Diagnosis and red flags in Multiple sclerosis
- 1. 1 Red Flags in Multiple Sclerosis
- 2. Amr Hasan, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology - Cairo University 2016 Red Flags in Multiple Sclerosis
- 4. Multiple Sclerosis Diagnosis 4 • Diagnosis relies on clinical judgment. • MS is extremely variable. • There is no specific test. • The diagnosis has dramatic implications.
- 5. Multiple Sclerosis Diagnosis 5 Diagnosis of MS includes To prove it is M.S To exclude other diagnoses
- 6. How to diagnose MS? 6 Clinical: • History and examination. • Evidence of CNS involvement. • Dissemination in space and time. Paraclinical: • Neuroimaging. • Evoked potentials. • CSF analysis.
- 7. 7
- 8. Diagnostic Criteria • Dawson criteria: 1916 • Schumacher criteria: 1965 • Poser criteria: 1983 • McDonald criteria: 2001 • McDonald criteria: 2005 • McDonald criteria: 2010 All criteria require dissemination in time and space
- 9. Summarized Diagnostic Criteria 1. Dissemination in space: Objective evidence of neurological deficits localized to two separate parts of the CNS 2. Dissemination in Time: Onset of neurological deficits separated by at least one month 3. Rule out other explanations! 2010 2014
- 10. Diagnostic Criteria 2005 • Incorporate use of MRI • Clinically Isolated Syndrom + MRI Dissemination in space + MRI Dissemination on time = Earlier MS Diagnosis August DIS DIT November
- 11. New Diagnostic Criteria 2010 • Incorporate use of MRI • Clinically Isolated Syndrom + MRI Dissemination in space + MRI Dissemination on time = Earlier MS Diagnosis August DIS DIT August
- 13. Magnetic resonance imaging T2 weighted images showing plaques 13
- 14. Magnetic resonance imaging T1 weighted Pre & Post Contrast 14
- 15. 15
- 16. 16 2. VEP
- 20. 20
- 21. Diagnostic tools 21 CSF examination: • Abnormal in 85% to 90% of patients with MS. • Elevated total IgG, an elevated IgG ratio, an increased IgG synthesis rate, • Presence of two or more oligoclonal bands in the CSF that are not present in a simultaneously drawn serum sample
- 22. CSF examination 22 IgG index: • [IgGCSF/albuminCSF]/[IgGserum/albuminserum] MS patients elevated IgG index (>1.7). (normal is <0.77)
- 23. 23 Oligoclonal Bands in CSF
- 24. Multiple Sclerosis Diagnosis 24 Diagnosis of MS includes To prove it is M.S To exclude other diagnoses
- 25. Mental map for diagnosis of MS 25 Clinical/Paraclinical/Imaging Typical for MS Fulfills Criteria Atypical for MS Red Flags Present Work Up for Alternative Diagnoses Clinical/Imaging Follow Up Alternative Diagnosis Established Further clinical/imaging typical for MS MS Diagnosis Typical for MS not Fulfilling Criteria Clinical/Imaging Follow Up
- 26. The Red Flags 26
- 27. Red flags 27 • Major red flags point fairly definitively to a non-MS diagnosis • Intermediate red flags point to poor agreement and uncertainty among raters about the weighting of the flag for differential diagnosis in MS • Minor red flags suggest that a disease other than MS should be considered and fully explored, but an MS diagnosis is not excluded.
