Epoxide
- 2. 2 • Epoxides are cyclic three member ethers containing oxygen atom as member of ring. Epoxides are also called oxiranes. • The C—O—C bond angle for an epoxide must be near to 60°, a considerable deviation from the tetrahedral bond angle of 109.5°. • Thus, epoxides have angle strain, making them more reactive than other ethers.
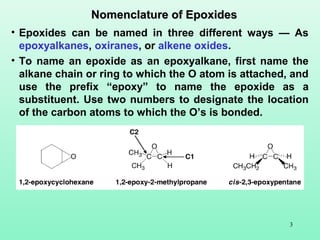
- 3. 3 • Epoxides can be named in three different ways — As epoxyalkanes, oxiranes, or alkene oxides. • To name an epoxide as an epoxyalkane, first name the alkane chain or ring to which the O atom is attached, and use the prefix “epoxy” to name the epoxide as a substituent. Use two numbers to designate the location of the carbon atoms to which the O’s is bonded. Nomenclature of EpoxidesNomenclature of Epoxides
- 4. 4 • Epoxides can also be named as derivatives of oxirane, the simplest epoxide having two carbons and one oxygen atom in a ring. • The oxirane ring is numbered to put the O atom at position one, and the first substituent at position two. • In most of cases, no number is used for a substituent in a monosubstituted oxirane. O O CH3 oxirane (epoxyethane) 2-methyloxirane (epoxypropane) O CH3 O CH3H3C O CH3 CH3 2-ethyloxirane (1,2-epoxybutane) 2,3-dimethyloxirane (2,3-epoxybutane) 2,2-dimethyloxirane (1,2-epoxy-2-methy- propane)
- 5. 5 • Epoxides are also named as alkene oxides, since they are often prepared by adding an O atom to an alkene. To name an epoxide in this way: Mentally replace the epoxide oxygen with a double bond. Name the alkene. Add the word oxide at the end. H2C CH2 O H2C CH3 O CH3 ethene (ethylene) oxirane (ethylene oxide) prop-1-ene (propylene) 2-methyloxirane (propylene oxide)
- 6. 6 Preparation of epoxidePreparation of epoxide There are two main laboratory methods for the preparation of epoxides: Epoxidation of alkenes by reaction with peroxy acids. Base-promoted ring closure of vicinal halohydrins.
- 7. 7 Epoxidation of alkenes – oxidationEpoxidation of alkenes – oxidation Epoxides are very easy to prepare via the reaction of an alkene with a peroxy acid. This process is known as epoxidation. C C R O O O H O R O O H+ + alkene peroxy acid Epoxide Carboxylic acid oxidation A commonly used peroxy acid is -peroxyacetic acid (CH3CO2OH), - peroxy trifluoroacetic acid, peroxy - benzoic acid, - peroxy m-chlorobenzoic acid, etc. Also carried out by using hydrogen peroxide and NaOH.
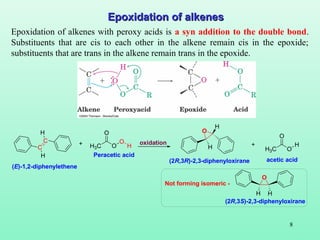
- 8. 8 Epoxidation of alkenesEpoxidation of alkenes Epoxidation of alkenes with peroxy acids is a syn addition to the double bond. Substituents that are cis to each other in the alkene remain cis in the epoxide; substituents that are trans in the alkene remain trans in the epoxide. C C H H H3C O O O H O H H H3C O O H+ +oxidation Peracetic acid acetic acid (E)-1,2-diphenylethene (2R,3R)-2,3-diphenyloxirane O H H (2R,3S)-2,3-diphenyloxirane Not forming isomeric -
- 9. 9 Epoxidation of alkenesEpoxidation of alkenes Addition of an O atom from either side of the trigonal planar cis-alkene leads to the same compound - an achiral meso compound that contains two stereogenic centers. H3C O O H+ acetic acid O H H3C CH3 H C C H CH3H3C H (Z)-but-2-ene H3C O O O H+ oxidation Peracetic acid O H CH3H3C H + O is added below the plane O is added above the plane (2R,3S)-2,3- dimethyloxirane (2S,3R)-2,3- dimethyloxirane pair of achiral meso compounds are formed Addition of an O atom from either side of the trigonal planar trans-alkene leads to the same compound - an enantiomeric compounds. C C H CH3H H3C H3C O O O H O H H3C CH3 H+ oxidation Peracetic acid(E)-but-2-ene O H CH3 H3C H + + H3C O O H acetic acid O is added below the plane O is added above the plane (2R,3R)-2,3- dimethyloxirane (2S,3S)-2,3- dimethyloxirane pair of enantiomers are formed
- 10. 10
- 11. 11
- 12. 12 • Organic compounds that contain both a hydroxy group and a halogen atom on adjacent carbons are called halohydrins. It was synthesized by the treatment of halogen followed by hydrolysis. • In halohydrins, an intramolecular version of the Williamson ether synthesis can occur to form epoxides. From vicinal halohydrinsFrom vicinal halohydrins C C Alkene C C O Epoxide X2 HOH C C XHO HO- vicinal halohydrin
- 13. 13 From vicinal halohydrins - stereochemistryFrom vicinal halohydrins - stereochemistry Substituents that are cis to each other in the alkene remain cis in the epoxide. This is because formation of the bromohydrin involves anti addition, and the ensuing intramolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction takes place with inversion of configuration at the carbon that bears the halide leaving group. C C HH C C HH O Br2 HOH HO- vicinal halohydrin C C H Br HO H C C H Br - O H -Br- (Z)-but-2-ene cis-2,3-epoxybutane (2R,3S)-2,3-dimethyloxirane C C H H C C H H O trans-2,3-epoxybutane Br2 HOH HO- vicinal halohydrin C C Br HO H H C C Br - O H H -Br- (E)-but-2-ene (2R,3R)-2,3-dimethyloxirane
- 14. Which of the following will produce the epoxide below? Question A.a, b B.a, c C. b, c D. b, d E. c, d
- 15. 15 Reactions of EpoxidesReactions of Epoxides • Recall that epoxides do not contain a good leaving group. • Epoxides do contain a strained three-membered ring with two polar bonds. • Nucleophilic attack opens the strained three-membered ring, making it a favorable process even with a poor leaving group.
