Disorders of Biliary System
- 1. Cognito ergo sum. Descartes I think, therefore I am…!
- 2. CPC 4.2.3 Fay is a 42y woman who is a local real estate agent. You are a local GP. At a charity function last night She approached you and asked for your advice about her abdominal problems. You advised her to come in to see you at your surgery. Abdominal problems…(differential diagnosis) Professional ethics… Counseling, SNAP & five A’s…
- 3. CPC 4.2.3 Abdominal symptoms: Upper abdominal discomfort with bloating & wind. Burps after meal , stomach feels full & windy. ? worsening. Duration Symptoms for many months . Relation to food/fat Yes , makes it worse. Pain 3-4/10, ill defined , cramping . Nausea vomiting Nausea occasional , no vomiting. Wt loss No Anorexia No Dysphagia No Bowel habit constipation , No pus, blood PR. Diet usually eats once a day, often fast foods. Little fruits & veggies. Lots of coffee ….? Risk
- 4. CPC 4.2.3 Alchohol 2-3 glasses of wines/night. 12-15 on weekends, more when she finalizes a deal. (Hepatitis, pancreatitis, gall stones) Marriage Married to an accountant, no children but has 3 lap dogs . (hydatid dis, echinococcosis.) Medication She is on COCP , (Budd-Chiari sy) Allergies None PMS Nil significant. PSH Tonsillectomy & adenoidectomy at 5 years, appendicectomy at 14y. (Viral Hepatitis)
- 5. Investigations Upper abdominal USS – numerous gallstones in thick-walled gallbladder LFT – elevated GGT* , Alk Phos normal*…? Fasting glucose- 7.0 mmol/l Lipid profile - Total Chol 7.2 , Trig. 2.8, HDL 2.0, LDL-5.1. Rectal examination – Hard stool in the rectum, no hemorrhoids or fissures.
- 6. CPC 4.2.3 –Discuss D.D. Gastritis Peptic ulcer Liver disease… many..! Fatty liver * Gallstones chronic constipation * irritable bowel syndrome Diverticulosis / Diverticulitis Pancreatitis - chronic Any thing else ??
- 7. “ Thought is Free & Powerful” --William Shakespeare “Human mind is the most powerful weapon in the world…! - Osama bin laden…!
- 8. Pathology of Biliary Disorders Dr. Shashidhar Venkatesh Murthy Associate Prof. & Head of Pathology School of Medicine.
- 9. Anatomy:
- 10. Physiology: Bile – Micelles of cholesterol, phospholipids, bile salts & bile pigmint (bilirubin, biliverdin) Fat in food Cholecystokinin Bile secretion. Cholesterol (Fat crystal) - Bile salts (soap) Excess cholesterol, low bile salt Stone formation. Stasis, Inflammation, infection Ca
- 11. Biliary Disorders: 95% - Chole-cystitis/lithiasis. Extrahepatic Obstruction: Dislodged gallstones Ca. CBD, Ca. Head of pancreas. inflammatory stricture of CBD accidental surgical ligation of CBD. Intrahepatic Obstruction: Biliary atresia – congenital. Primary Biliary cirrhosis Sclerosing cholangitis. Cystic fibrosis (mucosiscidosis) – thick bile. Common Disorders: Cholecystitis Cholelithiasis & Choledocholithiasis. Adeno Carcinoma
- 12. Cholecystitis: Inflammation of gallbladder. Risk factors: Most common Gallstones ( FFFF …!) Pathogenesis: Obstruction, inflammation, infection. Types: Acute, Chronic, Cholesterosis. Complications: Empyema, rupture.
- 13. Acute Cholecystitis: 90% Cholelithiasis. 10% non-calculous Females common. Outflow obstruction by a small gallstone. Infection – E.coli. Empyema. Risk of perforation, peritonitis, fistula Gall stone ileus when stone enters GIT. Serum amylase normal (high with pancreatitis). Mild jaundice in 20% - obstructive. Acute inflammation, hemorrhage, ede – neutrophils. Gangrenous cholecystitis : when obstruction is severe compromising blood supply. Green-black necrotic.
