e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4.pptx
- 1. Chapter 1: COLD WAR Topics: • A Case Study: The Cuban Missile Crisis • What is the Cold War?- Meaning and Significance • Emergence of Power Blocks- Eastern Alliance and Western Alliance • Arenas of Cold War • Rise of NAM and challenge to Bi- polarity • The New International Economic Order [NIEO] • India and Cold War
- 2. MIND MAP In 1962, the Soviet Union placed nuclear missiles in Cuba. Known as the CUBAN MISSILE CRISIS, this led to one of the flash points of conflicts between the USSR and the USA but ended without any real military conflict. What is cold war?: The end of the Second W.W.[1945] marked the birth of two super powers: the USA and the USSR. The mutual suspicion between them, their arms race, building alliances and accompanied by a real ideological difference came to be termed as cold war. The cold war, however, cold not become a real war due to the Logic of Deterrence. To expand and exercise their influence, both the super powers began building alliances by incorporating the newly independent and smaller nations. The US-led alliance came to be known as Western Alliance [NATO Block] and the USSR-led alliance came to be known as Eastern Alliance [WARSAW Block]. The newly independent nations formed Non Aligned Movement [NAM] to stay away from both the power blocks. They played many crucial role to prevent the cold war escalating into a real conflict. After the end of the cold war, and in an Unipolar world, the NAM has lost much of its relevance as a political group. It is now working more as an economic pressure group.
- 4. THE CUBAN MISSILE CRISIS The Communist-ruled CUBA was an ally of the SOVIET UNION and received both diplomatic and financial aid from it. CUBA is located off the southern coast of the USA. Fearing an invasion from the USA and overthrow the communist ruler of Cuba, FIDEL CASTRO, the leader of the Soviet Union, NIKITA KHRUSHCHEV, decided to place nuclear missiles in Cuba. Realising that the installation of these weapons put the USA under fire from a close range,[and the US security under threat from the USSR], the American president JOHN F. KENNEDY ordered the American warships to intercept any Soviet ship heading to CUBA. A military clash was looking imminent. However, diplomatic negotiations became successful and the Soviet ships turned back. The entire incident came to be known as the CUBAN MISSILE CRISIS and became a high point of cold war. Q. What led to the flash point of conflict between the USA and the USSR IN 1962?
- 8. Topic 2: What is The Cold War? Cold war referred to the competition, tensions and a series of confrontations between the USA and the USSR, backed by their respective allies. This was accompanied by a real ideological conflict as well. That is: A. The Western Alliance, headed by the US represented the ideology of liberal democracy and capitalism. B. The Eastern Alliance, headed by the USSR, was committed to the ideology of Socialism and Communism. Q “The end of the Second W.W. was considered the beginning of the cold war.” How?: The II W.W. was fought between 1939-1945 and the Allied Forces [the USA, the USSR, Britain and France] defeated the Axis Power [Germany, Italy and Japan] The war ended when the USA dropped atom bombs on Japan in 1945. Critics of this US decision argued that it was not necessary because Japan was about to surrender. Actually, the USA objective was to stop the Soviet Union from making military and political gains in Asia and elsewhere and to project the US supremacy over the Soviet Union.
- 13. However, supporters of the US decision argued that dropping of the atom bomb was necessary to end the war quickly and to stop further loss of American and allied lives. What ever may be the motives, the consequences of the II W.W. was the rise of two new and greatest powers on the global stage with the ability to influence events anywhere on the earth. And the cold war was the outcome of the competitions and rivalry between them. Q. Why did not the cold war become a real or actual war? OR [ How did the cold war manage to ensure human survival? ] The destruction caused by the use of atom bombs would be too costly for any country to bear. When the two super powers are in possession of nuclear weapons capable of inflicting death and destructions, a full fledged war was unlikely. In spite of provocations, neither side would want to risk a war since no political gains would justify the destructions of their societies. In the event of a nuclear war, both sides will be so badly harmed that it will be impossible to declare one side or the other as the winner. Even if one of them tries to attack and disable the nuclear weapons of its rival, the other would still be left with enough weapons of mass destructions [WMD] to inflict unacceptable damage. This deterrence relationship prevents war but not the rivalry between powers. This is called “LOGIC OF DETERRENCE”.
