ILOA Galaxy Forum SEA Indonesia -- Djamaluddin
- 1. Indonesia Space Activities Prof. Dr. Thomas Djamaluddin
- 2. Introduction Space technology and information technology are the most important technololgies in modern life, not only in global and national scale, but also in personal activities. Space technology is used for telecommunication, survaillance, and navigation. Indonesia as maritime continent, with 13,466 named islands (~17,000 islands, including no-name islands) needs space technology. Since space technology is close related to aeronautics technology, Indonesia has “National Institute of Aeronautics and Space”, in which space and aeronatics (aerospace) science and technology developments, as well as policy studies, are conducted.
- 3. A Brief History of Aerospace Activities in Indonesia • The Aviation Board was established on 1955 based on Government Regulation No. 5/1955. This board later changed to become the National Aeronautics and Space Council of the Republic of Indonesia (DEPANRI) by Presidential Decree No. 99/1993. DEPANRI is chaired by the President of Republic of Indonesia with members consisting of State Minitry of Research and Technology (also as vice chairman and acting chairman), Minister of Foreign Affairs, Minister of Trade and Industry, Minister of Defence, and State Minister of Development Planning. • Space technology activities in Indonesia started in the 1960s. In 1962 PRIMA (Proyek Roket Ilmiah dan Militer Awal) – the Primilinary Project on Scientific and Military Rocket was stared. The first rocket produced by this project (i.e. Kartika) was launched on 14 August 1964 from Launching Station at Pameungpeuk, West Java. • National Institute of Aeronautics and Space (LAPAN) was established based on Presidential Decree No. 236/1963. • In 1976 Indonesia became the third country using telecommunication satellite, PALAPA.
- 4. • Space Law No. 21/2013 was enacted on 6 August 2013. A Brief History of Aerospace Policies in Indonesia
- 5. Indonesian Space Policies in Space Law No. 21/ 2013 • The space law consists of general policies related to space activities, i.e. space science, remote sensing, aerospace technology mastery, space launch and space commercial activities. • LAPAN as government institution has authority to conduct of all space activities in Indonesia, in addition to current duty as aerospace research and development institution. • LAPAN is directly responsible to the President of Indonesia, while its activities are technically coordinated by a ministry for research and technology. • The space law is intended to promote self-sufficiency and national competitiveness, to encourage space exploration and utilization for national prosperity and productivity, to ensure space activity sustainability, to provide law basis for space activities, to ensure security and safety in space activities, to ensure the implementation of international agreement, and to support national defence and integrity.
- 7. LAPAN MAIN COMPETENCES SPACE SCIENCE & ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE AERONAUTICS & SPACE TECHNOLOGY REMOTE SENSING AERONAUTICS & SPACE POLICY Development of National capability in utilizing of remote sensing technology for earth observation with focus on development of National Remote Sensing Data Bank to support data needs from Ministry, Local Goverment, Military and Police. Development of Unmanned Air Vehicle (UAV/drone) & Air Transport design, Satellite Development & its components and sounding rocket development and its spin off for peaceful purposes Development of Decision Support System for space Weather and dynamic of equator atmosphere Drafting of Government Regulation and President Regulation according to National Decree on Space and guidlines in international forum.
