount); } public enterClub(@Secured(“Wooster Approved”) Club club){ enterClubCode(club); } @TranslateIncoming public void talkTo(String message, Person listener){ talkToCode(message, listener); } @TranslateReturn public String listenTo(Person talker){ return listenToCode(talker); } }
- 60. Logging Aspect @Aspect public class LoggingAspect { private Log4JLogger log = new Log4JLogger("Jeeves"); @Before("@within(Logging) && execution(public * *.*(..)") public void logExecution(JoinPoint joinPoint){ log.info(joinPoint.getSignature().toString()); } }
- 61. Caching Aspect @Aspect public class CachingAspect { @Autowired private Cache cache; @Around("@annotation(Cacheable)") public Object checkCache(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{ Object result = cache.get(joinPoint.getTarget().hashCode()); if (result != null){ return result; } result = joinPoint.proceed(); cache.put(joinPoint.getTarget().hashCode(), result); return result; } }
- 62. Generate Lies @Cached public String generateLieForAuntAgatha(String situation, Date occurrence){ return lieGeneratingCode(situation, occurrence); }
- 63. Add Logging Aspect @Cached public String generateLieForAuntAgatha(String situation, Date occurrence){ log.info(joinPoint.getSignature().toString()); return lieGeneratingCode(); }
- 64. Add Cached Aspect @Cached public String generateLieForAuntAgatha(String situation, Date occurrence){ log.info(joinPoint.getSignature().toString()); Object result = cache.get(joinPoint.getTarget().hashCode()); if (result != null){ return result; } result = lieGeneratingCode(); cache.put(joinPoint.getTarget().hashCode(), result); return result; }
- 65. Transactional Aspect @Aspect public class TransactionalAspect { @Autowired private TransactionService transactionService; @Around("@annotation(Transactional)") public Object doTransaction(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){ transactionService.startTransaction(); try{ Object result = joinPoint.proceed(); transactionService.commitTransaction(); return result; } catch (Throwable e) { transactionService.rollbackTransaction(); throw e; } } }
- 66. Transferring Money @Transactional public void transferMoney(int amount, Account accountFrom, Account accountTo){ withdrawFromAccount(accountFrom, amount); depositToAccount(accountTo, amount); }
- 67. Add Transaction Aspect @Transactional public void transferMoney(int amount, Account accountFrom, Account accountTo){ log.info(joinPoint.getSignature().toString()); transactionService.startTransaction(); try{ withdrawFromAccount(accountFrom, amount); depositToAccount(accountTo, amount); transactionService.commitTransaction(); return result; } catch (Throwable e) { transactionService.rollbackTransaction(); throw e; } }
- 68. Secured Aspect @Aspect public class SecuredAspect { @Autowired private SecurityService securityService; @Before("* *.*(@annotation(Secured) Club club)") public void checkSecured(JoinPoint joinPoint){ Annotation[][] annotations = ((MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature()).getMethod().getParameterAnnotations(); if (!securityService.checkAccess(joinPoint.getArgs()[0], annotations[0][0])){ throw new SecurityException(); } } }
- 69. Enter Club public enterClub(@Secured(“Wooster Approved”) Club club){ enterClubCode(club); }
- 70. Add Secured Aspect public enterClub(@Secured(“Wooster Approved”) Club club){ log.info(joinPoint.getSignature().toString()); Annotation[][] annotations = ((MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature()).getMethod().getParameterAnnotations(); if (!securityService.checkAccess(joinPoint.getArgs()[0], annotations[0][0])){ throw new SecurityException(); } enterClubCode(club); }
- 71. Translation Aspect @Aspect public class TranslationAspect { @Autowired private TranslationService translationService; @Around("@annotation(TranslateIncoming)") public void translateIncoming(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) { Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); args[0] = translationService.translateMessage((String) args[0]); joinPoint.proceed(args); } @AfterReturning(value = "@annotation(TranslateReturn)", returning = "message") public String translateReturn(Object message){ return translationService.translateMessage((String) message); } }
- 72. Talking to foreign jobbie @TranslateIncoming public void talkTo(Person listener, String message){ talkToCode(listener, message); } @TranslateReturn public String listenTo(Person talker){ return listenToCode(talker); }
- 73. Add Translate Aspect @TranslateIncoming public void talkTo(String message, Person listener){ log.info(joinPoint.getSignature().toString()); Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); args[0] = translationService.translateMessage((String) args[0]); talkToCode(args[0], args[1]); } @TranslateReturn public String listenTo(Person talker){ log.info(joinPoint.getSignature().toString()); message = listenToCode(talker); return translationService.translateMessage(message); }
- 74. Steve Erdman Senior Developer, Wharton Computing steve.erdman77@gmail.com





