- 14. TOPIC NO 3: THE EMERGENCE OF TWO POWER BLOCS Formation of the power blocks by the super powers intensified the rivalry and competition between them. The Western Alliance It was led by the USA. It was named Western because many of the west European nations sided with the US. The western alliance was formalised into an organisation- NORTH ATLANTIC TREATY ORGANISATION [NATO], formed in 1949. Originally, it was an association of 12 nations which practiced liberal democracy and capitalist economic system. [Today there are 30 member nations.] It was declared that “an armed attack on any one of them would be considered as an attack on all of them. Each of these states would be obliged to help the other.” Examples of few NATO members: The USA, the UK, France, Spain, Italy, Portugal, etc. In East, South-East and West Asia, the US built an alliance system called SOUTH EAST ASIAN TREATY ORGANISATION [SEATO] and CENTRAL TREATY ORGANISATION [CENTO]. Some of these countries are like Pakistan Philippines and South Korea.
- 18. THE US CONTAINMENT POLICY: TO RESIST THE SOVIET COMMUNIST EXPANSION
- 19. THE EASTERN ALLIANCE: It was led by the USSR [UNION OF SOVIET SOCIALIST REPUBLIC]. It was named Eastern because many of the East European nations sided with the USSR and remained within its sphere of influence. The members [originally 8 members] of the Eastern Alliance entered into a pact with each other, called the WARSAW Pact, to protect each other under the leadership of the USSR. The prominent members of this group include: The USSR, Poland, Hungary, Romania, etc The members of the Eastern Alliance practiced Communism and Socialism in their politics and economy. To match the regional adventure by the US, the Soviet Union and China began building close relationship with regional countries like Vietnam, North Korea and Iraq.
- 25. International alliances during the Cold War Era were determined by the requirements of the super powers as well as the calculations of the newly independent and smaller nations. Q. How did building the alliances help the super powers? OR Q.Even after possessing nuclear weapons, why did the super powers need allies? The smaller states were helpful for the super powers in gaining access to: 1. vital resources, such as oil and minerals. [Eg. Saudi Arab is a close ally of the USA] 2. territory, from where the super powers could launch their weapons and troops. [Eg. The US aid to Pakistan was against the Communist Afghanistan] 3. locations, from where they could spy on each other. 4. economic support, in the sense that the small allies together could help pay for military expenses. [Eg. The allied forces led by the US against Iraq was militarily and financially supported by Turkey and Saudi Arab] Q. Why did the smaller nations decide to side with one or the other super powers? They got the promise of protection, weapons and economic aid against their local rivals, mostly their neighbours with whom they had rivalries. Eg. Pakistan…….India South Korea……..North Korea
- 26. TOPIC NO:4- ARENAS OF THE COLD WAR Meaning: It refers to the areas where crisis and war occurred or threatened to occur between the alliance systems but did not cross certain limits. Example: The KOREAN Crisis [1950-53], the BERLIN Crisis [1958-62], the CONGO Crisis [1960s], intervention in VIETNAM [1956-74]and AFGANISTAN [1970s]. In all these cases, crises deepened, a great many lives were lost, military build ups reported, diplomatic negotiations failed. But the world was spared a nuclear war and a global war. How? Role of NAM……… Role of the UN and the UN Peace-keeping Force………. Logic of Deterrence………. Sustainable diplomatic negotiations………. Arms control treaties.[Such as the Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty, Arms Control Treaty, etc.]………
- 35. TOPIC 5: Rise of the NAM and challenge to bipolarity The idea of NAM originated at the Afro-Asian Conference at Bandung, Indonesia, in 1956. The founding members of the NAM included:[G-5] 1. J.L.Nehru [INDIA] 2. Josip Broz Tito [YUGOSLAVIA] 3. G.A.Nasser [EGYPT] 4. Sukarno [INDONESIA] 5. Kwame Nkrumah [GHANA] Factors contributed to the rise of NAM: A. Friendship and cooperation among these newly independent countries. B. Growing cold war tension and its widening arena. C. The entry of many newly decolonised nations of Asia, Africa and Latin America. NAM offered them a third option – not to join either of the alliances. The first NAM summit [members-25] was held at Belgrade in Yugoslavia in 1961. The latest was the 18th summit [members-120] held at Baku in Azerbaijan in Oct, 2019.