- 14. Chronic Cholecystitis: Females. Recurrent acute / chronic. Thick fibrotic wall. Thick bile – biliary gravel. Diffuse infiltration by chronic inflammatory cells. Aschoff-Rokitansky sinuses - glands being pushed through muscular layer. (black arrow). Due to increased luminal pressure (obstruction).
- 15. Cholesterosis : Strawberry GB. Yellow-speckled strawberry apprearance. Cholesterol filled macrophages in the superficial mucosa. Clinically not significant. May present as chronic cholecystitis.
- 16. Cholesterolosis of gallbladder mucosa Cholesterol filled Foamy macrophages in mucosal folds
- 17. Complications of Cholecystitis: Obstruction Cholecystitis Cholangitis Biliary colic Jaundice Empyema Liver abscess Mucocele Pancreatitis. Peritonitis Carcinoma Fistula formation Gall stone ileus. Gallstone ileus
- 18. Cholelithiasis: Cholelithiasis/gall stones – 95% of GB dis . Incidence: West 20-40%, Asian 2-4%. 70-80% asymptomatic Mixed 80% - (cholesterol, ca+, bile, blood) Pure 20% - Pigment *, Cholesterol. Severe colicky Upper abdomen Rt shoulder. Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia Obstruction. Fat intolerance clay stools - typical in chronic.
- 19. Risk Factors: Cholelithiasis Cholesterol Stones: Race/Demog– Western Age Female sex Oral contraceptives Pregnancy Obesity Rapid weight reduction Gallbladder stasis Disorders of bile acid metabolism Hyperlipidemia syndromes Pigment Stones: Race/Demog – Asians Hemolysis syndromes Biliary infections Inflammatory bowel disorders. Ileal resection or bypass. Cystic fibrosis Chronic Pancreatitis. 80% Idiopathic. 75% in American Pima race.
- 20. Cholelithiasis: Crystallization of bile within biliary system. Risk factors: female gender, obesity, diabetes mellitus ( FFFF …!) Pathogenesis: Cholesterol is made soluble by bile salts and lecithins. More cholesterol or less bile salts chol. Monohydrate crystals stone. Four Etiologic factors. Supersaturation – excess Cholesterol – crystals. Calcium Microprecipitation - Nucleation. Stasis - Mucous trap crystals – aggregation Stone growth.
- 21. Cholelithiasis: Morphology & Types: Mixed (Chol+Ca+Bile salt)* Multiple, faceted, yellow-grey. Rarely pure cholesterol-Yellow spiky. Bile pigment stones (black/brown). % Calcium = radio opaque Complications: Obstruction cholecystitis, Empyema, liver abscess, perforation, fistulae, mucocele, Cholangitis, P ancreatitis, Obstructive jaundice, Gall stone ileus (intestinal obst), Carcinoma (rare).
- 23. Gallstones + Chronic Cholecystitis Note: Multiple, Faceted, golden yellow – grey stones. thickened inflammed gall bladder. Ulceration at neck suggest occlusion by small stone.
- 24. Cholecystitis & Gallstones Note thickened gallbladder wall. Inflammation. Mixed cholesterol & bile pigment stones.
- 25. Gallstones (mixed) Note: Yellowish shiny faceted stones, and thick inflammed gallbladder.
- 26. Pure Cholesterol Gallstones, bleeding. Round, yellow, spiky, bleeding.
- 27. Cholesterol Gallstones, bleeding. Round, yellow, spiky, bleeding. Note thickened inflammed gall bladder.
- 29. Pigment stones in hemolytic anemia Note: Dark Black friable soft stones – Bilirubin
- 30. Gall stones in CBD Stones in CBD Stonees in GB 20% of mixed chol. stones and >50% of pigment stones are radio-opaque
- 32. “ What we think, we become” --Buddha
- 33. Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Autoimmune, Chronic, progressive Destruction of intrahepatic bile ducts, portal inflammation & scarring – cholestasis. Leading to cirrhosis and liver failure. Females common (6:1) Insidious onset of Pruritis & cholestatic jaundice. Markedly high ALP, +ve antimitochondrial Ab. Histopathology: Portal inflammation, bile stasis, bile plugs & lakes, Later stages cirrhosis – Firm fibrotic, nodular, greenish, Shrunken.