- 8. LOCATION OF LAPAN FACILITIES Jakarta Rumpin Bandung Tanjungsari Pameungpeuk Watukosek Rancabungur Kototabang Pontianak Parepare Biak
- 9. ROAD MAP OF SATELLITE TECHNOLOGY PROGRAM
- 10. LAPAN-A2 / ORARI LAPAN-A3 / IPB LAPAN-A1 / TUBSAT Mission Video Surveilence Earth Surveilance, maritime monitoring, Amateur Communication Experimental remote sensing, maritime monitoring, Science exp. Payload Analog Video Camera, Low resolution VideoCam Digital Space Camera, Analog Video Camera, AIS, APRS 4 band pushbroom imager, Hi res DigitalCam, AIS, APRS Spectral resolution PAL Camera (752 x 582 pixel) Digital Camera (2048 x 2044 pixel) Analog Camera (752 x 582 pixel) 450 - 520 nm; 520 - 600 nm; 630 690 nm; 760 - 900 nm Spatial resolution 5 m ( 3,5 km swath), 200m (80 km swath) 4 m (7 km swath), 5 m (3,5 km swath) 18 m (100 km swath) / 4 m (7 km) Orbit 635 km, 97,6 deg 650 km, 8 deg, Near-Equatorial 650 km, 97,6 deg Data TX, and TT&C S-Band : 2220 MHz, UHF : 437,325 MHz S-Band : 2220 MHz, UHF : 437,425 MHz X-Band : 8116 - 8284 MHz, UHF : 437,325 MHz Downlink rate 5 Mbps 5 Mbps 105 Mbps Total weight 57 kg 74 kg 115 kg Dimension 450 x 450 x 270 mm 500 x 470 x 360 mm 500 x 500 x 700 mm Launch 2007 2nd quarter 2015 End of 2015
- 11. Mision Experimental remote sensing (Validation of Optical data pre- processing algorithm) Experimental remote sensing. (Development of SAR Micro-Sat for Maritime and agriculture monitoring) Payload Visible and Near Infrared imager experimental, Shyntetic Aperture Radar Experimental (deployable dimension 450 x 70 cm), AIS Spectral/discrimina- tion mode NIR Bolometer camera, Selectable with 10 nm interval. L-band; HH, HV, VH, VV polarimetry Spatial resoluition 5 m ( 3,5 km swath), 1 km 30 m (100 km) Orbit 650 km, 97,6 deg 650 km, 97,6 deg Payload TX, TTC X-band, S-band X-Band, S-band Downlink rate 200 Mbps 200 Mbps Dimension Max 60x60x80 cm³ Max 60x60x80 cm³ Weight 150 kg 200 kg LAPAN-A4 LAPAN-A5
- 12. LAPAN’s Equatorial Satellite Mission • Meanwhile, the temporal resolution of patrol-boat-based radar and AIS receiver is very low considering the vast water region. Therefore, satellite-based AIS is truly a solution for Indonesian problem combining with UAV and SAR satellite technology. • Since Indonesian territory is spread along the equator, LAPAN decide the operation of maritime surveillance satellite at the beginning at low inclination orbit, so that the satellite may pass Indonesia as much as SSO orbit pass the North/South pole (14 times in 24 hours at 650 km orbit).
- 13. Space-borne AIS for Maritime Surveillance • AIS (Automatic Identification System) is a system that can monitor ships, based on GPS and VHF digital communication. It is regulated by IMO to be installed in ships weighing 300 tons and above. • By placing AIS receiver on the satellite, its coverage will be larger compared to the one usually placed on the seashore by maritime authority.
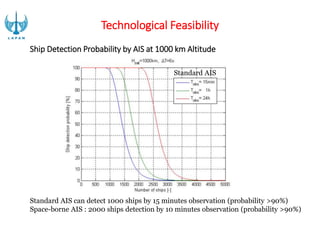
- 14. Technological Feasibility The development of satellite-based AIS has been done since 2007 by the US military experimental satellite TACSAT-2. At the moment, commercial entities like Orbcomm, Com Dev, SpaceQuest dan Kongsberg Seatex has developed satellite AIS receiver. Plot of AIS Messages Collected by Nano-satellite Tracking of Ships (NTS) - Canada
- 15. Standard AIS can detect 1000 ships by 15 minutes observation (probability >90%) Space-borne AIS : 2000 ships detection by 10 minutes observation (probability >90%) Standard AIS Technological Feasibility Ship Detection Probability by AIS at 1000 km Altitude