- 39. Significance of the NAM Non alignment should not be meant as isolationism. Because it means remaining aloof from world affairs. In fact, the NAM countries played an active role in mediating between the two rival alliances in the cause of peace and stability. NAM was also not neutrality. Because neutrality refers to a policy of staying out of war, not taking any position on the war and not helping to end the war. The truth was that the NAM nation worked vigorously to prevent war between others and tried to end wars. Soon after its inception, the NAM grew into a popular international movement, joined by countries of various political system and interests. The strength of the NAM was based on their unity and their resolve to remain non aligned despite the attempt by the two super powers to bring them into their respective alliances.
- 40. TOPIC 6: NEW INTERNATIONAL ECONOMIC ORDER [NIEO] Traditionally, the world economy post second W.W. was principally guided by two ideologies: Capitalist [led by the USA] and Socialist [led by the USSR]. The NAM nations, many of them were categorised as LDCs [Least Developed Countries], did not join any of these two camps. So, it was a challenge for these nations to: a. be economically developed through faster industrialisation and agriculturally modernised, b. lift their people out of poverty and c. to remain economically independent and protect their political sovereignty, etc. The idea of a New International Economic Order [NIEO] originated with this realisation. The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development [UNCTAD] brought out a report in 1972 entitled: “TOWARDS A NEW TRADE POLICY FOR DEVELOPMENT”. The Report aimed at reforms in the global economic system so as to benefit the LDCs.
- 42. FEATURES OF THE PROPOSED REFORMS: A. To give the LDCs control over their natural resources which were earlier controlled and exploited by the developed western countries. B. To obtain access to Western markets so that the LDCs could sell their products and the global trade become more beneficial for the poorer economies. C. To reduce the cost of technology from the Western countries. D. To provide the LDCs with a greater role in international economic institutions.
- 43. AN ASSESSMENT OF THE NAM:………………………………………………………………. Is it dead or alive??? 1. In 1961, at the first summit at Belgrade, economic issues were not very important. The main role was to mitigate the effects of cold war and maintain global peace. 2. Since the inception of DÉTENTE in the 1970s, the focus was shifted to economic issues and NAM became more an economic pressure group. 3. By the late 1980s, the NIEO was resisted by the developed countries. The NAM nations also struggled to maintain their unity on the face of changing international situation. 4. With the disintegration of the USSR in 1991, cold war came to an end and non-alignment, both as an international movement and as core of India’s foreign policy, lost some of it’s earlier relevance and effectiveness. 5. Still today also the NAM retains some core values and enduring ideas. It reminds the decolonised nations of their historical affiliation and provides them a common platform to position as an alternative world order and become a powerful force in the international arena. 6. NAM nations are working vigorously on issues eg poverty alleviation, to control environmental pollution, to supply safe and pure drinking water, prevent hunger, disease & malnutrition, etc.
- 44. TOPIC 7: INDIA AND THE COLD WAR 1. India was one of the 5-founder members of the NAM. It led the NAM by a two-dimensional response to the ongoing cold war: - it stayed away from the two alliances; and -raised it’s voice against the newly decolonised nations becoming joining the Alliances. 2. India’s policy was neither negative nor passive. It was also not a policy of fleeing away. Rather, time and again India actively intervened in world affairs to soften the cold war rivalries and thereby prevented these escalating into a full scale war. Indian diplomats and leaders mediated in many such crises, eg in the case of the Korean crises. 3. India led many regional and international organisations [Nehru called these as genuine commonwealth of free and cooperating nations] which were not a part of the super power alliances to mitigate the effects of cold war. 4. The NAM served India’s interest in at least two ways: a. India could take global decisions and stances freely that served its own interest. b. India could balance one super power against the other keeping its national interest. So no super power could bully India.