- 34. Excess Bile - plugs Bile Obstruction leading to Cholestasis & Cholangitis Bile duct inflammation Bile staining
- 35. Cholestasis: Bile “plugs”, Bile “lakes” Bile Plugs Bile Lakes
- 36. Excess Bile Bile plug
- 41. Macronodular Cirrhosis - PBC
- 42. Macronodular Cirrhosis - PBC
- 43. Biliary Atresia in a 3m child. Dark bile stained liver tissue, cirrhosis & death before 2 years of age.
- 44. Neoplastic Disorders: (rare) Benign tumours: Bile duct adenoma, cystadenoma Malignant tumours: Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile duct carcinoma) Presents with Jaundice. Early spread with very poor prog nosis. Adenocarcinoma Ducts lined by cuboidal to columnar mucin secreting cells separated by desmoplastic (fibrotic) stroma.
- 45. Cholangiocarcinoma: Gross Microscopy: Glands in desmoplastic (fibrous) stroma
- 46. “ Outer world is the reflection of our inner world (thoughts) ” --Baba
- 47. Carcinoma Gallbladder: Females common 5th-7th decade Common - Lithiasis. abdominal pain, anorexia, High ALP. Commonly Adenocarcinoma Late diagnosis – Poor prognosis.
- 48. Carcinoma Gallbladder: Note irregular glandular structures and clusters of similar cells.
- 49. Carcinoma Bile duct: Usually an adenocarcinoma Increased incidence in ulcerative colitis Presents with obstructive jaundice – early diagnosis. Cholangiocarcinoma: Adeno Ca with biliary differentitation. Intrahepatic or extrahepatic. Thoratrast exposure. Increasing incidence. ? toxin
- 51. Adenocarcinoma: Normal Adeno Ca
- 53. Great wars & Great creations start first in human mind…! -- Thoughts are seeds with potential.
- 54. 38y F, Obese, abdominal colicky pain, Gallbladder: ? Type of stones Pure cholesterol Mixed cholesterol. Pigment Calcium Triple phosphate.
- 55. 38y F, Obese, abdominal colicky pain, Gallbladder: ? Type of stones Pure cholesterol Mixed cholesterol. Pigment Calcium Triple phosphate.
- 56. A 45y mildly obese woman, 1-week history of upper abdominal pain, fever, shaking chills, and occasional vomiting. Physical examination shows severe right upper quadrant tenderness. Laboratory studies include serum bilirubin of 1.0 mg/dL, AST of 25 U/L, ALT of 35 U/L, alkaline phosphatase of 220 U/L (high), WBC of 14,000/µL, and amylase of 95 U/L (normal). An ultrasound examination of the abdomen reveals a normal-appearing liver and bile duct and thickening of the wall of the gallbladder. Most likely diagnosis? Acute Cholecystitis Acute Pancreatitis Carcinoma pancreas Carcinoma Gall bladder Primary biliary cirrhosis.
- 57. 40y Black woman, indigestion, abdominal pain, Gallbladder: Most likely associated disease? Chronic Pancreatitis Diabetes mellitus Familial hypercholesterolemia Hyperparathyroidism Sickle cell disease
- 58. 69y M, Massive GI bleeding, jaundice. Section of liver ? Pathogenesis Cholangiocarcinoma Hepatocellular carcinoma Metastatic carcinoma Liver abscesses Tuberculosis.
- 59. 38y F, Obese, abdominal colicky pain, Gallbladder: ? Diagnosis Cholecystitis Cholesterosis Adenocarcinoma Cholelithiasis Primary Biliary Cirrhosis.
- 60. 38y F, Obese, abdominal colicky pain, Gallbladder: Most likely metabolic abnormality? Decreased bilirubin conjugation. Decreased serum albumin. Increased bilirubin uptake Increased hepatic calcium secretion. Increased hepatic cholesterol secretion.
- 61. Complications of Cholelithiasis include all the following EXCEPT : Secondary Biliary Cirrhosis Recurrent Cholangitis Liver Abscess Chronic Pancreatitis Primary Biliary cirrhosis.