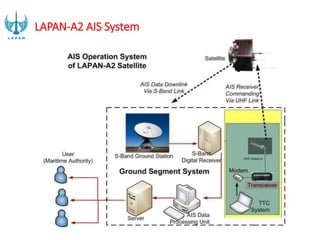
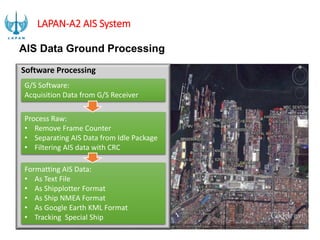
- 17. Software Processing G/S Software: Acquisition Data from G/S Receiver Process Raw: • Remove Frame Counter • Separating AIS Data from Idle Package • Filtering AIS data with CRC Formatting AIS Data: • As Text File • As Shipplotter Format • As Ship NMEA Format • As Google Earth KML Format • Tracking Special Ship AIS Data Ground Processing LAPAN-A2 AIS System
- 18. LAPAN-A2 satellite will be launched as auxiliary payload on PSLV mission at 2nd semester of 2015. LAPAN-A2 AIS System
- 19. LAPAN-A3/IPB SATELLITE (An Experimental Remote Sensing Satellite) • Cooperate with Bogor Agricultural University (IPB) for payload specification • Orbit: ~650 km, 97,6 deg • Payload; Experimental remote sensing, maritime monitoring, Science exp. 4 band pushbroom imager (450 - 520 nm; 520 - 600 nm; 630 690 nm; 760 - 900 nm), Hi res DigitalCam, AIS, APRS ~18 m (~100 km swath) Multispectral/ ~4 m (~7 km) Matrix RGB 115 kg End of 2015 • Weight: ~115 Kg
- 20. Satellite Development Capabilities • In-house design capabilities • In-house Satellite Assembly, Integration & Test (AIT) with thermal, vacuum chamber, Uniform Light Source, 10,000 & 100,000 clean room class. • Customize Satellite operation software • Satellite Platform and structure manufacturing • TTC and image reception satellite operation • In-house satellite components development: (Reaction wheels, Magnetic coils, Star Tracker, On Board Data Handling) • Image systematic pre-processing, (Geometric, Radiometric correction, atmosferic refraction & dispersion, blurring distortion, stochastic distorsion)
- 21. AERONAUTICS TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM LAPAN SURVEILLANCE UAV (LSU)
- 22. LSU Program Status AERONAUTICS TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM (cont’d)
- 23. VARIAN PROTOTYPE LSU LSU-01 Wing tail : 1900 mm Lenght : 1200 mm Take off : launch Maximum Payload : 0,5 kg Speed : 45 km/jam Max speed : 60 km/jam Airspeed Stall : 30 km/jam Machine : Brushless Fuel : Battery Max flight time : 50 menit Control System : Take off/landing by remote control & fly by autonomous LSU-02 Wing tail : 2400 mm Lenght : 1700 mm Maximum Payload : 3 kg Speed : 100 km/jam Max speed : 150 km/jam Airspeed Stall : 40 km/jam Machine : 2 Tax 32cc Fuel : Pertamax plus & oli full sintetic Tank : 3,5 liter Max flight time : 3,8 jam Control System : Take off/landing by remote control and fly by autonomous LSU-03 Wing tail : 3500 mm Lenght : 2500 mm Tail Height : 700 mm Center Wing : 900 mm Speed : 100 km/jam Max speed : 150 km/jam Airspeed Stall : 60 km/jam Maximum Payload : 10 kg Machine : 2 Tax 100cc Fuel : Pertamax Plus & Oli Full Sintetic Tank : 7 liter Max flight time : 5 jam Control System : Take off/landing by remote control and fly by autonomous AERONAUTICS TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM (cont’d)
- 24. VARIAN PROTOTYPE LSU LSU-04 Wing tail : 4000 mm Lenght : 3200 mm MTOW : 65 kg Speed : 100 km/jam Max speed : 160 km/jam Airspeed Stall : 60 km/jam Maximum Payload : 18 kg Machine : 11 HP Tank : Pertamax plus &oli full sintetic Tank : 8 liter Max flight time : 6 jam Control System: Take off/landing by remote control & flight by autonomous LSU-05 Wing tail : 5500 mm Lenght : 4100 mm Height : 1130 mm MTOW : 77 kg Empty Weight : 31 kg Payload Mass : 30 kg Fuel : 16 kg Take Off Ground Round : 60 meter Climb Rate : 600 ft/min Range : 840 km Endurance : 8 h Lending Ground Run : 83 meter Ceiling : 12000 ft Cruise Altitude : 3000 ft Cruise speed : 100km/h FADEX Wing tail : 3500 mm Lenght : 2800 mm Take Off mass : 10 kg Cruise Speed : 160 km/jam Cruise Altitude : 1000 m Max flight time : 0,5 jam Proppeller : Turboshaft Machine : 20 HP - 30 cc Fuel : gasoline Payload : 15 kg Tank : 2 liter Airframe : Composite Control System: Take off/landing by remote control & flight by autonomous AERONAUTICS TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM (cont’d)
