FERMENTATION TYPES .
- 1. PADMASHREE INSTITUTE OF MANEGMENT AND SCIENCE. Seminar topic on • Types Of Fermentation Process ; Presented by; Shylesh murthy I .A 2Ndyr Msc biotechnology PIMS
- 2. Fermentation
- 3. Traditional fermentation Traditional fermentation technology, as mentioned in the literary texts, is more than 3000 year old in India . The fermentation technology employed a variety of processes and was put to a large number of uses. It also laid the foundation of alchemy and chemistry. The term fermentation is derived from the Latinword Fermentum that stands for boiling. Fermentation is the process of digesting certain substances that leads to chemical conversion of organic substances into simpler compounds.
- 4. Fermentation Fermentation has been widely used for the production of a wide variety of substances that are highly beneficial to individuals and industry. Over the years, fermentation techniques have gained immense importance due to their economic and Environmental advantages. Ancient techniques have been further modified and refined to maximize productivity. This has also involved the development of new machinery and processes. Two broad fermentation techniques have emerged as a result of this rapid development: Solid State Fermentation (SSF). Submerged Fermentation (SmF).
- 5. At the research level, both SSF and SmF have been used;however, some techniques yielded better results than others.
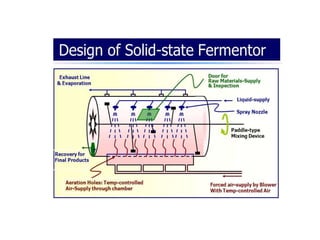
- 6. Solid State Fermentation Solid state (substrate) fermentation (SSF) has been defined as the fermentation process occurring in the absence or near-absence of free water. Solid state fermentation (SSF) is another method used for the production of enzymes, which involves the cultivation of microorganisms on a solid substrate, such as grains, rice and wheat. SSF employs natural raw materials as carbon source such as assava, barley, wheat bran, sugarcane bagasse.
- 8. Selection of Micro-organism This is one of the key factor for improved yields of the product. Bacteria, Yeast and Filamentous Fungi can be used. Filamentous Fungi has shown better results growing in the solid substrate fermentation. Substrate Substrate also plays important role in determining the growth of micro- organisms, there by increasing the product yield. Substrate is chosen such a way that it should provide physical support as well as nutrients to the growing culture.
- 9. Applications: Applications of SSF as described before, Solid State fermentation is being employed in various fields ranging from pharmacology to bioremediation, covering various aspects of biodiversity conservation. Production of Industrial Enzymes Production of Bio pesticides In Bioleaching In Bioremediation
- 11. Examples for Solid State Fermentation
- 13. Submerged fermentation: In the submerged process, the substrate used for fermentation is always in liquid state which contains the nutrients needed for growth. The fermentor which contains the substrate is operated continuously and the product biomass is continuously harvested from the fermenter by using different techniques then the product is filtered or centrifuged and then dried. Submerged fermentation is a method of manufacturing bio molecules in which enzymes and other reactive compounds are submerged in a liquid such as alcohol, oil or a nutrient broth.
- 14. The process is used for a variety of purposes, mostly in industrial manufacturing
- 15. Applications: Submerged Fermentation (SmF)/Liquid Fermentation (LF) SmF utilizes free flowing liquid substrates, such as molasses and broths. This fermentation technique is best suited for microorganisms such as bacteria that require high moisture. An additional advantage of this technique is that purification of products is easier.
- 16. fermentation process . Batch fermentation Continuous fermentation Batch fermentation ; Nutrients are added in the fermentation for the single time only the growth continuous until the particular nutrient are exhausted.