- 16. 16 • The reaction occurs readily with strong nucleophiles and with acids like HZ, where Z is a nucleophilic atom.
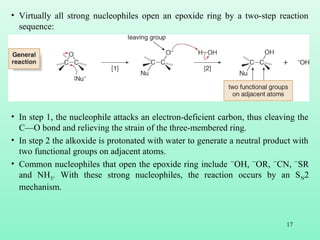
- 17. 17 • Virtually all strong nucleophiles open an epoxide ring by a two-step reaction sequence: • In step 1, the nucleophile attacks an electron-deficient carbon, thus cleaving the C—O bond and relieving the strain of the three-membered ring. • In step 2 the alkoxide is protonated with water to generate a neutral product with two functional groups on adjacent atoms. • Common nucleophiles that open the epoxide ring include ¯OH, ¯OR, ¯CN, ¯SR and NH3. With these strong nucleophiles, the reaction occurs by an SN2 mechanism.
- 18. 18 Examples:
- 19. 19 Let’s now consider the stereochemical consequences of the reaction of 1,2- epoxycyclohexane with ¯OCH3. Nucleophilic attack of ¯OCH3 occurs from the backside at either C—O bond, because both ends are similarly substituted. Since attack at either side occurs with equal probability, an equal amount of the two enantiomers (i.e. a racemic mixture) is formed.
- 20. 20 Optically inactive starting materials give optically inactive products!
- 21. 21 • Acids HZ that contain a nucleophile Z also open epoxide rings by a two-step sequence. • HCl, HBr and HI, as well as H2O and ROH in the presence of acid, all open an epoxide ring in this manner.
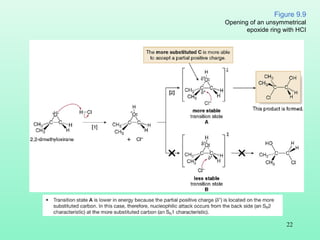
- 22. 22 Figure 9.9 Opening of an unsymmetrical epoxide ring with HCI
- 23. 23 • Ring opening of an epoxide with either a strong nucleophile or an acid HZ is regioselective because one constitutional isomer is the major or exclusive product. • Note that the site selectivity of these two reactions is exactly opposite.
- 24. • Epoxides can be opened by many strong nucleophiles. • Both regioselectivity and stereoselectivity must be considered. Ring-opening of Epoxides
- 25. Question • What is the product isolated when the epoxide below reacts with NaOCH3 in CH3 OH? • A) B) • C) D)
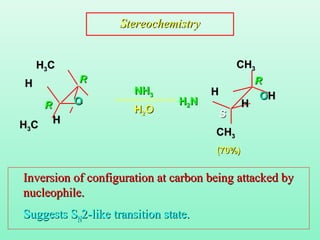
- 26. NHNH33 HH22OO (70%)(70%) RR SS RR RR StereochemistryStereochemistry HH33CC CHCH33 HH33CC CHCH33 OO HH HH HH HH OOHH HH22NN Inversion of configuration at carbon being attacked byInversion of configuration at carbon being attacked by nucleophile.nucleophile. Suggests SSuggests SNN2-like transition state.2-like transition state.
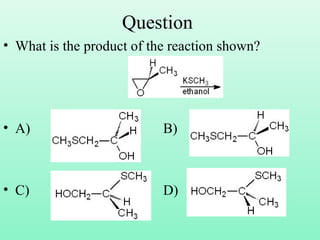
- 27. Question • What is the product of the reaction shown? • A) B) • C) D)
- 28. What are the product(s) of the following reaction? A. C. B. D. 1) CH3MgBr 2) H2OO HO OH HO OH Question
- 29. Question • What is the product isolated when the epoxide at the right reacts with CH3 OH and H2 SO4 ? • A) B) • C) D)
- 30. What is the product of the following reaction? A. C. B. D. HBr OH Br Br Br OH OH Br OH O Question