- 25. Program LSU progame achievement status LSU 02 in military 2012-2013 ( Ship On Board Take Off and Landing ) Battlefield maping, Dittop AD 1200 Ha (± 7 hours ) MURI record achievment (200 KM Autonumous) Flood monitoring REMOTE SENSING DATA AERONAUTICS TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM (cont’d)
- 26. LAPAN SURVEILLANCE AIRCRAFT (LSA) AERONAUTICS TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM (cont’d)
- 27. Status program LSA - AADP - UAV Research and Development of UAV :1 ton MTOW - Light and advanced Aircraft Research and Development ( Autonomous Control & Composite ) - Simulator System - Capacity Building (Master and Phd) AERONAUTICS TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM (cont’d)
- 28. LSA’s Program status Parameter Pengambilan Sample Lapangan Kondisi periode tanaman padi Biomas tanaman padi Tinggi tanaman padi Kerapatan tanaman Variabel fisik lainnya 0 SPESIFIKASI PESAWAT CESSNA 206 - Mesin : C o ntinental IO-520-A 285 hp (213 kW) - Tempat D u duk : one (crew) & five passengers - Length : 8,61 m - Wingspan : 10,97 m - Height : 2,83 m - Wing Area : 16,3 m2 - Airfoil : N A CA 2412 - Berat Ko song : 987 kg - Max. Takeoff We i ght : 1.632 kg Performance Kecepatan Maksimum : 151 knots (280 km/h) Kecepatan Cr uise : 142 knots (263 km/h) Kecepatan Stall : 54 knots (100 km/h) Jarak Tempuh : 840 mi (730 nmi, 1.352 km) Serving ceiling : 15.700 ft (4.785 m) A Deskripsi LSA-S15 Pesawat terbang ringan Untuk melakukan misi surveillance seperti pemetaan, monitor- ing, SAR dan lain se bagainya. Pesawat ini mempunyai basic design berupa pesawat glider bermo- tor, Airframe pesawat terbuat dari komposit dengan rangka utama terbuat dari batang logam s i li nder. Memiliki desain modular airframe yang dapat memudahkan pesawat diangkut dengan bagian ya ng terpisah-pisah. SPESIFIKASI PESAWAT STEMME S – 15 -Tipe : Sayap Tetap, Retractable Landing Gear - Airframe : C a rbon Fiber & Glass Fiber C o mposites - Mesin : Tunggal – ROTAX 914 F2 (4 cylinder 4 stroke) - Tempat D u duk : D u al (side by side) - Bahan Ba kar : AVGAS UL 91 atau 110LL - Jarak Tempuh : sampai dengan 604 nm/1119 km (75% power, 97 knot - Durasi Terbang : sampai dengan 6 jam 13 menit (FF 20.4 ltr/jam) - Service C e iling : Max 16.000 feet - Panjang Landasan yang dibutuhkan Take Off : Ground R o ll 425 m, 50ft obstacle 833m Landing R o ll : (tidak disebut dlm POH, lebih pendek drpd T/O) Gradient T/O : 591 ft/mnt – 3m/sec - Maks B e rat :1100 kgs - Payload : sampai dengan 148 kgs (1 pilot 70kg) - Minimal Crew : 1 (satu) orang POD Kamera Kamera & Rangkaian Kamera Pemanfaatan : MAINTENANCE Parameter Pengambilan Sample Lapangan Kondisi periode tanaman padi Biomas tanaman padi Tinggi tanaman padi Kerapatan tanaman Variabel fisik lainnya 0 - Length : 8,61 m - Wingspan : 10,97 m - Height : 2,83 m - Wing Area : 16,3 m2 - Airfoil : N A CA 2412 - Berat Ko song : 987 kg - Max. Takeoff We i ght : 1.632 kg Performance Kecepatan Maksimum : 151 knots (280 km/h) Kecepatan Cr uise : 142 knots (263 km/h) Kecepatan Stall : 54 knots (100 km/h) Jarak Tempuh : 840 mi (730 nmi, 1.352 km) Serving ceiling : 15.700 ft (4.785 m) A Deskripsi LSA-S15 Pesawat terbang ringan Untuk melakukan misi