- 45. [Cont..] 5. However, India’s policy of non alignment was criticised mainly on two grounds: A. India’s non aligned stand was said to be unprincipled. In the name of pursuing it’s national interest, India often refused to take a firm stand on crucial international issues. B. It is suggested that India was inconsistent and took contradictory stands. For eg having criticised others for joining alliances, India signed the Treaty of Friendship in 1971 with the USSR for 20 years. So, this was regarded by many observers as India joining the Soviet camp. However, India justified its stand saying that it needed diplomatic and military support especially in the context of the Bangladesh crisis.
- 46. CH: 1- THE COLD WAR ERA Max.Marks: 20 mins Time Allowed: 45 Q1. Which international organisation brought out a report entitled: Towards a New Trade Policy for Development? [1] Q2. Non-alignment is not about neutrality. In this context, what does neutrality refer to? [1] Q3. The Second World War was fought during the period: [1] a. 1938-1947 b. 1938-1946 c. 1939-1945 d. 1939-1948 Q4. Why did the USA object to the Soviet deployment of nuclear missiles in Cuba? [1] Q5. Identify the following sentence as true or false. If false, correct it. [1] The Soviet Union used its influence in the Western Europe, backed by the very large presence its armies in this region so that these countries remain a part of its alliance Q6. The cold war also led to several shooting wars. Give any two examples. [1] Q7. Why is it said that the end of the Second W.W. was the beginning of the cold war? [2] Q8. As a leader of the NAM, what was India’s two-fold response to the ongoing cold war? [2] Q9. How did India’s non-aligned posture serve its interest directly? Give any two. [2] Q10. How the smaller nations were benefitted by joining the super power alliances? [2] Q11. Despite the NAM losing its earlier relevance and effectiveness, it still continues with some core values and enduring ideas. How? Draw any two points to substantiate the statement. [2] Q12. What is the Logic of Deterrence? How did it prevent the super power rivalry from emerging into a real war? [4]
- 47. ASSIGNMENT: Q1. What made Cuba an ally of the USSR? [1] Q2. How did the Cuban missile crisis end? [1] Q3. “The W.W.II spread to South East Asia, including India.” T or F ?? If False, correct, [1] Q4. What does “neutrality” and “isolationism” mean in international politics ? [2] Q5. What does arenas of cold war mean? [1] Q6. “The cold war also led to several shooting war.” List two of its destructive outcome. [2] Q6. What does arms control treaties mean? Give examples also. [2] Q7. What role was played by the NAM to prevent the cold war from becoming a real war. Give any two. [2] Q8. What does Western Alliance mean? [2] Q9. What does Eastern Alliance mean? [2] Q10. “Cracks and splits appear within the Alliances.” Give one example. [2]
- 48. ASSIGNMENT 1. What are the LDCs? [1] 2. What was the Indian government’s view on signing the Treaty of Friendship with the USSR in 1971? [2] 3. Read the following situation: “Nehru reposed great faith in a genuine commonwealth of free and cooperating nations.” Identify this organisation Nehru talked about: a. The UN b. League of Nations c. NAM d. UNCTAD 4. “Isolationism sums up the foreign policy of the US from the American war of Independence in 1787 up to the beginning of the W.W.I.” What did isolationism mean here? b. Only confined to the continents of The Americas. c. Not establishing colonies, unlike that of the European nations. d. Did not form any alliance. e. Remaining aloof from the world affairs. 5. Which of the following is not true w.r.t Logic of deterrence? f. The cold war did not become a real war. g. The 2 super powers entered into arms race. h. The formation of the NAM did not take place before the W.W.II i. The Alliance system was established by the super powers.
- 49. 6. How did the 2 super powers threat to divide the entire world into two camps? By: a. Joining the arms race. b. Establishing the Alliance system c. Including the decolonised nations in their respective camps. d. Building nuclear weapons. 7. Division of the world into 2 camps first appeared in: e. Americas b. Europe c. Asia d. the UN. 8. Western Alliance basically means the countries belonging to: f. Western Americas b. West Asia c. Western Europe d. Nuclear powers of the Western. 9. Why was the USSR worried that the US was planning to invade Cuba? Because----- g. As Cuba was its neighbour, the US was planning to capture it. h. President Castro of Cuba was an enemy of the USA. i. Cuba was a communist country. j. There was a boarder dispute between Cuba and the USA. 10. According to the supporters of the US decision to drop atom bomb on Japan, this action was necessary to----------------------------------.
