dheeraj
- 1. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- 2. What is ERP? “ An initiative launched by organizations to better manage all enterprise-wide business processes using a common integrated database and shared data management applications and reporting tools.”
- 3. Basis For the Development of ERP An organization’s critical business processes often cut across many of the organization’s functional business boundaries (e.g., Order Processing) In most organizations, each business process has it’s own separate set of data needs and applications that operate as distinct “systems” within the organization. The results of this approach: Function-Centric View in Business Units: The functional units (e.g., sales, accounting, production, etc.) are only concerned with the applications and data needs of their portion of the business process. Operational Inefficiencies: By viewing the complete process as a series of distinct pieces – the organization is introducing operational inefficiencies and information sharing challenges into the process. These information sharing challenges include: 1) data redundancy (same data elements in numerous locations) 2) program redundancy (many programs doing the same thing) 3) lack of systems integration (flow of information between systems)
- 4. Basis For the Development of ERP (An Example) ACCOUNTING PURCHASING PRODUCTION LOGISTICS SALES Customer Order
- 5. Evolution of ERP The vision of an integrated information system to fully support operations began on the factory floor in the 1960s through the 1970s The development of Materials Planning Software (MRP) allowed plants managers to plan the production and raw materials requirements by working backwards from the sales forecast: 1 – Identify Demand: The production manager looked at marketing and sales forecast of demand (What is the production needed?). 2 – Review Current Production Schedule: The production manager would then look at the current production schedule in relation to the planned demand (Who is needed for production?). 3 - Raw Materials for Production: The production manager would identify what raw materials will be needed based on the production schedule and the sales forecast (How much do we need?). 4 – Plan Raw Materials Orders: The production manager would then project when purchase orders would need to be sent to the key suppliers in the value chain (When will the supplies arrive?).
- 6. Evolution of ERP The growing acceptance of EDI and EFT technologies by firms allowed trading partners in the value chain to both send and receive time-critical business transactions, avoiding the cost and delays resulting from using paper purchase order and invoice systems. In the 1980s, MRP II was developed to integrate the financial function into the planning process: “ Instead of having one set of numbers for the operating system in manufacturing and one set kept by the financial people – once the manufacturing people have numbers that are valid, the financial people can use these to get their numbers. Of course, whenever there are two systems – the numbers are bound to be different. With MRP II, everybody can be working to the same set of numbers But that’s only the technical difference. The big difference comes in the way management uses these tools…MRP II becomes a company game plan for manufacturing, marketing, engineering, and finance.” Oliver Wright, The Executives Guide to Successful MRP II, 1982
- 7. Evolution of ERP By the late 1980s and early 1990s, company downsizing and corporate reorganizations pushed companies to fully explore how IT could be used to reduce process costs and improve operational efficiency. By the early 1990s, organizations began to explore how they could reengineer their existing business processes to “squeeze out” costly process inefficiencies & improve relationships with value chain trading partners. It was this climate that led five former IBM systems analysts to develop the system Systemanalyse und Programmentwicklung in Manheim, Germany – SAP. - In 1988 the SAP AG firm released SAP R/3 a fully integrated software system that has distinct modules for each key business process (12 modules linked to a single open architecture client/server system) - By 2000, SAP AG had 22,000 employees in 50 countries – and 10 million users at 30,000 installations around the world. - Main Competitors: PeopleSoft, J.D. Edwards, Oracle, and Baan.
- 8. Evolution of ERP SAP R/3 Approach WF (Work Flow) IS (Industry Solutions) PS (Project System) CO (Controlling) AM ( Fixed Assets Mgt) FI (Financial Accounting) R/3 Client / Server MM (Materials Management) PP (Production Planning) SD (Sales & Distribution) PM (Plan Maintenance) HR (Human Resources) QM (Quality Mgt) NOTE: The approach allows for the “linking” of applications from SAP business partners – 3,000 business partners world-wide
- 9. Why Undertake ERP? Integrate Financial Information: ERP ensures that there is a consist and credible set of financial information since all of the functional areas use the same integrated system. Integrate Customer Order Information: ERP provides a single environment from the time the customer places an order until the customer receives the order – instead of having order information spread across a number of distinct systems. Standardize and Speed Up Manufacturing Processes: Many organizations have found it difficult to manage production in the current “merger and acquisition” business environment. ERP ensures that a single standardized process is employed resulting in: increased productivity and reduced head count. Reduce Inventory: ERP – along with new IT technologies – has made it possible to better manage both supplier side inventory and retailer side inventories through real-time information sharing with the firm’s value chain trading partners. Standardize HR Information: ERP allows the firm to better estimate and track what resources are required to support their business processes – thus optimizes the firm’s needed workforce.