surveillance seperti pemetaan, monitor- ing, SAR dan lain se bagainya. Pesawat ini mempunyai basic design berupa pesawat glider bermo- tor, Airframe pesawat terbuat dari komposit dengan rangka utama terbuat dari batang logam s i li nder. Memiliki desain modular airframe yang dapat memudahkan pesawat diangkut dengan bagian ya ng terpisah-pisah. - Mesin : Tunggal – ROTAX 914 F2 (4 cylinder 4 stroke) - Tempat D u duk : D u al (side by side) - Bahan Ba kar : AVGAS UL 91 atau 110LL - Jarak Tempuh : sampai dengan 604 nm/1119 km (75% power, 97 knot - Durasi Terbang : sampai dengan 6 jam 13 menit (FF 20.4 ltr/jam) - Service C e iling : Max 16.000 feet - Panjang Landasan yang dibutuhkan Take Off : Ground R o ll 425 m, 50ft obstacle 833m Landing R o ll : (tidak disebut dlm POH, lebih pendek drpd T/O) Gradient T/O : 591 ft/mnt – 3m/sec - Maks B e rat :1100 kgs - Payload : sampai dengan 148 kgs (1 pilot 70kg) - Minimal Crew : 1 (satu) orang POD Kamera Kamera & Rangkaian Kamera Pemanfaatan : MODIFICATION POD APPLICATION Stu dy Ar ea Subang – Indramayu, Jawa Barat • Lahan sawah : irigasi dan tadah hujan 11 Subang Jalur terbang LSA Titik pengamatan Indramayu Descending Ascending Akuisisi Radarsat APPLICATION TEST BBSDLP-PUSTEKDATA-PUSTEKBANG Cessna 2 0 6 PK-LPNLSA (LAPAN SU RVEILLANCE AIRCRAFT) SPESIFIKASI PESAWAT CESSNA 206 - Mesin : C o ntinental IO-520-A 285 hp (213 kW) - Tempat D u duk : one (crew) & five passengers - Length : 8,61 m - Wingspan : 10,97 m - Height : 2,83 m - Wing Area : 16,3 m2 - Airfoil : N A CA 2412 - Berat Ko song : 987 kg - Max. Takeoff We i ght : 1.632 kg Performance Kecepatan Maksimum : 151 knots (280 km/h) Kecepatan Cr uise : 142 knots (263 km/h) Kecepatan Stall : 54 knots (100 km/h) Jarak Tempuh : 840 mi (730 nmi, 1.352 km) Serving ceiling : 15.700 ft (4.785 m) PUSTEKBANG L A PAN RU MPIN Jl. R a ya L A PAN, S u k amulya Ru mpin—Bogor Deskripsi LSA-S15 Pesawat terbang ringan Untuk melakukan misi surveillance seperti pemetaan, monitor- ing, SAR dan lain se bagainya. Pesawat ini mempunyai basic design berupa pesawat glider bermo- tor, Airframe pesawat terbuat dari komposit dengan rangka utama terbuat dari batang logam s i li nder. SPESIFIKASI PESAWAT STEMME S – 15 -Tipe : Sayap Tetap, Retractable Landing Gear - Airframe : C a rbon Fiber & Glass Fiber C o mposites - Mesin : Tunggal – ROTAX 914 F2 (4 cylinder 4 stroke) - Tempat D u duk : D u al (side by side) - Bahan Ba kar : AVGAS UL 91 atau 110LL - Jarak Tempuh : sampai dengan 604 nm/1119 km (75% power, 97 knot - Durasi Terbang : sampai dengan 6 jam 13 menit (FF 20.4 ltr/jam) - Service C e iling : Max 16.000 feet - Panjang Landasan yang dibutuhkan Take Off : Ground R o ll 425 m, 50ft obstacle 833m Landing R o ll : (tidak disebut dlm POH, lebih pendek drpd T/O) Gradient T/O : 591 ft/mnt – 3m/sec - Maks B e rat :1100 kgs - Payload : sampai dengan 148 kgs (1 pilot 70kg) - Minimal Crew : 1 (satu) orang AERONAUTICS TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM (cont’d)
- 29. NATIONAL TRANSPORTATION AERONAUTICS TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM (cont’d)
- 30. Program Status of N-219 TRANSFER OF TECHNOLOGY 14 SPESIALIS WIND TUNNEL TEST PROCUREMENT (60-70%) & DETAIL DESIGN(90%) FIRST CUTTING DETAIL PART MANUFACTURING ROLL OUT 10 AGUSTUS 2015 FIRST FLIGHT DESEMBER 2015 AERONAUTICS TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM (cont’d)