- 50. 11. Failure to resolve the missile crisis in 1961, would have led to: a. War between the US and the USSR. b. The US invasion of Cuba. c. A devastating nuclear warfare. d. All of the above. 12. The W.W.II spread out to the South East Asia that included nations like: e. China and Pakistan. f. China and Myanmar. g. Myanmar and Sri lanka. h. Japan and China. 13. Match the following: a. NATO-------1. Romania b. WARSAW----2. Portugal c. CENTO------3. Middle East d. NAM--------4. Indonesia 14. In which of the following crisis, the UN Secy Gen played a key mediatory role? a. Vietnam b. Korea c. Germany d. Congo
- 51. 15. Assertion: The smaller nations were helpful for the super powers in the Alliance system. Reason: The super powers made these nations to pay for military expenses. a. Statement A is correct. But statement B is not the reason. b. Statement A is correct. Statement B is its reason. c. Both the statements are incorrect. d. Both the statements are correct. But are not linked to each other. 16. As the cold war did not eliminate rivalries, it led to e. Arms race. f. Economic aid to poor nations to make them their allies. g. Building regional and diplomatic alliances. h. All of these. 17. The USA had a military misadventure in i. China. j. Cuba k. Vietnam. l. Germany.
- 52. 18. Cold war ended with the a. Collapse of the Berlin Wall. b. Disintegration of the USSR. c. Diplomatic resolution of the Cuban Missile Crisis. d. Formation of the NAM.
![Chapter 1:
COLD WAR
Topics:
• A Case Study: The Cuban Missile
Crisis
• What is the Cold War?- Meaning
and Significance
• Emergence of Power Blocks-
Eastern Alliance and Western
Alliance
• Arenas of Cold War
• Rise of NAM and challenge to Bi-
polarity
• The New International Economic
Order [NIEO]
• India and Cold War](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-1-320.jpg)
![MIND MAP
In 1962, the Soviet Union placed nuclear missiles in Cuba. Known as the CUBAN MISSILE CRISIS, this led to one of
the flash points of conflicts between the USSR and the USA but ended without any real military conflict.
What is cold war?: The end of the Second W.W.[1945] marked the birth of two super powers: the USA
and the USSR. The mutual suspicion between them, their arms race, building alliances and accompanied by a real
ideological difference came to be termed as cold war.
The cold war, however, cold not become a real war due to the Logic of Deterrence.
To expand and exercise their influence, both the super powers began building alliances by incorporating the newly
independent and smaller nations. The US-led alliance came to be known as Western Alliance [NATO Block] and the
USSR-led alliance came to be known as Eastern Alliance [WARSAW Block].
The newly independent nations formed Non Aligned Movement [NAM] to stay away from both the power blocks. They
played many crucial role to prevent the cold war escalating into a real conflict. After the end of the cold war, and in
an Unipolar world, the NAM has lost much of its relevance as a political group. It is now working more as an
economic pressure group.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-2-320.jpg)

![THE CUBAN MISSILE CRISIS
The Communist-ruled CUBA was an ally of the SOVIET UNION
and received both diplomatic and financial aid from it.
CUBA is located off the southern coast of the USA.
Fearing an invasion from the USA and overthrow the
communist ruler of Cuba, FIDEL CASTRO, the leader of the
Soviet Union, NIKITA KHRUSHCHEV, decided to place
nuclear missiles in Cuba.
Realising that the installation of these weapons put the USA
under fire from a close range,[and the US security under threat
from the USSR], the American president JOHN F. KENNEDY ordered the
American warships to intercept any Soviet ship heading to CUBA.
A military clash was looking imminent. However, diplomatic
negotiations became successful and the Soviet ships turned back.
The entire incident came to be known as the CUBAN MISSILE CRISIS
and became a high point of cold war.
Q. What led to the flash point of conflict between the USA and the USSR IN 1962?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-4-320.jpg)



![Topic 2: What is The Cold War?
Cold war referred to the competition, tensions and a series of confrontations between the USA and the USSR,
backed by their respective allies.