![Autowiring Lists
@AutoWired
private Car[] cars;
private void setCars(Car[] cars){
this.cars = cars;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjectionandaspectorientedprogramming-140819155105-phpapp01/85/Dependency-Injection-and-Aspect-Oriented-Programming-presentation-22-320.jpg)


![Basic Messaging
public class BasicHelloMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjectionandaspectorientedprogramming-140819155105-phpapp01/85/Dependency-Injection-and-Aspect-Oriented-Programming-presentation-26-320.jpg)



![Separate Messaging
public class HelloWorldMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StandardOutMessageRenderer renderer = new StandardOutMessageRenderer();
renderer.render();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjectionandaspectorientedprogramming-140819155105-phpapp01/85/Dependency-Injection-and-Aspect-Oriented-Programming-presentation-30-320.jpg)

![Central Managed
public class HelloWorldMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MessageProvider provider = new SimpleMessageProvider();
MessageProvider provider = new RegistryMessageProvider();
MessageRenderer renderer = new StandardOutMessageRenderer();
renderer.setMessageProvider(provider);
renderer.render();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjectionandaspectorientedprogramming-140819155105-phpapp01/85/Dependency-Injection-and-Aspect-Oriented-Programming-presentation-34-320.jpg)



![Dependency Injected
public class HelloWorldMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext();
ctx.load("classpath:di-central-app-context.xml");
ctx.refresh();
MessageRenderer renderer = ctx.getBean("messageRenderer");
renderer.render();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjectionandaspectorientedprogramming-140819155105-phpapp01/85/Dependency-Injection-and-Aspect-Oriented-Programming-presentation-38-320.jpg)





























![Secured Aspect
@Aspect
public class SecuredAspect {
@Autowired
private SecurityService securityService;
@Before("* *.*(@annotation(Secured) Club club)")
public void checkSecured(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Annotation[][] annotations = ((MethodSignature)
joinPoint.getSignature()).getMethod().getParameterAnnotations();
if (!securityService.checkAccess(joinPoint.getArgs()[0],
annotations[0][0])){
throw new SecurityException();
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjectionandaspectorientedprogramming-140819155105-phpapp01/85/Dependency-Injection-and-Aspect-Oriented-Programming-presentation-68-320.jpg)

![Add Secured Aspect
public enterClub(@Secured(“Wooster Approved”) Club club){
log.info(joinPoint.getSignature().toString());
Annotation[][] annotations = ((MethodSignature)
joinPoint.getSignature()).getMethod().getParameterAnnotations();
if (!securityService.checkAccess(joinPoint.getArgs()[0],
annotations[0][0])){
throw new SecurityException();
}
enterClubCode(club);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjectionandaspectorientedprogramming-140819155105-phpapp01/85/Dependency-Injection-and-Aspect-Oriented-Programming-presentation-70-320.jpg)
![Translation Aspect
@Aspect
public class TranslationAspect {
@Autowired
private TranslationService translationService;
@Around("@annotation(TranslateIncoming)")
public void translateIncoming(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
args[0] = translationService.translateMessage((String) args[0]);
joinPoint.proceed(args);
}
@AfterReturning(value = "@annotation(TranslateReturn)", returning = "message")
public String translateReturn(Object message){
return translationService.translateMessage((String) message);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjectionandaspectorientedprogramming-140819155105-phpapp01/85/Dependency-Injection-and-Aspect-Oriented-Programming-presentation-71-320.jpg)

![Add Translate Aspect
@TranslateIncoming
public void talkTo(String message, Person listener){
log.info(joinPoint.getSignature().toString());
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
args[0] = translationService.translateMessage((String) args[0]);
talkToCode(args[0], args[1]);
}
@TranslateReturn
public String listenTo(Person talker){
log.info(joinPoint.getSignature().toString());
message = listenToCode(talker);
return translationService.translateMessage(message);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjectionandaspectorientedprogramming-140819155105-phpapp01/85/Dependency-Injection-and-Aspect-Oriented-Programming-presentation-73-320.jpg)