- 10. The General ERP Process Product Analysis: The firm will hear the sales and marketing “pitches” from ERP firms that they believe meet their general business needs and objectives. Module Selection: The firm determines which of the ERP modules to implement to meet their current business needs. Process Analysis: The ERP firm will provide consultants to help their client identify the processes impacted by the selected ERP modules. The consultants will then do a complete analysis of those processes to establish data and processing needs. Data Analysis: In order for ERP systems to function properly, all ERP systems must have a single integrated data repository for ALL data items used by the firm. Therefore, consultants are required to establish the standardized database. Applications Integration: In order for ERP to run properly, the existing legacy systems applications have to be modified to use the new ERP environment. New hardware and software may have to be purchased to run the ERP system. Testing and Installation: The new system must be tested to ensure it meets the desired firm specifications. Employee Training: The employees must learn the new system.
- 11. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Help Desk Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling Sample PeopleSoft System
- 12. Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service CRM Modules Sample CRM System ----------------------- Marketing, Sales, Customer Support, and Telemarketing
- 13. Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Supply-Chain Modules Sample SCM System ---------------------- Takes Orders, Fulfills Orders, Manages Inventory Demand Planning Inventory Planning Enterprise Planning
- 14. Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Supply-Chain Modules SCM often includes Planning Modules to forecast Sales Demand, Inventory Demand, Global Logistics Demand Planning Inventory Planning Enterprise Planning
- 15. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Financial Modules Sample Financials ------------------------ Receives feeds into AR, AP, GL to provide reports, Also manages Assets
- 16. Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling Enterprise Data Warehouse Global Data Repository ----------------------- Holds data from all corporate systems, provides several ways to deliver corporate reports, often provides detailed analytics, and detailed KPIs.
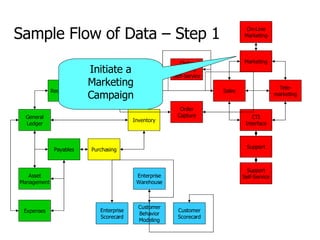
- 17. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling Sample Flow of Data – Step 1 Initiate a Marketing Campaign
- 18. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling Sample Flow of Data – Step 2 Campaign generates Sales Volume handled by the Sales Channels directly, or through Telemarketing
- 19. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling Sample Flow of Data – Step 3 Sales Order is captured and processed by the Order Capture module
- 20. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling Sample Flow of Data – Step 4 CRM, through an interface, sends the Sales Order to the Supply-Chain Order Management module
- 21. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling Sample Flow of Data – Step 5 Through integration, Inventory is asked to pick/pack/ship the Order to the Customer
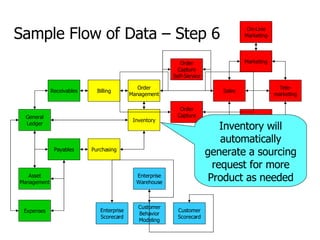
- 22. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling Sample Flow of Data – Step 6 Inventory will automatically generate a sourcing request for more Product as needed
- 23. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling Sample Flow of Data – Step 7 Additional Product processing (PO, receipt, adjustments) will be controlled by Purchasing, Paying for Product is handled by AP
- 24. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling Sample Flow of Data – Step 8 Shipped Orders will be invoiced through the Billing module
- 25. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling Sample Flow of Data – Step 9 Collecting payments on invoices, past due balances, and fees will be controlled by Receivables (AR)
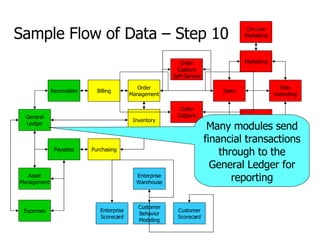
- 26. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling Sample Flow of Data – Step 10 Many modules send financial transactions through to the General Ledger for reporting
- 27. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling Sample Flow of Data – Step 11 After shipping, Order Management will keep CRM updated to reflect Customer activity