- 31. LAPAN has been succesfully launched its rockets in Pameungpeuk Test Flight Station, Jawa Barat since 2008, RX- 320 on 2008, 19 May and RX-420 on 2009, 2 July. Moreover LAPAN were already testing on RX-550 mainly static test in 2011 and 2012. Further work LAPAN is going to retest RX 420. Meanwhile for RX-550, the bigest rocket developed by LAPAN wish make its flight test in 2015. • 2008 : RX-320 STATIC & FLIGHT TEST • 2009 : RX-420 STATIC & FLIGHT TEST • 2010 : RX-550 DESIGN • 2011 : RX-550 STATIC TEST • 2012 : RX-550 STATIC TEST • 2013 : RX-550 (SINGLE STAGE) FLIGHT TEST • 2014 : RX-550 (DOUBLE STAGES) FLIGHT TEST Currently status : LAPAN’s satellite launcher called Rocket Sonda designing and integrating autonomously. ROAD MAP OF ROCKET TECHNOLOGY PROGRAM
- 32. Succesfully flown RSX 100 / RX 1210 RX 320 Succesfully flown Static test RX 450 Static test RCX 100H2 (liquid rocket) Space port In Morotai Island PROGRAM STATUS OF ROCKET TECHNOLOGY Succesfully flown RKX EDF / RKX TJ
- 33. Informasi lahan sawah Kabupaten OKU Timur Several activities such as distribution of mid and high resolution data to user have been already done by Lapan to implementing the Inpres No. 6, 2012, about “Provision, Utilyzing, Quality Control, Proccesing and Distributing High Resolution Remote Sensing Data”. In oder to strengthen those activities, Lapan also has received and distributed LDCM/ Landsat-8’s data to user; ie. K/L, local government, TNI/Police, and private Mei 3, 2013,
- 34. Strenghtening Facility Antena X-band 6.1 meter Antena X-band 5,4 meter Antena X-band 6.1 meter (Rumpin) Antena L-band 1,5 meter (Pekayon)
- 36. Receiving, Processing and Management Remote Sensing Data System SPOT-5 /6 data receiving and processing systems Controlling room Antenna control system Receiving and Processing Data System In Balai Penginderaan Jauh Parepare Processing and management data system in Jakarta MODIS and NPP data processing systems Landsat data processing system Database Server
- 37. Data Availability until 2014ata) Spatial Res Data Period Locations Low MTSAT-1R Okt 2008 – Now Indonesia Feng Yun-1D 2003 – 2011 Indonesia NOAA-18 2005 – Now Indonesia NOAA-19 2009 – sekarang Indonesia Terra/Aqua 2006 – sekarang Indonesia NPP Feb 2012 – sekarang Indonesia Mid ALOS AVNIR 2006 – 2011 Jawa, Sumatera, Bali, Nusa Tenggara, Kalimantan SPOT-2 Apr 2006 – Jun 2009 Indonesia SPOT-4 Apr 2006 – Jan 2013 Indonesia Landsat-5 1990 – 2009 Indonesia Landsat-7 2001 – sekarang Indonesia Landsat-8 Apr 2013 – sekarang Indonesia Rapid Eye 2012 -2013 Kalimantan, Jawa, Sumatera
- 38. Data Availability (cont’d) Spatial Res Data Period Locations High SPOT-5 2005, Jan 2013 – now Sumatera, Jawa, Sulawesi, Nusa Tenggara, Kalimantan, Papua SPOT-6 Jan 2013 – now Sumatera, Jawa, Papua, Sulawesi, Kalimantan Pleiades Jun 2013 – now Province and cities in Indonesia ALOS Prism Jun 2006 – Oct 2009 Jawa, Sumatera, Bali, Nusa Tenggara, Kalimantan, Papua Ikonos 2000 – 2004, 2007, 2008, 2011 NAD, Papua, Jakarta, Jateng, Jatim, Papua Quickbird 2006 – 2010 Sumatera, Kalimantan, Papua, Jabar, Jatim World View 2010 – 2012 Maluku, Papua Geo Eye 2009 – 2011 Maluku, Papua, Jawa SAR TerraSAR-X 2010 – 2013 Jakarta, Riau, Jambi, Kalteng, Kaltim, Jateng, L. Timor, Nusa Tenggara ALOS Palsar 2006 – 2010 Kalimantan, Sumatera, Jawa Radarsat 2009 – 2010 Kalimantan
- 39. SPOT-7SPOT-6 Landsat-9Landsat-8 (LDCM) Himawari-8Himawari-7 JPSS-1 MetOp-C NPP 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Terra Aqua NOAA-19 Himawari-6 SPOT-4 Landsat-7 SPOT-5 ALOS-2 SAOCOM-1A FY-3FFY-3EFY-3DFY-3CFY-3B Daily acquired Planed in 2012 Planed below 2013 Acquisition Planing (2012-2020)