This was accompanied by a real ideological conflict as well. That is:
A. The Western Alliance, headed by the US represented the ideology of liberal democracy and capitalism.
B. The Eastern Alliance, headed by the USSR, was committed to the ideology of Socialism and Communism.
Q “The end of the Second W.W. was considered the beginning of the cold war.” How?:
The II W.W. was fought between 1939-1945 and the Allied Forces [the USA, the USSR, Britain and France]
defeated the Axis Power [Germany, Italy and Japan]
The war ended when the USA dropped atom bombs on Japan in 1945.
Critics of this US decision argued that it was not necessary because Japan was about to surrender. Actually,
the USA objective was to stop the Soviet Union from making military and political gains in Asia and elsewhere
and to project the US supremacy over the Soviet Union.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-8-320.jpg)




![ However, supporters of the US decision argued that dropping of the atom bomb was necessary to end the war quickly and to stop
further loss of American and allied lives.
What ever may be the motives, the consequences of the II W.W. was the rise of two new and greatest powers on the global stage
with the ability to influence events anywhere on the earth. And the cold war was the outcome of the competitions and rivalry
between them.
Q. Why did not the cold war become a real or actual war?
OR
[ How did the cold war manage to ensure human survival? ]
The destruction caused by the use of atom bombs would be
too costly for any country to bear.
When the two super powers are in possession of nuclear weapons
capable of inflicting death and destructions, a full fledged war was unlikely.
In spite of provocations, neither side would want to risk a war
since no political gains would justify the destructions of their societies.
In the event of a nuclear war, both sides will be so badly harmed that it will be impossible to declare one side or the other as the
winner.
Even if one of them tries to attack and disable the nuclear weapons of its rival, the other would still be left with enough weapons of
mass destructions [WMD] to inflict unacceptable damage.
This deterrence relationship prevents war but not the rivalry between powers.
This is called “LOGIC OF DETERRENCE”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-13-320.jpg)
![TOPIC NO 3: THE EMERGENCE OF TWO POWER BLOCS
Formation of the power blocks by the super powers intensified the rivalry and competition between them.
The Western Alliance
It was led by the USA.
It was named Western because many of the west European nations sided with the US.
The western alliance was formalised into an organisation-
NORTH ATLANTIC TREATY ORGANISATION [NATO], formed in 1949.
Originally, it was an association of 12 nations which practiced liberal democracy and
capitalist economic system. [Today there are 30 member nations.]
It was declared that “an armed attack on any one of them would be considered as an
attack on all of them. Each of these states would be obliged to help the other.”
Examples of few NATO members: The USA, the UK, France, Spain, Italy, Portugal, etc.
In East, South-East and West Asia, the US built an alliance system called SOUTH EAST ASIAN TREATY
ORGANISATION [SEATO] and CENTRAL TREATY ORGANISATION [CENTO]. Some of these countries are like
Pakistan Philippines and South Korea.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-14-320.jpg)




![THE EASTERN ALLIANCE:
It was led by the USSR [UNION OF SOVIET SOCIALIST REPUBLIC].
It was named Eastern because many of the East European nations sided with the USSR and remained within its
sphere of influence.
The members [originally 8 members] of the Eastern Alliance entered into a pact with each other, called the
WARSAW Pact, to protect each other under the leadership of the USSR.
The prominent members of this group include: The USSR, Poland, Hungary, Romania, etc
The members of the Eastern Alliance practiced Communism and Socialism in their politics and economy.
To match the regional adventure by the US, the Soviet Union and China began building close relationship with
regional countries like Vietnam, North Korea and Iraq.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-19-320.jpg)





![ International alliances during the Cold War Era were determined by the requirements of the
super powers as well as the calculations of the newly independent and smaller nations.
Q. How did building the alliances help the super powers?
OR
Q.Even after possessing nuclear weapons, why did the super powers need allies?
The smaller states were helpful for the super powers in gaining access to:
1. vital resources, such as oil and minerals. [Eg. Saudi Arab is a close ally of the USA]
2. territory, from where the super powers could launch their weapons and troops. [Eg. The US aid to Pakistan was against
the Communist Afghanistan]
3. locations, from where they could spy on each other.