- 28. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling Sample Flow of Data – Step 12 Periodically (perhaps Monthly) data from all systems is transferred to the Data Warehouse
- 29. General Ledger Payables Receivables Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Marketing Sales Back Office is Financials and Supply-Chain combined Basic CTI Framework connects to PBX (phone) Basic ERP & CRM System CTI Interface Tele- Marketing Support module handles all Customer Service
- 30. General Ledger Payables Receivables Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Web & On-Line Take existing PeopleSoft functionality to the web without re-inventing the wheel
- 31. General Ledger Payables Receivables Asset Management Expenses Billing Order Management Inventory Purchasing Order Capture Support Self-Service CTI Interface Support On-Line Marketing Marketing Tele- marketing Sales Order Capture Self-Service Help Desk Enterprise Warehouse Enterprise Scorecard Customer Scorecard Customer Behavior Modeling PeopleSoft Modules: Financials , Supply Chain , CRM & EPM
- 32. How Much Does an ERP Package Cost? The total cost of an ERP Implementation can vary significantly depending upon: 1) The Size and Geographical Distribution of the Company 2) The Size of the ERP Package (How Many Modules?) 3) The Addition of New Hardware to Support ERP 4) The Addition of New Systems Software to Support ERP 5) Consultants’ and Analysts’ Fees (Can be VERY Expensive) 6) Time Required for Implementation (Disruption of Business) 7) Training Costs (Both Time and Money) A large company may spend from $50 million to $500 million for an integrated ERP system. Meta group did a survey of the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) of ERP (including hardware, software, consulting) at 63 companies (small through large) in a range of industries and found that the average cost was $15 million . The high was $300 million and the low was $400,000.
- 33. How Much Does an ERP Package Cost? $14.5 Billion Systems Manufacturer World-Wide Operations Install ERP in their Turbocharging Systems Division which encompasses 11 countries, 18 sites and 9 languages. ERP implementation will be complex and have a huge database Estimated Costs: 1) $30 million in software license fees 2) $200 million in consulting fees 3) Millions in hardware integration costs 4) Millions in software integration costs 5) Millions in training costs Time to Implement System: Four to Six Years Business Example: Allied Signal, Inc.
- 34. How Long Until the Firm Sees a Return on their Investment in ERP? A Meta Group Study of 63 companies that took 8 months after an average implementation time of 24 months (31 months total) to see any benefits from their ERP initiative. BUT, the medium annual cost savings from the new ERP system was $1.6 million Examples: 1) Pitney Bowes: ERP cut overall operations costs by 28%. Sales Reps can now give price quotes in 15 minutes rather than hours resulting in a 4% increase in sales - $160 million. 2) Toro: Spent $25 million and four years on their ERP project with no initial quantifiable return. Sales to large national retailers like Sears and Home Depot resulted in $10 million due to inventory reduction benefits. 3) FoxMeyer: Is suing SAP AG claiming the ERP implementation caused their bankruptcy.
- 35. Why Do Some Companies Have More Success With ERP Than Other Companies? Loss of Top Management Support: Commitment by the firm’s top management to the successful completion of the ERP project decreases over time. Improper Cost Estimation: Ability of the firm to properly identify the TRUE cost and time commitments that will be required by the firm. MOST ERP projects experience cost overruns! Realistic Expectations: The assumption that an ERP system will cure fundamental business problems that are not curable by any software application Select Proper ERP Implementation: Executives do not take enough time for proper analysis of the ERP impact during the project planning phase. (Requirements?) Cultural Impacts: People throughout the organization resist the changes made to business processes to support new ERP system. Training Costs: Some firms under budget or skimp on employee ERP system training (People Costs) IT Customization and Integration: The IT shop is bogged down in ERP integration
- 36. QUESTIONS??