- 28. Outline The Red Flags 28 • Clinical • Lab • Imaging
- 29. Outline The Red Flags 29 • Clinical • Lab • Imaging
- 31. Clinical Red Flags (Major) 31 Bone lesions 30 Histiocytosis; Lung involvement 30 Sarcoidosis; Lymphomatoid granulomatosis Multiple cranial neuropathies or polyradiculopathy 30 Chronic meningitis, including sarcoidosis and tuberculosis; Lyme disease Peripheral neuropathy 30 B12 deficiency; adrenoleukodystrophy; metachromatic leukodystrophy, Lyme disease Tendon xanthomas 30 Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis
- 32. Clinical Red Flags (Major) 32 Cardiac disease 29 Multiple cerebral infarcts; brain abscesses with endocarditis or right to left cardiac shunting Myopathy 29 Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy (e.g., MELAS); Sjögren's syndrome Renal involvement 29 Vasculitis; Fabry disease, systemic lupus erythematosus
- 33. Clinical Red Flags (Major) 33 Extrapyramidal features 28 Whipple's disease; multisystem atrophy; Wilson's disease Livedo reticularis 28 Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome; systemic lupus erythematosus; Sneddon's syndrome Retinopathy 28 Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy; Susac, and other vasculitides (retinal infarction); neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis Diabetes insipidus 28 Sarcoidosis; histiocytosis; neuromyelitis optica Increase serum lactate level 27 Mitochondrial disease
- 34. Clinical Red Flags (Major) 34 Hematological manifestations 27 Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; vitamin B12 deficiency; Wilson's disease (hemolytic anemia); copper deficiency Mucosal ulcers 27 Behçet's disease Myorhythmia 27 Whipple's disease Hypothalamic disturbance 26 Sarcoidosis; neuromyelitis optica; histiocytosis Recurrent spontaneous abortion or thrombotic events 26 Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome; thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; metastatic cancer with hypercoagulable state
- 35. Clinical Red Flags (Major) 35 Rash 26 Systemic lupus erythematosus; T-cell lymphoma; Lyme disease, Fabry disease Arthritis, polyarthalgias, myalgias 26 Systemic lupus erythematosus; Lyme disease; fibromyalgia Amyotrophy 25 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; syringomyelia; polyradiculpathy Headache or meningismus 25 Venous sinus thrombosis; chronic meningitis; lymphoma or glioma, vasculitis, systemic lupus erythematosus Persistently monofocal manifestations 24 Structural lesion (e.g., Chiari malformation); cerebal neoplasm
- 36. Clinical Red Flags (Intermediate) 36 Sicca syndrome 23 Sjögren's syndrome Gastrointestinal symptoms 22 Whipple's disease; celiac disease and other malabsorptive states that lead to B12 or copper deficiency Loss of hearing 21 Susac's syndrome; glioma; vertebrobasilar infarction Fulminant course 20 Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; intravascular lymphoma; acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Increase serum ACE level 20 Sarcoidosis; histiocytosis Prominent family history 19 Depending on pattern of inheritance suggested by family history: hereditary spastic paraparesis; leukodystrophy; Wilson's disease; mitochondrial disorder; CADASIL Constitutional symptoms 19 Sarcoidosis; Whipple's disease, vasculitis
- 37. Clinical Red Flags (Intermediate) 37 Progressive ataxia alone 18 Multisystem atrophy; hereditary spinocerebellar ataxia; paraneoplastic cerebellar syndrome Neuropsychiatric syndrome 1 7 Susac's syndrome; systemic lupus erythematosus; Wilson's disease, GM2 gangliosidosis Seizure 16 Whipple's disease; vasculitis; metastases Uveitis 15 Sarcoidosis; lymphoma; Behcet's disease Pyramidal motor involvement alone 13 Primary lateral sclerosis variant of ALS; hereditary spastic paraparesis Gradually progressive course from onset 13 HTLV-1 associated myelopathy; adrenomyeloneuropathy; adrenoleukodystrophy; metachromatic leukodystrophty, B12 deficiency
- 38. Clinical Red Flags (Minor) 38 Brainstem syndrome 7 Pontine glioma; cavernous angioma; vertebrobasilar ischemia Myelopathy alone 9 Chiari type 1 malformation; cord compression including cervical spondylosis; B12 or copper deficiency; HTLV1 Onset before age 20 10 Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy; leukodystrophy; Friedrich's ataxia Abrupt onset 11 Cerebral infarction; cerebral hemorrhage; cerebral venous sinus thrombosis Onset after age 50 12 Cerebral infarction; amyloid angiopathy; lymphoma
- 39. Clinical Red Flags 39 • Dementia CADASIL • Speech disoders Aphasia • Stroke like events Antiphospholipid Syndrome. CNS vasculitis. • Prominent psychiatric illness
- 40. Clinical Red Flags 40 • Extrapyramidal disorders Rest tremors Dystonia Chorea Tics Dyskinesia • Steroid dependence Neurosarcoid CNS lymphoma
- 41. Clinical Red Flags 41 • Fever at the onset. • Dermatologic involvement , other than psoriasis. • Endocrinologic disease other than autoimmune thyroid disease.
- 42. Outline The Red Flags 42 • Clinical • Lab • Imaging
- 43. Outline The Red Flags 43 • Clinical • Lab • Imaging
- 45. Laboratory Red Flags 45 • CBC: Marked cell count abnormality • High ESR • +ve ANA
- 46. Laboratory Red Flags CSF 46 • Cell count: >50 White blood cells CNS Lymphoma CNS vasculitis • Cell differential: Neutrophilic predominance CNS Whipple CNS Lupus • Protein: Significant elevation(>100 mg/dl) Neurosarcoid Spinal stenosis • Glucose: Low glucose(<2/3 serum glucose) Neurosarcoid CNS Lymphoma
- 47. Labs UPON red flags 47 CNS Inflammatory/Autoimmune Disease: • ANA,CRP, Anti DS DNA,C3,C4, ANCA panel, Chest CT, eye exam, conjunctival biopsy, Pathergy skin test (Behcet's), Skin biopsy if suspicious rash present, CTA, angiogram . CNS Infection: • Brucella antibodies, HIV test, HTLV1, and CSF antibodies (if isolated myelopathy with a lesion on spinal MRI), ESR, small bowel biopsy for whipple .