- 40. PROGRAM ACHIEVEMENT AND REMOTE SENSING ACTIVITY 1. Indonesia’s National Carbon Accounting System (INCAS) 2. Development of Remote sensing data bank, Bank Data Penginderaan Jauh Nasional (BDPJN) UKP4 and BIG 3. Supporting; a. Maritim - ZPPI, coral reef, mangrove and mariculture b. Mitigation SPBK, hotspot, potentatial flooding, disater emergency respons, active vulcanos information. c. Natural Resources and environtment Paddy growth phase, rural areas, cloud 4. Academic advisor mahasiswa ITS, IPB, UGM, UI, UNNES, UB, etc), Directing Ditjenbun, BBSDLP, BPBD Kalbar, Dishut Riau, Ditjen PHKA, Kanwil Pajak Jateng, etc Servicing KLH, BBSDLP, Dinas Perikanan, BPPT, Ditjen PHKA, UKP4, etc) Informasi Spasial Zona Potensi Penangkapan Ikan (ZPPI) Environment development and disaster mitigation Development model for Disaster mitigation of vulcano maping Forest land and Kalimantan island forest (2000-2009) Forest land and Sumatera island forest (2000-2009)
- 41. 41 5. Contributing in Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD+ Nasional), where LAPAN succesfully developed near real time information system for forest monitoring in order to fulfill UKP4 need; ie.. Daily Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) daily and daily NDVI 16-daily including composite image. Terra/Aqua MODIS in 2009-2012 based on Google Earth. 6. International organizations, such as LandGate Australia, JAXA, ASEAN Secretariat, UN WFP, UN SPIDER, UN ESCAP, CARE International, GIC-AIT, ADRC, and WWF also use Remote sensing information to support disaster mitigation, and Sentinel data completed the aerial data and Carbon Accounting System. PROGRAM ACHIEVEMENT AND REMOTE SENSING ACTIVITY (cont’d)
- 42. SPACE AND ATMOSPHERE SCIENCE Space Weather Monitoring Space Debris Communication Frequency Area Prediction Development of early warning systems and disaster mitigation base on satellite act an early warning system of rain fall (Sahadev version 2.0). Sadewa (Satellite Disaster Early Warning System) or Disaster early warning system base on MTSAT Space debris monitoring cooperate with BAPETEN for measuring the impact of space object radiation Dissemination of ionosphere information utilization for radio communications and Single Frequency of GPS measurement, have been widely used, especially by the military. R&D result of space weather monitoring is sosialized to related institutions such as :BMKG, PPGL, Basranas, Bappeten, Angkasa Pura, TNI AU, LPD Sumedang,BPD Pontianak, BPD Watukosek, BPPR Pameungpek, Dislitbang TNI – AU,Mahasiswa Politeknik Pos Indonesia, Universitas Telkom
- 43. SPACE WEATHER MONITORING NETWORK
- 44. -Radio communication frequency monitoring inter locations (real time) -Ionosonda data real time Radio communication frequency prediction (monthly) Sintilasi appearance prediction(monthly)
- 45. ASTINA : Is a multi-media display of an information system in the field of atmospheric science and technology which are constructed as a component of a decision support system to help users obtain information in accordance with the requirements as the basis for decision-making and policy-related sectors such as information services: weather, climate, agriculture, transportation, energy, environment, water resources, health, disaster management and education. ASTINA ROOM
- 46. • Parameter information of Indonesia’s atmosphere based on Google Earth : MTSAT ir-1, Ch-TRRM, Ch prediction, resolution 5 km and 50 km 1. ARJUNA : AtmospheRic JoUrNey Arcade (Lorong Penjelajahan Atmosfer) Arjuna is a three-dimensional visual media where users can conduct exploration into the Earth's atmosphere to see the satellite-based observations, radar, airborne and in situ, as well as the prediction of atmospheric conditions short, medium and long-based dynamic models and statistical ASTINA ROOM COMPONENTS :
