Electrolysis1.ppt
- 2. Learning Objectives • By the end of the lesson I will be able to: • 1) Understand the process of electrolysis. • 2) Explain how we can use electrolysis to extract aluminium from its ore.
- 3. 1. Electrolytes contain positive and negative ions. 2. During electrolysis, positive and negative electrodes are put into the electrolyte. 3. The positive electrode is called the anode. 4. The negative electrode is called the cathode. 5. The negative ions (called anions) are attracted to the anode. 6. At the anode, the negative ions lose electrons to become atoms/molecules. 7. The positive ions (called cations) are attracted to the cathode. 8. At the cathode, the positive ions gain electrons to become atoms/molecules
- 4. Match up the words with their descriptions Test for Oxygen Test for Hydrogen Electrolyte Relights a glowing splint Makes a ‘popping’ noise when lit The substance being broken down Splitting a substance using electricity Electrolysis Positive electrode Negative electrode Anode Cathode Anion Negative ion Positive ion Cation
- 5. Match up the words with their descriptions Test for Oxygen Test for Hydrogen Electrolyte Relights a glowing splint Makes a ‘popping’ noise when lit The substance being broken down Splitting a substance using electricity Electrolysis Positive electrode Negative electrode Anode Cathode Anion Negative ion Positive ion Cation
- 6. Electrolysis is splitting up substances using electricity (Lysis is latin for splitting)
- 7. What is electrolysis? • Electric current is used to breakdown a substance made up of ions • An electrolyte is the name for the substance being broken down
- 8. •Positive •Anode •Negative •Is •Cathode Don’t get stressed in the exam: Remember PANIC
- 9. •Oxidation •Is •Loss of electrons •Reduction •Is •Gain of electrons. Don’t get stressed in the exam: Remember OILRIG
- 10. Electrolysis Apparatus Cathode (-ve electrode) power supply Anode (+ve electrode) Electrolyte
- 11. Electrolysis Apparatus Cathode (-ve electrode) power supply Anode (+ve electrode) Electrolyte
- 12. Electrolysis Apparatus Cathode (-ve electrode) Anode (+ve electrode) Electrolyte: this is what will be electrolysed power supply Watch the video and answer the questions in task 4.
- 13. Electrolysis of Molten NaCl + - - + CATHODE ANODE Na+ Cl- Na+ Cl- Na+ Cl- Na+ Cl- The metal goes to the cathode and the non metal goes to the anode.
- 14. Electrolysis – Half equations A half-equation shows you what happens at one of the electrodes during electrolysis. Electrons are shown as e-. A half-equation is balanced by adding, or taking away, a number of electrons equal to the total number of charges on the ions in the equation. Negative ions or neutral atoms lose electrons at the positive electrode and are oxidised. For example, chlorine is produced during the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution: 2Cl- - 2e- → Cl2
- 15. Nasty QoWC Question from the Exam. • Aluminium is extracted from its ore Bauxite (Aluminium Oxide Al2O3) using electrolysis. Explain how electrolysis is used to extract aluminium. (7 marks) • Watch the video and use it to help you answer this question.
- 16. Aluminuim oxide electrolysis • Molten aluminium oxide is created by dissolving the aluminium in molten cryolite. • This forms the electrolyte, through which electricity can pass. • An electric current is passed through the electrolyte. • This causes the aluminium oxide to split into aluminium and oxygen. • Oxygen ions are negative (anions) and go to the anode. • Aluminium ions are positively charged (cations) and go to the cathode. There is a build up of pure aluminium at the cathode which can be removed and allowed to cool.
- 17. + - Zn+ Zn+ Zn+ Zn+ Zn+ Zn+ Zn+ Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Zn+ positive electrode negative electrode molten zinc chloride (ions free to move) (anode) (cathode)
- 18. + - Zn+ Zn+ Zn+ Zn+ Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Zn+ The positively charged zinc ions are attracted to the negative electrode
- 19. + - Zn+ Zn+ Zn+ Zn+ Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Zn+ The negatively charged chloride ions are attracted to the positive electrode
- 21. Anode Cathode = bromide ion = lead ion
- 22. O.I.L.R.I.G. •Oxidation is loss of electrons •Reduction is gain of electrons
- 23. Anode Cathode = bromide ion = lead ion At the cathode: Pb+ gains electrons to form lead metal. It is REDUCED. At the anode: Br- loses electrons to form bromine gas. It is OXIDISED.
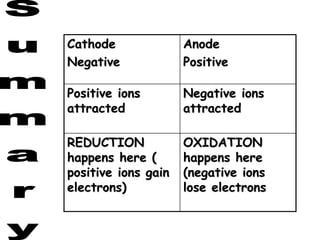
- 24. Cathode Negative Anode Positive Positive ions attracted Negative ions attracted REDUCTION happens here ( positive ions gain electrons) OXIDATION happens here (negative ions lose electrons
- 25. True or False • Electrolysis is the splitting of a substance using electricity. • The anode is negative. • Anions are negative • Aluminium oxide is found in bauxite. • Cathode is negative. • Cations are negative.
- 26. Stand up sit down 1. One person names a topic. 2. All pupils write a key word to do with the topic on a whiteboard 3. The person who chose the topic has 30 seconds to name as many key words to do with the topic as they can. 4. If the word the pupil has written down is said they have to sit down. 5. The aim for the topic chooser is to get everyone to sit down. 6. The aim for the pupils writing down a word is to out fox the topic chooser with a relevant but obscure word.