- 62. 62y F, Abd. Pain & jaundice. Gall bladder biopsy ? Diag Cholecystitis Cholesterosis Adenocarcinoma Aschoff-Rokitansky sinuses Primary Biliary Cirrhosis.
- 63. 38y F, jaundice. Gall bladder ? Pathogenesis Excess Bilirubin Low cholesterol Low Bile Salts Infection. Cholestasis.
- 64. 34y M, alcholic, mild icterus and malaise 6 months. Liver biopsy. ? diagnosis Acute alcoholic Hepatitis Chronic Persistent Hepatitis. Hepatitis C infection Fatty Liver Alcoholic Cirrhosis
- 65. 42y M, alcoholic, recurrent fatigue. Liver biopsy. ? Diagnosis Acute Hepatitis Chronic Active hepatitis. Chronic Persistant hepatitis. Fulminant Hepatitis. Cirrhosis.
- 66. 26y fem, medical student, day before pathology exam presents with mild scleral icterus. Physical Examination normal, Liver function tests: Protein total-7.9, Albumin 4.8 g/dl, AST-36 U.L, ALT 16 U/L, ALP-36 U/L, Total Bilirubin 4.9, direct 0.7 mg/dl. Icterus resolves week later after exams. Most likely diagnosis? Alcoholic hepatitis. Primary biliary cirrhosis. Gilbert Syndrome. Acute HAV infection. Acetaminophen poisoning.
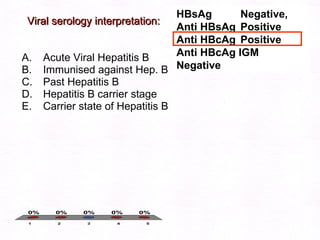
- 67. Viral serology interpretation: Acute Viral Hepatitis Immunised against Hep. B Chronic Hepatitis B Hepatitis B carrier stage Fulminant hepatitis B HBsAg Positive, Anti HBcAg Positive Anti HBcAg IGM Negative Anti HBsAg Negative
- 68. CPC-2.3– C ore L earning I ssues : Major CLI: Pathology of Cholecystitis – Acute, Recurrent & Chronic. Gross, Microscopy & complications. Pathology of Cholelithiasis – Causes, Types, Morphology Gross & Micro, Complications (choledocholithiasis) Minor CLI: Carcinoma of gall bladder & biliary tract. Primary Biliary cirrhosis. Parasites & other forms of biliary atresia,.
- 69. “ The ancestor of every action is a thought.” --Ralph Waldo Emerson
- 70. 34y M, alcoholic, homosexual- icterus and fever 6 months. Liver biopsy. ? diagnosis Acute Hepatitis Chronic active Hepatitis. Cirrhosis Carcinoma Fulminant Hepatitis Hepatitis Cirrhosis
- 71. 34y M, icterus and fever. Liver biopsy. ? diagnosis Acute Hepatitis Chronic Persistent Hepatitis. Chronic active Hepatitis Fulminant Hepatitis Cirrhosis
- 72. 56y chronic alcoholic, 2 days fever, abdomen distended, tender, tap yielded cloudy yellow fluid with 98% neutrophils, Blood culture E.coli. Patient dies 3 days later. Image shows his liver. Most Likely diagnosis? A1 antitrypsin deficiency HEV infection Hereditary hemochromatosis Primary sclerosing cholangitis Alcoholic cirrhosis
- 73. 58y M, alcoholic, distended abdomen & icterus. Liver biopsy. ? diagnosis Chronic active hepatitis. Chronic Persistant hepatitis. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Cirrhosis Chronic alcoholic hepatitis.