- 48. Labs UPON red flags 48 CNS Neoplasm/ Infiltrative Disorder: • CSF cytology and flow cytometry, CXR, CT Chest AbdomenPelvis, Pelvic ultrasound, Mammogram, LDH, skeletal series, bone scan, Brain biopsy. CNS vasculopathy/Ischemic Disease: • Notch3 mutations in CADASIL , MRA, CTA, standard angiogram, thrombophilia panel, Lupus anticoagulant .
- 49. Labs UPON red flags 49 Dysmyelinating/ Metabolic Disorders: • Lumbar puncture • EMG/NCVs • biochemical studies • buccal or rectal mucosa biopsy for electron microscopy if neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (NCL) suspected • Brain biopsy (rarely needed): fingerprint profiles, curvilinear and rectilinear bodies by E.M. in NCL oligodendrocytes; diffuse white matter gliosis by light microscopy in NCL.
- 50. Labs UPON red flags 50 Urine/blood for biochemical studies, including levels of: • WBC arylsulfatase A, Very long chain fatty, Fasting arterial lactate, Quantitative plasma amino acid and Urine organic acid analyses. Nutritional deficiency/Toxicity: • Vitamin B12, Copper and Zinc Levels, Ceruloplasmin, Folate, Heavy metal screen.
- 52. 52 “The most common reason for falsely attributing a patient’s symptoms to multiple sclerosis is faulty interpretation of the magnetic resonance imaging.” Famous Dictum Loren A. Rolak 2007
- 53. 53 The Red Flags
- 54. MRI Red Flags (Major) 54 Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis 30 Behçet's disease; vasculitis; chronic meningitis, antiphospholipid or anticardiolipin antibody syndromes Cortical infarcts 29 Embolic disease; thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; vasculitis Hemorrhages/microhemo rrhages 29 Amyloid angiopathy; Moya Moya disease; CADASIL; vasculitis Meningeal enhancement 29 Chronic meningitis; sarcoidosis; lymphomatosis; CNS vasculitis
- 55. MRI Red Flags (Major) 55 Calcifications on CT scans 28 Cysticercosis; toxoplasmosis, mitochondrial disorders Selective involvement of the anterior temporal and inferior frontal lobe 27 CADASIL Lacunar infarcts 27 Hypertensive ischemic disease; CADASIL; Susac syndrome Persistent Gd- enhancement and continued enlargement of lesions 27 Lymphoma; glioma; vasculitis; sarcoidosis
- 56. MRI Red Flags (Major) 56 Simultaneous enhancement of all lesions 26 Vasculitis; lymphoma; sarcoidosis T2-hyperintensity in the dentate nuclei 26 Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis T1-hyperintensity of the pulvinar 25 Fabry disease; hepatic encephalopathy; manganese toxicity Large and infiltrating brainstem lesions 24 Behçet's disease; pontine glioma Predominance of lesions at the cortical/subcortical junction 23 Embolic infarction; vasculitis; progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
- 57. MRI Red Flags (Intermediate) 57 Hydrocephalus 23 Sarcoidosis or other chronic meningitis; lymphoma or other CNS neoplasm Punctiform parenchymal enhancement 23 Sarcoidosis; vasculitis T2-hyperintensities of U-fibers at the vertex, external capsule and insular regions 22 CADASIL Regional atrophy of the brainstem 21 Behçet's disease; adult onset Alexander's disease Diffuse lactate increase on brain MRS 21 Mitochondrial disease Marked hippocampal and amygdala atrophy 21 Hyperhomocystinemia Symmetrically distributed lesions 20 Leukodystrophy T2-hyperintensities of the basal ganglia, thalamus and hypothalamus 20 Behçet's disease; mitochondrial encephalomyopathies; Susac's syndrome; acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
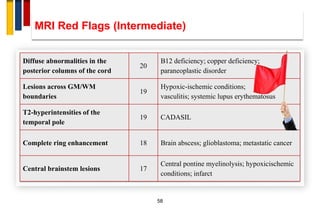
- 58. MRI Red Flags (Intermediate) 58 Diffuse abnormalities in the posterior columns of the cord 20 B12 deficiency; copper deficiency; paraneoplastic disorder Lesions across GM/WM boundaries 19 Hypoxic-ischemic conditions; vasculitis; systemic lupus erythematosus T2-hyperintensities of the temporal pole 19 CADASIL Complete ring enhancement 18 Brain abscess; glioblastoma; metastatic cancer Central brainstem lesions 17 Central pontine myelinolysis; hypoxicischemic conditions; infarct
- 59. MRI Red Flags (Intermediate) 59 Predominant brainstem and cerebellar lesions 1 7 Behçet's disease; pontine glioma Lesions in the center of CC, sparing the periphery 1 7 Susac's syndrome Dilation of the Virchow-Robin spaces 15 Hyperhomocystinemia; primary CNS angiitis Cortical/subcortical lesions crossing vascular territories 14 Ischemic leukoencephalopathy; CADASIL; vasculitis
- 60. MRI Red Flags (Intermediate) 60 Large lesions with absent or rare mass effect and enhancement 1 3 Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy No “occult” changes in the NAWM 1 3 Lyme disease, isolated myelitis, CADASIL No enhancement 8 Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy; ischemic lesions; metachromatic leukodystrophy No optic nerve lesions 9 Metastatic carcinoma; gliomatosis cerebri; toxoplasmosis No spinal cord lesions 10 Multiple infarcts; vasculitis; progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy Large lesions 11 Glioblastoma; lymphoma; progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy No T1 hypointense lesions (black holes) 11 Ischemic degenerative leukoencephalopathy; progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy Marked asymmetry of WM lesions 12 Glioblastoma; lymphoma; cerebral infarction
- 62. 62
- 63. 63
- 64. 64 Normal Aging • Periventricular caps and bands • Mild atrophy with widening of sulci and ventricles • Punctate and sometimes even confluent lesions in the deep white matter (Fazekas I and II).