4. economic support, in the sense that the small allies together could help pay for military expenses. [Eg. The allied forces
led by the US against Iraq was militarily and financially supported by Turkey and Saudi Arab]
Q. Why did the smaller nations decide to side with one or the other super powers?
They got the promise of protection, weapons and economic aid against their local rivals, mostly their neighbours with whom they
had rivalries.
Eg. Pakistan…….India
South Korea……..North Korea](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-25-320.jpg)
![TOPIC NO:4- ARENAS OF THE COLD WAR
Meaning: It refers to the areas where crisis and war occurred or threatened to occur
between the alliance systems but did not cross certain limits.
Example: The KOREAN Crisis [1950-53], the BERLIN Crisis [1958-62], the CONGO
Crisis [1960s], intervention in VIETNAM [1956-74]and AFGANISTAN [1970s].
In all these cases, crises deepened, a great many lives were lost, military build ups
reported, diplomatic negotiations failed. But the world was spared a nuclear war and a
global war. How?
Role of NAM………
Role of the UN and the UN Peace-keeping Force……….
Logic of Deterrence……….
Sustainable diplomatic negotiations……….
Arms control treaties.[Such as the Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty, Arms Control
Treaty, etc.]………](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-26-320.jpg)


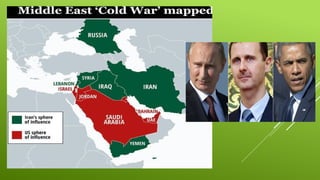




![TOPIC 5: Rise of the NAM and challenge to bipolarity
The idea of NAM originated at the Afro-Asian Conference at Bandung, Indonesia, in 1956.
The founding members of the NAM included:[G-5]
1. J.L.Nehru [INDIA]
2. Josip Broz Tito [YUGOSLAVIA]
3. G.A.Nasser [EGYPT]
4. Sukarno [INDONESIA]
5. Kwame Nkrumah [GHANA]
Factors contributed to the rise of NAM:
A. Friendship and cooperation among these newly independent countries.
B. Growing cold war tension and its widening arena.
C. The entry of many newly decolonised nations of Asia, Africa and Latin America. NAM offered them a third option
– not to join either of the alliances.
The first NAM summit [members-25] was held at Belgrade in Yugoslavia in 1961.
The latest was the 18th
summit [members-120] held at Baku in Azerbaijan in Oct, 2019.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-35-320.jpg)




![TOPIC 6: NEW INTERNATIONAL ECONOMIC ORDER [NIEO]
Traditionally, the world economy post second W.W. was principally guided by two ideologies: Capitalist [led by
the USA] and Socialist [led by the USSR].
The NAM nations, many of them were categorised as LDCs [Least Developed Countries], did not join any of
these two camps.
So, it was a challenge for these nations to:
a. be economically developed through faster industrialisation and agriculturally modernised,
b. lift their people out of poverty and
c. to remain economically independent and protect their political sovereignty, etc.
The idea of a New International Economic Order [NIEO] originated with this realisation. The United Nations
Conference on Trade and Development [UNCTAD] brought out a report in 1972 entitled: “TOWARDS A NEW
TRADE POLICY FOR DEVELOPMENT”.
The Report aimed at reforms in the global economic system so as to benefit the LDCs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-40-320.jpg)



![TOPIC 7: INDIA AND THE COLD WAR
1. India was one of the 5-founder members of the NAM. It led the NAM by a two-dimensional response to the
ongoing cold war:
- it stayed away from the two alliances; and
-raised it’s voice against the newly decolonised nations becoming joining the Alliances.
2. India’s policy was neither negative nor passive. It was also not a policy of fleeing away. Rather, time and again India
actively intervened in world affairs to soften the cold war rivalries and thereby prevented these escalating into a full
scale war. Indian diplomats and leaders mediated in many such crises, eg in the case of the Korean crises.
3. India led many regional and international organisations [Nehru called these as genuine commonwealth of free and
cooperating nations] which were not a part of the super power alliances to mitigate the effects of cold war.