- 74. Viral serology interpretation: Acute Viral Hepatitis Immunised against Hep. B Past Hepatitis B Hepatitis B carrier stage Fulminant hepatitis B HBsAg Negative, Anti HBcAg Negative Anti HBcAg IGM Negative Anti HBsAg Positive
- 75. 69y Female, Chronic bronchitis. Died following chronic Cardiac failure. Liver specimen. Likely diagnosis? Alcoholic Hepatitis Dubin-Johnson Syndrome Alcoholic cirrhosis Nutmeg liver Metastatic deposits
- 76. Viral serology interpretation: Acute Viral Hepatitis B Immunised against Hep. B Past Hepatitis B Hepatitis B carrier stage Carrier state of Hepatitis B HBsAg Negative, Anti HBsAg Positive Anti HBcAg Positive Anti HBcAg IGM Negative
- 77. 59y Male, Alcoholic, presents with fatigue, anorexia. Normal liver function tests. Liver specimen. Likely diagnosis? Dubin-Johnson Syndrome Alcoholic cirrhosis Alcoholic Hepatitis Fatty Liver Nutmeg liver
- 78. Histopathology Image is from lung biopsy of a 61 year male chronic smoker. What is the most likely type of carcinoma? Small cell carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Metastatic deposits Squamous carcinoma Lung abscesses
- 79. The gross image of lung specimen from a 59year old male heavy smoker presented with high fever, shortness of breath. Likely type of pneumonia? Lobar pneumonia Interstitial pneumonia Broncho pneumonia Fungal pneumonia Carcinomatous pneumonia
- 80. 42y male smoker presented with recurrent cough & dyspnoea. Image shows cut section of his lung. What is the most likely diagnosis? Emphysematous bullae Panlobular emphysema Centrilobular emphysema Chronic Bronchitis + Emphysema. Smokers lung with Silicosis
- 81. 46 year male on treatment for lymphoma presents with pallor, shortness of breath and mild jaundice. Image shows his blood film appearance. What is the most likely type of anemia? Anemia of chronic disorder Megaloblastic anemia Hemolytic anemia Aplastic anemia Iron deficiency Anemia
- 82. 12 year old girl presents with two week history of fever and joint pain. The image shows her heart specimen. What feature of the disease is shown by the arrow? MI with pericarditis. Bacterial endocarditis Pancarditis Endocarditis Pericarditis
- 83. 78year female presents with prolonged weakness, fatigue and anemia. She has palpable spleen & few enlarged cervical Lymphnodes. Image shows her blood film. What is the most likely diagnosis? Acute myeloid leukaemia Acute lymphatic leukaemia Chronic myeloid leukaemia Chronic lymphatic leukaemia Non-hodgkins lymphoma
- 84. Self Assessment is the key…! Whether new information is "stored" or "dumped" depends, then, on our Interest , Reciting, Writing & Reviewing the information. Source: http://www.web-us.com/memory/human_memory.htm Retention of Learning Time Delay No review Review 7 Days 33% 83% 63 Days 14% 70%
- 85. Reminder…. Online quiz, Winners club, Authors club. Not compulsory now… * Important.. Formative – Does not affect your results. Personal road sign.. Where am I going ? Time limited… Am I in time ? Procrastination doesn’t help. Please evaluate me..!
- 86. Living becomes a glorious experience only when there is tolerance and love. Willingness to compromise with other people’s ways of living and cooperation in common tasks, these make happy and successful societies. Divine Discourse, 17th February 1980 - Baba. Love is Selfless Service.
- 87. 5 A’s & SNAP Ask: 1. patients with diabetes, hypertension, hyperlidaemia, obesity or existing vascular disease Assess: 2.Number of cigarettes or equivalent/day, Dependance 3.readiness to change/motivation Advise: 4.provide written information, 5.motivational interviewing Assist: 6.NRT ? Bupropion(Zyban) 7.Support Arrange: 8.referral to QUIT 9.follow up with the GP SNAP Counseling: Smoking, Nutrition, Alcohol & Physical Activity.
- 88. Silence… To the question "Who am I?" the only relevant answer is silence. You need to discard all answers in words, including "I am Nothing" or "I am the Cosmic Self" or "I am the Self" - and just stick to the question "Who am I?". All other answers are just thoughts. Thoughts can never be complete. Only Silence is complete. Thoughts are not the goal in themselves. Their goal is Silence. When you ask the question "Who am I?" you get no answer, there is silence. That is the real answer. For your soul is solidified silence. This solidified silence is wisdom, is knowledge. The easy way to silence the thoughts is to arouse the feelings. For, through feelings only peace, joy and love dawn. And they are all your very nature. - Sri Sri Ravishankar