Epistaxis
- 2. • Write down the causes of epistaxis & its management. • List various causes for epistaxis. Name the vessels which contribute in the formation of Little’s area. • Enumerate common local causes for epistaxis. Describe Keisselbach's plexus with diagram. • Discuss possible treatment modalities to manage a case of epistaxis in a 30 years old person, who could not be managed by first aid measures • Write about the blood vessels in the nose causing epistaxis. Enumerate the different non-surgical and surgical methods for control of epistaxis.
- 3. •Definition –Bleeding from inside the nasal cavity •Causes –Idiopathic (55 %) –Local /Locoregional –General
- 4. Local and locoregional causes • Congenital: – Hereditary hemorrhagic telengiectasia • Trauma: – Nose picking, injury to nose / face / skull base, nasal surgery, foreign body • Infection: – Vestibulitis, sinusitis, atrophic rhinitis, rhinosporodiosis, rhinoscleroma • Neoplasms: – Angiofibroma, hemangioma, inverted papilloma, malignancy • Deviated nasal septum with spur
- 5. General causes • Hypertension • Bleeding disorders – Hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, leukemia • Drugs – Aspirin, anticoagulants (blood thinners) • Physiological – Cold + dry climate, high altitude, vicarious menstruation, violent exertion, barotrauma • Liver and kidney failure • Exanthematous fevers
- 6. Common causes of epistaxis • Children: Nose picking, foreign body, viral exanthemas • Adolescent: Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma, trauma, sinusitis • Adults: sinusitis, trauma • Elderly: hypertension, malignancy
- 7. Sites of epistaxis • Little’s area/Kiesselbach’s plexus (80-90 %) – Common in children and young people • Woodruff’s venous (?) plexus – Common in elderly, hypertensives • Retro - columellar vein – Common in young children • Others: Septal turbinate, hemorrhagic nodules
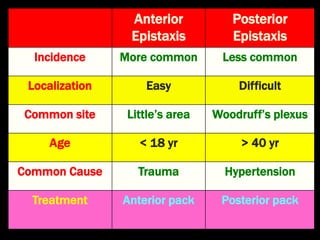
- 9. Anterior Epistaxis Posterior Epistaxis Incidence More common Less common Localization Easy Difficult Common site Little’s area Woodruff’s plexus Age < 18 yr > 40 yr Common Cause Trauma Hypertension Treatment Anterior pack Posterior pack
- 10. Evaluation of patients with epistaxis • Mode of onset, duration, frequency, amount, side, site, previous bleeding • Nasal trauma, purulent nasal discharge • Hypertension, hepatic diseases, family history of bleeding, bleeding from other sites, use of anticoagulants, aspirin • Measurement of pulse and blood pressure
- 11. Investigations • Hemoglobin, Packed Cell Volume, platelet count • Blood grouping • Bleeding Time, Clotting Time • Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time • Prothrombin Time • Diagnostic Nasal Endoscopy (D.N.E.) • Contrast C.T. scan of nose and paranasal sinus
- 12. General treatment • Record pulse and blood pressure • Reassurance • Bed rest in sitting position with back rest / support and leaning forward • Adequate sedation (Diazepam) • Inj. Ethamsylate 500 mg IV TDS • Amlodipine / Nifedipine for hypertension • IV fluids / blood transfusion for shock
- 13. Anterior epistaxis • Pinch nostrils + ice pack Bleeding continues • Insert cotton pledgets soaked in 1: 1000 adrenaline in nasal cavity Bleeding continues • Chemical cautery with AgNO3 or electrical cautery (if bleeder is localized) or anterior nasal packing
- 14. Anterior epistaxis • Pinch nostrils + apply ice pack • Insert cotton pledgets soaked in 1: 1000 adrenaline in nasal cavity • Chemical cautery with AgNO3 (20%) • Electrocautery (if bleeder is localized) • Anterior nasal packing
- 17. Chemical cautery
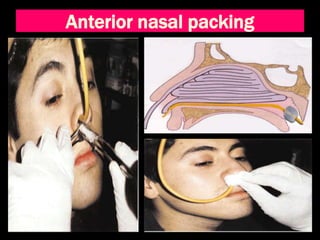
- 18. Anterior nasal packing • Performed with – Liquid paraffin & antibiotic cream in ribbon gauze – Vaseline gauze – Bismuth Iodoform Paraffin Paste gauze – Merocel tampoon – Simpson balloon • Left inside the nostrils for 48 -72 hrs under antibiotic cover
- 19. Anterior nasal packing with ribbon gauze • Ribbon gauze soaked in liquid paraffin and antibiotic cream/ BIPP Pack/ Vaseline • Both nasal cavities packed tightly by layering from floor to roof • Pack removed after 48 -72 hrs • Systemic antibiotics administered to prevent sinus infection and toxic shock syndrome
- 23. Posterior epistaxis • Posterior + anterior nasal packing – Post nasal gauze pack – Foley’s catheter – Brighton balloon (double lumen) – Epistat balloon (double lumen) – Bivona balloon (triple lumen) • Pack left in situ for 48-72 hrs under antibiotic cover
- 24. Antero-Posterior Nasal Packing with gauze pack
- 25. Posterior nasal packing • Post nasal pack prepared by tying 3 ribbon gauze strips to a piece of gauze roll • 2 Foley’s catheters passed through each nostril and their ends brought out via mouth • 2 ends of gauze strips attached to nasal pack are tied to catheter tips & withdrawn from nose
- 26. • Pack that follows ribbon gauze strips, is guided into nasopharynx with index finger • Ribbon gauze strips tied over a gauze piece on columella and anterior nasal packing done • 3rd gauze strip brought out from mouth and taped to cheek • Pack removed after 48-72 hrs
- 27. Posterior nasal gauze pack
- 29. Tying of pack to catheter tip
- 30. Guiding pack into the nasopharynx
- 31. Tying of anterior strips
- 34. Antero - Posterior Nasal Packing with Foley’s catheter
- 35. Foley’s catheter
- 37. Catheter tip in nasopharynx
- 42. Bivona triple lumen catheter
- 43. Surgical intervention for refractory/ intractable epistaxis 1. Arterial ligation by external approach – External carotid artery ligated in neck, distal to superior thyroid artery – Internal maxillary artery ligated in pterygo-palatine fossa (Caldwell-Luc operation) – Anterior or posterior ethmoidal artery ligated in orbit (Lynch- Howarth incision)
- 47. 2. Angiography and embolization 3. S.M.R. or Septoplasty – Impacted DNS 4. Septo-dermoplasty – Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia 5. Endoscopic cautery and clipping – Anterior or posterior ethmoidal artery – Sphenopalatine artery
- 50. MCQs 1. Commonest cause of epistaxis in elderly is a. Hypertension b. Sinusitis c. Trauma d. Malignancy 2. Commonest cause of epistaxis in children is a. Adenoids b. Infection c. Nasal allergy d. Nose picking
- 51. 3. Toxic shock syndrome is causedby a. Staph aureus b. Streptococcus c. E. coli d. Gonococcus 4. In hereditaryHemorrhagic telangiectasia: a. Bleedingtime is prolonged b. Clotting time is prolonged c. Platelet count is decreased d. Coagulation profile is normal