4. The NAM served India’s interest in at least two ways:
a. India could take global decisions and stances freely that served its own interest.
b. India could balance one super power against the other keeping its national interest. So no super power could bully
India.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-44-320.jpg)
![[Cont..]
5. However, India’s policy of non alignment was criticised mainly on two grounds:
A. India’s non aligned stand was said to be unprincipled. In the name of pursuing it’s
national interest, India often refused to take a firm stand on crucial international issues.
B. It is suggested that India was inconsistent and took contradictory stands. For eg
having criticised others for joining alliances, India signed the Treaty of Friendship in 1971
with the USSR for 20 years. So, this was regarded by many observers as India joining the
Soviet camp. However, India justified its stand saying that it needed diplomatic and military
support especially in the context of the Bangladesh crisis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-45-320.jpg)
![CH: 1- THE COLD WAR ERA
Max.Marks: 20 mins Time Allowed: 45
Q1. Which international organisation brought out a report entitled: Towards a New Trade Policy for Development? [1]
Q2. Non-alignment is not about neutrality. In this context, what does neutrality refer to? [1]
Q3. The Second World War was fought during the period: [1]
a. 1938-1947
b. 1938-1946
c. 1939-1945
d. 1939-1948
Q4. Why did the USA object to the Soviet deployment of nuclear missiles in Cuba? [1]
Q5. Identify the following sentence as true or false. If false, correct it. [1]
The Soviet Union used its influence in the Western Europe, backed by the very large presence its armies in this region so that these
countries remain a part of its alliance
Q6. The cold war also led to several shooting wars. Give any two examples. [1]
Q7. Why is it said that the end of the Second W.W. was the beginning of the cold war? [2]
Q8. As a leader of the NAM, what was India’s two-fold response to the ongoing cold war? [2]
Q9. How did India’s non-aligned posture serve its interest directly? Give any two. [2]
Q10. How the smaller nations were benefitted by joining the super power alliances? [2]
Q11. Despite the NAM losing its earlier relevance and effectiveness, it still continues with some core values and enduring ideas. How?
Draw any two points to substantiate the statement. [2]
Q12. What is the Logic of Deterrence? How did it prevent the super power rivalry from emerging into a real war? [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-46-320.jpg)
![ASSIGNMENT:
Q1. What made Cuba an ally of the USSR? [1]
Q2. How did the Cuban missile crisis end? [1]
Q3. “The W.W.II spread to South East Asia, including India.” T or F ?? If False, correct, [1]
Q4. What does “neutrality” and “isolationism” mean in international politics ? [2]
Q5. What does arenas of cold war mean? [1]
Q6. “The cold war also led to several shooting war.” List two of its destructive outcome. [2]
Q6. What does arms control treaties mean? Give examples also. [2]
Q7. What role was played by the NAM to prevent the cold war from becoming a real war. Give any two. [2]
Q8. What does Western Alliance mean? [2]
Q9. What does Eastern Alliance mean? [2]
Q10. “Cracks and splits appear within the Alliances.” Give one example. [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-47-320.jpg)
![ASSIGNMENT
1. What are the LDCs? [1]
2. What was the Indian government’s view on signing the Treaty of Friendship with the USSR in 1971? [2]
3. Read the following situation: “Nehru reposed great faith in a genuine commonwealth of free and cooperating
nations.” Identify this organisation Nehru talked about:
a. The UN b. League of Nations c. NAM d. UNCTAD
4. “Isolationism sums up the foreign policy of the US from the American war of Independence in 1787 up to the
beginning of the W.W.I.” What did isolationism mean here?
b. Only confined to the continents of The Americas.
c. Not establishing colonies, unlike that of the European nations.
d. Did not form any alliance.
e. Remaining aloof from the world affairs.
5. Which of the following is not true w.r.t Logic of deterrence?
f. The cold war did not become a real war.
g. The 2 super powers entered into arms race.
h. The formation of the NAM did not take place before the W.W.II
i. The Alliance system was established by the super powers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-250509123138-84229697/85/e20ca699-e6c9-4c93-bd0b-f90c69d8c7b4-pptx-48-320.jpg)