- 47. National Space Development Master Plan • In the Space Laws No. 21/2013, it is mentioned that LAPAN should prepare a Master Plan for the implementation of national space guidelines. The master plan drawn up for a period of 25 (twenty five) years. Therefore, the current master plan is being drawn up, both academic and legal draft of President Regulation. The master plan has been proposed as one of national legislation program (prolegnas) in 2014. • The master plan will be prepared taking into account basic capabilities and the national and international strategic environment. The master plan contains the vision and mission, policies, strategies and short, medium, and long-term strategic plans.
- 48. • The main issues in the master plan includes • the construction of national observatory to support space science; • to strengthen national remote sensing data bank; • to strengthen aeronautics technology for developing UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) and transport aircraft; • to develop national satellite for remote sensing, telecommunication, and navigation, starting from developing micro-satellite; • to develop rockets for satellite launching, starting from developing sounding rockets; • and to build aerospace port in Eastern Indonesia; • as well as to strengthen space policy studies. • To enhance public awareness, space science and technology education center should be built in locations of LAPAN’s station all over Indonesia. • The national aerospace master plan should be supported by preparing human resources and related industries. • National and international cooperation on space science, technology, and policy studies should be encouraged. National Space Development Master Plan
- 49. THANK YOU
Editor's Notes
- #10: Satelit SDA dan satelit komunikasi
- #26: Rencana muri desember 2014 dgn LSU-03
- #42: Informasi inderaja juga digunakan oleh organisasi internasional untuk berbagai keperluan, diantaranya oleh LandGate Australia, JAXA (Japan Aerospace and Exploration Agency), ASEAN Secretariat, UN WFP (United Nation World Food Program), UN SPIDER (United Nation Platform for Space Based Information for Disaster Emergency Response), UN ESCAP (United Nation for Economic and Social Committee for Asia and the Pacific), CARE International, GIC-AIT (Geo-informatics Center Asian Institute and Technology), ADRC (Asian Disaster Reduction Center), dan WWF (World Wide Fund). Mereka menggunakan data inderaja untuk mendukung informasi terkait mitigasi bencana, pembentukan sentinel Asia dalam rangka menghubungkan informasi kebencanaan dari data kedirgantaraan serta untuk keperluan Carbon Accounting System.
- #44: According to space weather monitoring in Indonesia, now we have space weather observation networks. There are many observatories at Kototabang, Pontianak, Manado, Biak, Kupang, Watukosek, Pameungpeuk, Sumedang, and Bandung as the center. At Kototabang observatory we have fluxgate magnetometer, ionosonde, VHF radar, scintillation monitor, and also Automatic Link Establishment (ALE) to monitoring of HF radio propagation condition. At Pontianak observatory, we have similar equipments. They are magnetometer, ionosonde, TEC & scintillation monitor, MF-radar, and Automatic Link Establishment. The similar equipments, there are at Manado, Biak, Kupang, Watukosek, Pameungpeuk, Sumedang, and Bandung. Especialy, at Sumedang and Watukosek observatories, we have telescope and radio spectrograph for monitoring solar activities.