- 65. 65 Normal Aging
- 66. These white matter changes are classified according to Fazekas: 66 • Mild - punctate WMLs: Fazekas I) • Moderate - confluent WMLs: Fazekas II - in the deep white matter can be considered normal in aging. • Severe - extensive confluent WMLs: Fazekas III - always abnormal.
- 67. 67 Infarctions
- 68. 68 Infarctions
- 69. 69 Distribution of white matter lesions
- 70. 70
- 71. 71
- 72. 72
- 73. 73
- 74. 74
- 75. 75 MRI Red Flags Diffuse/Symmetric matter involvement Adult Onset AD Leukodystrophy
- 76. 76 MRI Red Flags Diffuse/Symmetric white matter involvement HIV Associated Neurocognitive Disorder
- 77. 77 Nonspecific White Matter T2 lesions • Smoking • Hypertension • Diabetes • Toxic • Radiation • Chemotherapy • Congenital
- 78. 78 MRI Red Flags Atypical brainstem lesionsNeuro-Behçet
- 79. 79
- 80. 80 MRI Red Flags CADASIL Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy
- 81. 81 MRI Red Flags Primary CNS Vasculitis Hemorrhage
- 82. 82 MRI Red Flags Amyloid Angiopathy Microhemorrhage
- 83. 83 MRI Red Flags Poorly defined lesion border/ U fiber involvement Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
- 84. 84 Tumefactive MS • Post-gadolinium, there may be some peripheral enhancement, often with an incomplete ring. • These lesions can be distinguished from gliomas or intraparenchymal abscesses, which typically have a closed-ring enhancement.
- 85. 85 MRI Red Flags Leptomeningeal enhancement Neurosarcoidosis
- 86. 86 MRI Red Flags
- 87. 87 MRI Red Flags Increasing lesion size/persistent enhancement One month later Primary CNS Lymphoma
- 88. 88 Neurologic symptoms + Incidental/Nonspecific brain MRI abnormality = MS
- 89. 89 The Incidentals Capillary Pontine Telengectasia
- 92. 92 CIS RED FLAGS
- 93. 93
- 94. 94
- 95. 95
- 96. D.D. OF M.S. IN MRI 96 1. Age-related changes 2. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis 3. CNS vasculitis 4. Behçet disease 5. Sjögren syndrome 6. Sarcoidosis 7. Metastatic neoplasm 8. CADASIL (cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy) 9. Binswanger disease 10. Migrainous ischemia
- 97. D.D. OF M.S. IN MRI 97 11. Cerebrovascular disease 12. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy 13. Inherited white matter diseases 14. Effects of radiation therapy or drugs 15. CNS lymphoma 16. Lyme disease 17. HTLV-1 infection 18. CNS lupus 19. Mitochondrial encephalopathies 20. Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
- 98. Mental map for diagnosis of MS 98 Clinical/Paraclinical/Imaging Typical for MS Fulfills Criteria Atypical for MS Red Flags Present Work Up for Alternative Diagnoses Clinical/Imaging Follow Up Alternative Diagnosis Established Further clinical/imaging typical for MS MS Diagnosis Typical for MS not Fulfilling Criteria Clinical/Imaging Follow Up
- 99. THANK YOU






















![CSF examination
22
IgG index:
• [IgGCSF/albuminCSF]/[IgGserum/albuminserum]
MS patients elevated IgG index (>1.7). (normal is <0.77)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diagnosisandredflags2016-160708214044/85/Diagnosis-and-red-flags-in-Multiple-sclerosis-22-320.jpg)