Developing Applications Using Host Processing Instead of DSPs
- 1. Developing Applications with Host Media Processing David Asher
- 2. Host Media Processing: What We’re Talking About Using a general-purpose computing platform To create a telephony application
- 3. Market Trend: Host Media Processing Lower acquisition costs, sometimes Lower provisioning and maintenance costs Eliminate special hardware associated costs More failure recovery options
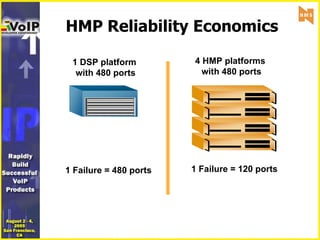
- 4. HMP Reliability Economics 1 DSP platform with 480 ports 4 HMP platforms with 480 ports 1 Failure = 480 ports 1 Failure = 120 ports
- 5. HMP Application Economics ~ $4k for 1U Dual Xeon 120 application sessions rated capacity ~ $33 per session HW cost Reduction in total cost of ownership no platform integration and test no special hardware inventory, tracking, failures, replacements, repairs, tech support
- 6. Distributed Media Processing Single large DSP media server Small media servers “built-in” to each application App Servers Media Server App Servers HMP HMP HMP HMP HMP
- 7. Primary Features IVR Operations Play prompt, record and play messages, detect DTMF tones, ASR & TTS interface Audio processing operations Automatic gain control, voice activity detector, acoustic DTMF detector Enhanced media services Transcoding (audio and video), conferencing VoIP call connections RTP packetization, SIP signaling, encryption
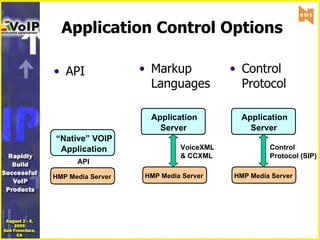
- 8. Application Control Options Application Server Application Server Application Server Application Server Application Server Application Server API VoiceXML & CCXML Control Protocol (SIP) Markup Languages API Control Protocol IP Media Server IP Media Server HMP Media Server “ Native” VOIP Application “ Native” VOIP Application “ Native” VOIP Application IP Media Server IP Media Server HMP Media Server IP Media Server IP Media Server HMP Media Server
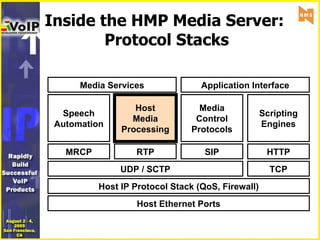
- 9. Inside the HMP Media Server: Protocol Stacks Host Ethernet Ports Host IP Protocol Stack (QoS, Firewall) UDP / SCTP TCP RTP Host Media Processing HTTP Scripting Engines Media Control Protocols SIP MRCP Speech Automation Application Interface Media Services
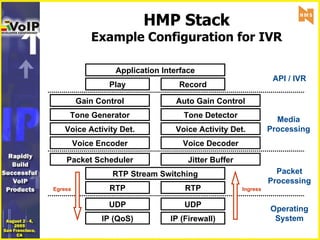
- 10. HMP Stack Example Configuration for IVR IP (QoS) UDP IP (Firewall) UDP RTP Egress Ingress RTP Packet Scheduler Jitter Buffer Auto Gain Control Voice Decoder Voice Activity Det. Tone Detector RTP Stream Switching Media Processing Record Play Application Interface Packet Processing Voice Activity Det. Tone Generator Voice Encoder Gain Control Operating System API / IVR
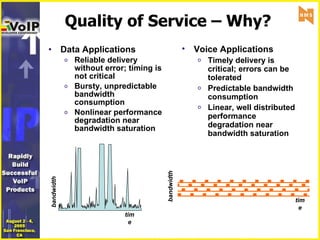
- 11. Quality of Service – Why? Data Applications Reliable delivery without error; timing is not critical Bursty, unpredictable bandwidth consumption Nonlinear performance degradation near bandwidth saturation Voice Applications Timely delivery is critical; errors can be tolerated Predictable bandwidth consumption Linear, well distributed performance degradation near bandwidth saturation time bandwidth bandwidth time
- 12. Quality of Service – What? time Jitter Increase or Packet Loss Events Available Bandwidth Voice Class Data Class
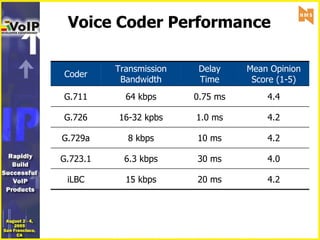
- 13. Voice Coder Performance 20 ms 30 ms 10 ms 1.0 ms 0.75 ms Delay Time 4.2 4.0 4.2 4.2 4.4 Mean Opinion Score (1-5) 6.3 kbps G.723.1 Transmission Bandwidth Coder 15 kbps iLBC 8 kbps G.729a 16-32 kpbs G.726 64 kbps G.711
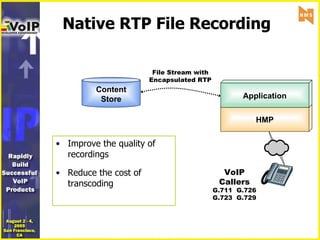
- 15. Native RTP File Recording Improve the quality of recordings Reduce the cost of transcoding Content Store File Stream with Encapsulated RTP VoIP Callers G.711 G.726 G.723 G.729 HMP Application
- 16. Types of Attack or Misuse Source: IDC, 2003 CSI/FBI Computer Crime and Security Survey
- 17. SECURITY IS YOUR RESPONSIBILITY !!! An HMP platform is a computer like any other It is vulnerable to many Internet security threats The application developer is responsible for building secure applications!
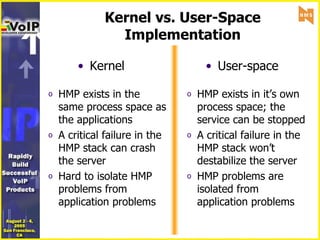
- 18. Kernel vs. User-Space Implementation Kernel User-space HMP exists in the same process space as the applications A critical failure in the HMP stack can crash the server Hard to isolate HMP problems from application problems HMP exists in it’s own process space; the service can be stopped A critical failure in the HMP stack won’t destabilize the server HMP problems are isolated from application problems
- 19. HMP Density Roadmap Montecito (4-Way) Tanglewood (16-Way) Dual 2.4 GHz Dual 64-Bit Based on Intel CPU Roadmap
- 20. DSP vs. HMP ?? DSP Very high density High transcoding requirement Low power requirement PSTN interfaces and signaling HMP Lower density Need to deploy on generalized servers VOIP-only
- 21. Is HMP Inevitable ?? New processing requirements that favor DSP economics Security – encryption Wideband audio (conferencing) Video transcoding, transrating, resizing, and conferencing …